Macbecin
Macbecin belongs to the ansamycin family of antibiotics and was first isolated from actinomycete bacteria.[1][2] Macbecin possesses potent antitumor properties.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
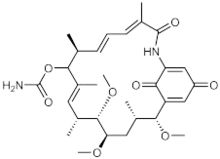
| IUPAC name
(4E,6Z,8S,10E,12R,13S,14R,16S,17R)-13,14,17-trimethoxy-4,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3,20,22-trioxo-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(21),4,6,10,18-pentaen-9-yl carbamate | |
| Other names
Macbecin I | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H42N2O8 | |
| Molar mass | 558.66308 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
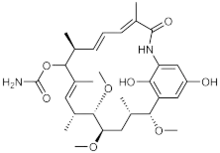
| IUPAC name
(4E,6Z,8S,10E,12R,13S,14R,16S,17R)-20,22-dihydroxy-13,14,17-trimethoxy-4,8,10,12,16-pentamethyl-3-oxo-2-azabicyclo[16.3.1]docosa-1(22),4,6,10,18,20-hexaen-9-yl carbamate | |
| Other names
Macbecin II | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H44N2O8 | |
| Molar mass | 560.67896 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Structure
Macbecin has an unusual macrocyclic lactam structure. There are two variants Macbecin I and II which correspond to the oxidized 1,4-benzoquinone and reduced hydroquinone respectively.
Mechanism of action
Macbecins mechanism of action is in part due to heat shock protein Hsp90 protein inhibition.[3]
References
- Tanida S, Hasegawa T, Higashide E (February 1980). "Macbecins I and II, new antitumor antibiotics. I. Producing organism, fermentation and antimicrobial activities". J. Antibiot. 33 (2): 199–204. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.33.199. PMID 7380729.
- Muroi M, Izawa M, Kosai Y, Asai M (February 1980). "Macbecins I and II, new antitumor antibiotics. II. Isolation and characterization". J. Antibiot. 33 (2): 205–12. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.33.205. PMID 7380730.
- Bohen SP (June 1998). "Genetic and Biochemical Analysis of p23 and Ansamycin Antibiotics in the Function of Hsp90-Dependent Signaling Proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (6): 3330–9. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.6.3330. PMC 108914. PMID 9584173.
External links
- Macbecin+I at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Macbecin+II at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.