Meruda Takkar
Meruda Takkar is a geological feature located north of Khadir Bet in the Great Rann of Kutch, Kutch district, Gujarat, India. It has a presence of Syenite rocks. It is described as a hill, an island, an outcrop as well as a monadnock.[1]
| Meruda Takkar | |
|---|---|
| Meruda Hill, Meruda island | |
 Meruda Takkar | |
| Highest point | |
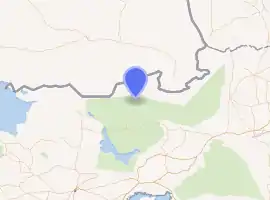
| Coordinates | 24.132318°N 70.310295°E |
| Geography | |
| Location | Great Rann of Kutch |
| Country | India |
| State | Gujarat |
| District | Kutch district |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Precambrian |
| Mountain type | Inselberg |
| Type of rock | Syenite |
| |
Location
Meruda Takkar is located in the Great Rann of Kutch between Khadir Bet in Kutch and Tharparkar in Pakistan. Kori creek is located on its west and the Sui village on the east. It is located in a desolate and militarily sensitive area controlled by the Border Security Force.[2][3]
Geology
The site was visited in 1968.[3] Forty-eight years later, a team from the geology department of the Kutch University visited the site in May 2019.[2]
It is located on the Nagarparkar Fault.[1] Based on the presence of the Syenite, a Precambrian basement rock, at the site; it is assumed that the Syenite rocks form the basement for the Kutch Basin sediments. They are considered equivalent to other Precambrian rock Erinpura Granite.[3][4][5] After 180 million years-long erosion, the Meruda Takkar and Nagarparkar hills are the only existing Syenite rocks in the region. The Jurassic and Cretaceous rocks forms the mainland and other uplands of Kutch while the upper layer are formed by 1500–2500 million years-old hard and crystalline rocks of Aravalli hill range.[2]
References
- Thakkar, M. G. (2017). "Geomorphological Field Guide Book on Kachchh Peninsula" (PDF). New Delhi: 9th International Conference on Geomorphology: 16. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-01-07. Retrieved 2020-08-27. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Khakhariya, Nimesh (2019-05-08). "In geologists' second visit in 48 years, hope rises of Jurassic-era find in Kutch". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 2020-08-29. Retrieved 2020-08-22.
- Bhimani, Sazina A. (2013-07-31). Study on groundwater salinization and formulation of management strategies for the coastal aquifers of Mundra region, Kutch district, Gujarat state (PDF) (Thesis). Department of Geology, Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda. pp. 36, 38, 46. hdl:10603/58602. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-08-29. Retrieved 2020-08-22.
- "Kutch Basin". National Data Repository. DGH, Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Government of India. 2015. Archived from the original on 2020-08-22.
- Sohoni, Parag S. (2000-12-31). Structural studies on central Kachchh mainland with special reference to quaternary tectonism (PDF) (Thesis). Department of Geology, Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda. pp. 24–25. hdl:10603/60120. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-08-29. Retrieved 2020-08-22.