Messina Chasmata
The Messina Chasmata /mɛˈsiːnə ˈkæzmətə/ are the largest canyon or system of canyons on the surface of the Uranian moon Titania, named after a location in William Shakespeare's comedy Much Ado About Nothing.[1] The 1,492 km (927 mi)- long feature includes two normal faults running NW–SE, which bound a down-dropped crustal block forming a structure called a graben.[2] The graben cuts impact craters, which probably means that it was formed at a relatively late stage of the moon's evolution,[3] when the interior of Titania expanded and its ice crust cracked as a result.[4] The Messina Chasmata have only a few superimposed craters, which also implies being relatively young. The feature was first imaged by Voyager 2 in January 1986.[2]
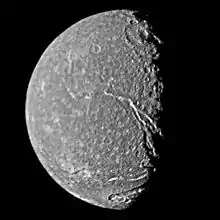
The Messina Chasmata are near the center of this Voyager 2 image of Titania.
References
- USGS/IAU (October 1, 2006). "Messina Chasmata on Titania". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology. Retrieved 2012-03-28.
- Smith, B. A.; Soderblom, L. A.; Beebe, A.; Bliss, D.; Boyce, J. M.; Brahic, A.; Briggs, G. A.; Brown, R. H.; Collins, S. A. (4 July 1986). "Voyager 2 in the Uranian System: Imaging Science Results". Science. 233 (4759): 43–64. Bibcode:1986Sci...233...43S. doi:10.1126/science.233.4759.43. PMID 17812889.
- Plescia, J. B. (December 30, 1987). "Cratering history of the Uranian satellites: Umbriel, Titania and Oberon". Journal of Geophysical Research. 92 (A13): 14, 918–14, 932. Bibcode:1987JGR....9214918P. doi:10.1029/JA092iA13p14918. ISSN 0148-0227.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Croft, S.K. (March 1989). New Geologic Maps of the Uranian Satellites Titania, Oberon, Umbriel and Miranda. Proceeding of Lunar and Planetary Sciences. 20. Lunar and Planetary Sciences Institute, Houston. p. 205C. Bibcode:1989LPI....20..205C.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
