Oct-1-en-3-one
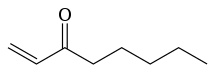
Oct-1-en-3-one (CH2=CHC(=O)(CH2)4CH3), also known as 1-octen-3-one, is the odorant that is responsible for the typical "metallic" smell of metals and blood coming into contact with skin.[1] Oct-1-en-3-one has a strong metallic mushroom-like odor with an odor detection threshold of 0.03–1.12 µg/m3 and it is the main compound responsible for the "smell of metal", followed by decanal (smell: orange skin, flowery) and nonanal (smell: tallowy, fruity).[2] Oct-1-en-3-one is the degradative reduction product of the chemical reaction of skin lipid peroxides and Fe2+. Skin lipid peroxides are formed from skin lipid by oxidation, either enzymatically by lipoxygenases or by air oxygen. Oct-1-en-3-one is a ketone analog of the alkene 1-octene.
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.116 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O | |
| Molar mass | 126.20 g/mol |
| Related compounds | |
Related enones |
Methyl vinyl ketone |
Related compounds |
1-Octene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Natural occurrences
It is also produced by Uncinula necator, a fungus that causes powdery mildew of grape.[3]
See also
- Odorant
- 1-Octen-3-ol, the alcohol analog that is used by mosquitoes as an odor cue
References
- D. Glindemann, A. Dietrich, H. Staerk, P. Kuschk (2006). "The Two Odors of Iron when Touched or Pickled: (Skin) Carbonyl Compounds and Organophosphines". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 45 (42): 7006–7009. doi:10.1002/anie.200602100. PMID 17009284.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Supporting information for the Glindemann article
- Darriet P, Pons M, Henry R, et al. (May 2002). "Impact odorants contributing to the fungus type aroma from grape berries contaminated by powdery mildew (Uncinula necator); incidence of enzymatic activities of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae". J. Agric. Food Chem. 50 (11): 3277–82. doi:10.1021/jf011527d. PMID 12009998.