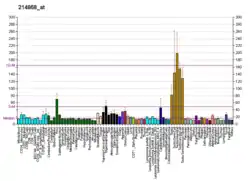
PIWIL1
Piwi-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PIWIL1 gene.[5][6][7]
This gene encodes a member of the PIWI subfamily of Argonaute proteins, evolutionarily conserved proteins containing both PAZ and Piwi motifs that play important roles in stem cell self-renewal, RNA silencing, and translational regulation in diverse organisms.
The encoded protein may play a role as an intrinsic regulator of the self-renewal capacity of germline and hematopoietic stem cells.[7]
References
- ENSG00000125207 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000275051, ENSG00000125207 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029423 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Cox DN, Chao A, Baker J, Chang L, Qiao D, Lin H (Jan 1999). "A novel class of evolutionarily conserved genes defined by piwi are essential for stem cell self-renewal". Genes Dev. 12 (23): 3715–27. doi:10.1101/gad.12.23.3715. PMC 317255. PMID 9851978.
- Sasaki T, Shiohama A, Minoshima S, Shimizu N (Aug 2003). "Identification of eight members of the Argonaute family in the human genome small star, filled". Genomics. 82 (3): 323–30. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00129-0. PMID 12906857.
- "Entrez Gene: PIWIL1 piwi-like 1 (Drosophila)".
Further reading
- Sharma AK, Nelson MC, Brandt JE, et al. (2001). "Human CD34(+) stem cells express the hiwi gene, a human homologue of the Drosophila gene piwi". Blood. 97 (2): 426–34. doi:10.1182/blood.V97.2.426. PMID 11154219.
- Qiao D, Zeeman AM, Deng W, et al. (2002). "Molecular characterization of hiwi, a human member of the piwi gene family whose overexpression is correlated to seminomas". Oncogene. 21 (25): 3988–99. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205505. PMID 12037681.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Tahbaz N, Kolb FA, Zhang H, et al. (2004). "Characterization of the interactions between mammalian PAZ PIWI domain proteins and Dicer". EMBO Rep. 5 (2): 189–94. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400070. PMC 1298981. PMID 14749716.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Liu X, Sun Y, Guo J, et al. (2006). "Expression of hiwi gene in human gastric cancer was associated with proliferation of cancer cells". Int. J. Cancer. 118 (8): 1922–9. doi:10.1002/ijc.21575. PMID 16287078. S2CID 8616640.
- Taubert H, Greither T, Kaushal D, et al. (2007). "Expression of the stem cell self-renewal gene Hiwi and risk of tumour-related death in patients with soft-tissue sarcoma". Oncogene. 26 (7): 1098–100. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209880. PMID 16953229.
- Sugimoto K, Kage H, Aki N, et al. (2007). "The induction of H3K9 methylation by PIWIL4 at the p16Ink4a locus". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 359 (3): 497–502. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.136. PMID 17544373.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.