PRPSAP1
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase-associated protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRPSAP1 gene.[5][6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000161542 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000015869 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
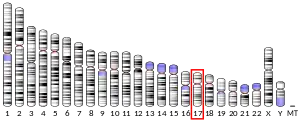
- Ishizuka T, Ahmad I, Kita K, Sonoda T, Ishijima S, Sawa K, Suzuki N, Tatibana M (Jan 1997). "The human phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase-associated protein 39 gene (PRPSAP1) is located in the chromosome region 17q24-q25". Genomics. 33 (2): 332–4. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0207. PMID 8660991.
- "Entrez Gene: PRPSAP1 phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase-associated protein 1".
Further reading
- Tatibana M, Kita K, Taira M, et al. (1995). "Mammalian phosphoribosyl-pyrophosphate synthetase". Adv. Enzyme Regul. 35: 229–49. doi:10.1016/0065-2571(94)00017-W. PMID 7572345.
- Kita K, Ishizuka T, Ishijima S, et al. (1994). "A novel 39-kDa phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase-associated protein of rat liver. Cloning, high sequence similarity to the catalytic subunits, and a negative regulatory role". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (11): 8334–40. PMID 8132556.
- Ishizuka T, Kita K, Sonoda T, et al. (1996). "Cloning and sequencing of human complementary DNA for the phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase-associated protein 39". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1306 (1): 27–30. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(96)00030-9. PMID 8611620.
- Ishijima S, Asai T, Kita K, et al. (1997). "Partial reconstitution of mammalian phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase in Escherichia coli cells. Coexpression of catalytic subunits with the 39-kDa associated protein leads to formation of soluble multimeric complexes of various compositions". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1342 (1): 28–36. doi:10.1016/s0167-4838(97)00077-0. PMID 9366267.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.