Palei languages
The Palei languages constitute a branch of the Torricelli language family according to Laycock (1975) (quoted from Foley 2018). They are spoken in mountainous regions of eastern Sandaun Province, Papua New Guinea.
| Palei | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | eastern Sandaun Province, Papua New Guinea |
| Linguistic classification | Torricelli
|
| Glottolog | nucl1722 (Nuclear Palai) west2788 (West Palai) |
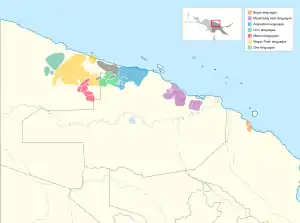 The Torricelli languages as classified by Foley (2018). Palei and Wapei languages are yellow. | |
Languages
Languages are:
- Nuclear Palai
- West Palai
- ? Kayik (Wanap)
Nambi (Nabi) = Metan may also belong here, or may be one of the Maimai languages, or separate within the Torriceli languages.
Pronouns
Pronouns in Palei languages are:[1]
Vocabulary comparison
The following basic vocabulary words are from from Laycock (1968),[2] as cited in the Trans-New Guinea database.[3] Nabi words are from Laycock (1968) and Voorhoeve (1971, 1975).[4][5]
gloss Aruop Agi Amol Nabi Wanap Yangum Mon head wantu paikwa wotuf peləf wah ear yaŋkole muᶇkwalnta taŋkən kik nuŋkul yiŋkuːl eye yolta juwol nəmalal nampəkat yilp yilkŋum nose mup tuwarka mipan minif təlom yimwar tooth na nai owayen naf nef awak tongue aləta naliya akaŋ wulaf kəːləp yalip leg ala safiel aŋ tip kelfek rak louse yimunə watokəl yimukun kakyerk yiməl yimul dog yimpa nəmpo yimpan pat yimpa yimpak pig bene bird ali nol alin napet kal al egg yoltə nəŋkoi yinalən ponorire; yufəlip yiplop yulp blood səna xaməŋka səneimpən amk komkok yuwanip bone pəniŋki kamənaŋkil lapən lə lekəl yiklia skin wiye jiwota yakən wiyírk saf yikisiw breast yimá nəmai yimawoŋ nəmap yimaŋkəf yimán tree nəmpə numwol nimpən nip nimp nim man makenti kamwol maikən məsəmiyen nyiŋkilpən almias woman simi wukora asək ri kekəntə wasi sun wa wota wan waf kentief təkŋan moon anyə uni ayen wunɨ keːnyif mərəŋkil water suku wul səpən sup; wer kuː sulp fire yimpu ni niŋ nɨ; wetai nif niw stone atauka səmpeiken et; rubukia kipru pikiyap one eso two piya piyami nantiyou mantio; ru poyomp piyak
References
- Foley, William A. (2018). "The Languages of the Sepik-Ramu Basin and Environs". In Palmer, Bill (ed.). The Languages and Linguistics of the New Guinea Area: A Comprehensive Guide. The World of Linguistics. 4. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton. pp. 197–432. ISBN 978-3-11-028642-7.
- Laycock, Donald C. 1968. Languages of the Lumi Subdistrict (West Sepik District), New Guinea. Oceanic Linguistics, 7 (1): 36-66.
- Greenhill, Simon (2016). "TransNewGuinea.org - database of the languages of New Guinea". Retrieved 2020-11-05.
- Voorhoeve, C.L. Languages of Irian Jaya: Checklist. Preliminary classification, language maps, wordlists. B-31, iv + 133 pages. Pacific Linguistics, The Australian National University, 1975. doi:10.15144/PL-B31
- Voorhoeve, C.L. "Miscellaneous Notes on Languages in West Irian, New Guinea". In Dutton, T., Voorhoeve, C. and Wurm, S.A. editors, Papers in New Guinea Linguistics No. 14. A-28:47-114. Pacific Linguistics, The Australian National University, 1971. doi:10.15144/PL-A28.47
- Foley, William A. (2018). "The Languages of the Sepik-Ramu Basin and Environs". In Palmer, Bill (ed.). The Languages and Linguistics of the New Guinea Area: A Comprehensive Guide. The World of Linguistics. 4. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton. pp. 197–432. ISBN 978-3-11-028642-7.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.