Paropamisus xeric woodlands
The Paropamisus xeric woodlands ecoregion (WWF ID:PA1322) covers the portion of northeastern Afghanistan north of the central mountain range and the Hindu Kush Mountains. The name is derived from the Old Persian name for the region - Parupraesanna ("Beyond the Hindu Kush"). While there are low canopy woodlands in the northeast of the ecorgegion, most of the territory is desert or xeric (dry) scrubland.[1][2][3][4]
| Paropamisus xeric woodlands | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
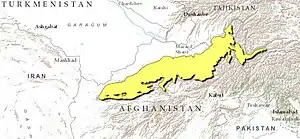 Ecoregion territory (in purple) | |
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Palearctic |
| Biome | Deserts and xeric shrublands |
| Geography | |
| Area | 92,804 km2 (35,832 sq mi) |
| Country | Afghanistan, Tajikistan |
| Coordinates | 36.25°N 66.75°E |
Location and description
The ecoregion stretches for 1,100 kilometres (680 mi) across northern Afghanistan, from the city of Herat in the west to the Wakhan Corridor in the east. The territory is on the north slopes of the mountains of central Afghanistan and the Hindu Kush. To the north is the Badghyz and Karabil semi-desert ecoregion, to the south are the Ghorat-Hazarajat alpine meadow and Hindu Kush alpine meadow ecoregions.
The terrain is rugged: elevations range from 371 metres (1,217 ft) to a high point of 5,592 metres (18,346 ft).[3]
Climate
The climate of ecoregion is Cold semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification (BSk)). This climate is characteristic of steppe climates intermediary between desert humid climates, and typically have precipitation is above evapotranspiration. At least one month averages below 0 °C (32 °F).[5][6]
Flora and fauna
Over 80% of the ecoregion is dry shrub. Another 8% is cultivated in crop agriculture (mostly along river valleys), and another 8% is sparse vegetation or bare ground.[3] Common vegetation is thornbush, Ziziphus, and Acacia. There are areas of woodland in the northeast of the ecoregion in Badakhshan Province, featuring wild almond, pistachio, willow, and buckthorn trees.[4] There are no endemic vertebrates, but the isolated areas support a range of non-endemic threatened and endangered species, including the near threatened Argali (Ovis ammon), the vulnerable Goitered gazelle (Gazella subgutturosa), the endangered Kulan (Equus hemionus), the near threatened Mountain weasel (Mustela altaica), and near threatened Sand cat (Felis margarita).[4]
Protected areas
Less than 1% of the ecoregion is officially protected.[3] These protected areas include:
- Dashti-Jum Nature Reserve (Tajikistan)
References
- "Paropamisus xeric woodlands". World Wildlife Federation. Retrieved March 21, 2020.
- "Map of Ecoregions 2017". Resolve, using WWF data. Retrieved September 14, 2019.
- "Paropamisus xeric woodlands". Digital Observatory for Protected Areas. Retrieved August 1, 2020.
- "Paropamisus xeric woodlands". The Encyclopedia of Earth. Retrieved August 28, 2020.
- Kottek, M., J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf, and F. Rubel, 2006. "World Map of Koppen-Geiger Climate Classification Updated" (PDF). Gebrüder Borntraeger 2006. Retrieved September 14, 2019.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Dataset - Koppen climate classifications". World Bank. Retrieved September 14, 2019.