Phrygian alphabet
The Phrygian alphabet is the script used in the earliest Phrygian texts.
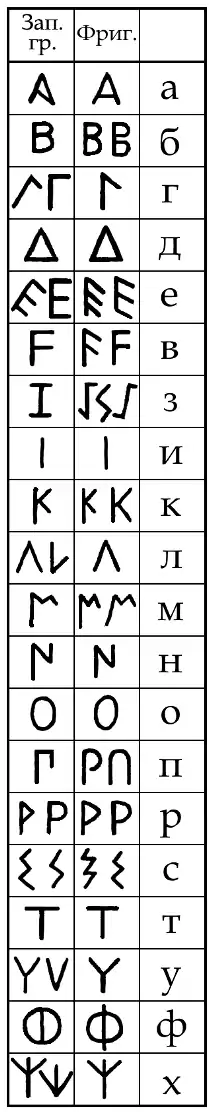
In the first column is the Greek alphabet, in the second - the Phrygian, and in the third, the corresponding sounds of the Bulgarian alphabet.
It dates back to the 8th century BC. from the Phoenician alphabet and is almost identical to the early West Greek alphabets.
The alphabet consists of 20 letters – 5 vowels (a, e, i, o, u) and 15 consonants (b, g, d, v, z, k, l, m, n, p, r, s, t, ph, kh). A variant of the Phrygian alphabet (with one additional letter - the so-called "Moesian s") was used in the inscriptions of the Mysian dialect. Words can be separated by three or four vertically spaced points. It is written from left to right as well as from right to left, and in multi-line inscriptions there is usually a spelling of boustrophedon. [1]
External links
 Media related to Phrygian alphabet at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Phrygian alphabet at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
