Platinum pentafluoride
Platinum pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the empirical formula PtF5. This red volatile solid has rarely been studied but is of interest as one of the few binary fluorides of platinum, i.e., a compound containing only Pt and F. It is hydrolyzed in water.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Platinum(V) fluoride | |
| Other names
Platinum pentafluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| F5Pt | |
| Molar mass | 290.07 |
| Appearance | red solid |
| Melting point | 75–76 °C (167–169 °F; 348–349 K) |
| Boiling point | 300–305 °C (572–581 °F; 573–578 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Platinum(IV) fluoride Platinum(VI) fluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The compound was first prepared by Neil Bartlett by fluorination of platinum dichloride above 350 °C (below that temperature, only PtF4 forms).[1]
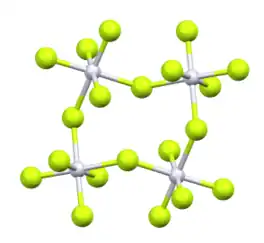
Its structure consists of a tetramer, very similar to that of ruthenium pentafluoride. Within the tetramers, each Pt adopts octahedral molecular geometry, with two bridging fluoride ligands.[2]
References
- Bartlett, N.; Lohmann, D. H. (1960). "Two New Fluorides of Platinum". Proceedings of the Chemical Society. London: 14–15. doi:10.1039/PS9600000001.
- Mueller, B. G.; Serafin, M. (1992). "Single-crystal investigations on PtF4 and PtF5". European Journal of Solid State Inorganic Chemistry. 29 (4–5): 625–633. doi:10.1002/chin.199245006.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.