Plum-headed finch
The plum-headed finch (Aidemosyne modesta) also known as cherry finch is a common species of estrildid finch found in Australia. It has an estimated global extent of occurrence of 100,000 – 1,000,000 km2.
| Plum-headed finch | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Estrildidae |
| Genus: | Aidemosyne Reichenbach, 1862 |
| Species: | A. modesta |
| Binomial name | |
| Aidemosyne modesta (Gould, 1837) | |
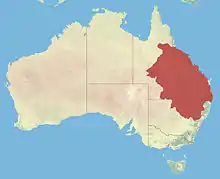 | |
| Approximate range | |
Habitat
It is found in dry savannah and subtropical/tropical (lowland) dry shrubland in Australia. The IUCN has classified the species as being of least concern.
Characteristics
It is a robust bird, with a stocky, strong beak and a long tail. It measures some 15 cm long. The scientific name emphasizes the absence of the flamboyant livery typical of many Australian species, as the brown tones predominate in the plumage of this bird; the upper part of the body (nape, back, wings and tail) is in fact a deep brown color, with a tendency to darken on the tail, while the ventral area (cheeks, throat, chest, abdomen and hips) is beige color that turns towards white in the central part of the belly and on the undertail. The bird distinguishes for its fine zebra like colouring, which is white and present on the eyebrows, neck, chest, hips and tail, while on the remiges are two rows of white spots. The beak is black, the legs are flesh-colored and the eyes are dark brown. In the male there are also a rust colored bib and a frontal stain of the same color (often with a brighter color tending to purple red), which in the female are reduced or absent, in any case with a predominance of brown on red; they also have less dense stripes.
The female is similar to the male but lacks the male's black chin spot.
The plum-headed finch breeds mainly from September to January in the south and from August to March in the north. The nest is round, laterally compressed chamber of green grass and is built in thick bushes. Four to six pure white eggs are laid.
Origin
Origin and phylogeny has been obtained by Antonio Arnaiz-Villena et al.[2] Estrildinae may have originated in India and dispersed thereafter (towards Africa and Pacific Ocean habitats).
References
- BirdLife International (2012). "Neochmia modesta". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Arnaiz-Villena, A; Ruiz-del-Valle V; Gomez-Prieto P; Reguera R; Parga-Lozano C; Serrano-Vela I (2009). "Estrildinae Finches (Aves, Passeriformes) from Africa, South Asia and Australia: a Molecular Phylogeographic Study" (PDF). The Open Ornithology Journal. 2: 29–36. doi:10.2174/1874453200902010029. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-18.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Neochmia modesta. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Neochmia modesta. |

