Polyetherimide
Polyetherimide (PEI) is an amorphous, amber-to-transparent thermoplastic with characteristics similar to the related plastic PEEK. Relative to PEEK, PEI is cheaper, but is lower in impact strength and usable temperature.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
PEI | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.800 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| (C37H24O6N2)n | |
| Molar mass | Variable |
| Appearance | Amber-to-transparent solid |
| Density | 1.27 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Because of its adhesive properties and chemical stability it became a popular bed material for FFF 3D printers.
Structure
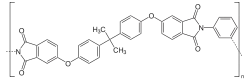
The molecular formula of the repeating unit of PEI is C37H24O6N2 and the molecular weight is 592.61 g/mol.[2]
Properties
The glass transition temperature of PEI is 217 °C (422°F). Its amorphous density at 25 °C is 1.27 g/cm3(.046 lb/in³). It is prone to stress cracking in chlorinated solvents. Polyetherimide is able to resist high temperatures with stable electrical properties over a wide range of frequencies. This high strength material offers excellent chemical resistance and ductile properties suitable for various applications, even those including steam exposure.[3]
Ultem
Ultem is a family of PEI products manufactured by SABIC as a result of acquiring the General Electric Plastics Division in 2007, developed by Joseph G. Wirth in the early 1980s. Ultem resins are used in medical and chemical instrumentation due to their heat resistance, solvent resistance and flame resistance. Ultem 1000 (standard, unfilled polyetherimide) has a high dielectric strength, inherent flame resistance, and extremely low smoke generation. Ultem has high mechanical properties and performs in continuous use to 340 °F (170 °C) and is easily machined and fabricated with excellent strength and rigidity.[4] Ultem 1000 has typical thermal conductivity of 0.22 W/m·K (but some sources give 0.122 W/m·K). It has "Questionable usage on alkaline solutions."[5]
References
- http://www.mcmaster.com/#ultem/=otzvqt Referenced Oct 7, 2013
- Scott, Chris. "polyetherimide information and properties". www.polymerprocessing.com. Retrieved 2018-04-30.
- "Injection Molding Material Selection Guide". www.abtecinc.com. Retrieved 2018-04-30.
- "Ultem PEI Plastic - Polyetherimide Sheets | Regal Plastics". www.regal-plastics.com. Retrieved 2018-04-30.
- https://www.asconumatics.eu/images/site/upload/_en/pdf1/00012gb.pdf
