Potez 53
The Potez 53 was a French low-wing enclosed cockpit single-seat cantilever monoplane racing aircraft built by Potez to specifically to compete in the 1933 Coupe Deutsch de la Meurthe race, which it won outright.[1][2]
| Potez 53 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The Potez 53 at Musée de l'Air et de l'Espace. | |
| Role | Racing aircraft |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Potez |
| First flight | 1933 |
| Number built | 3 |
Design and development
It was powered by a supercharged 9-cylinder 488.2 cu in (8.000 L) Potez 9B air-cooled radial engine driving a two-bladed fixed pitch propeller. The engine was specially designed for the competition, which limited displacement to 8 litres (490 cu in).[3] The primary structure and covering was wood.[3] The undercarriage retracted outwards into the undersides of the wings while the tailskid was fixed.[2]
Two machines were entered for the 1933 Coupe Deutsch de la Meurthe.[4] The first (racing no.10) was flown by Georges Détré, who won first place, covering the 2,000 km (1,200 mi) closed-circuit course with an average speed of 323 km/h (201 mph).[2][5] The other (racing no.12) was flown by Gustave Lemoine, who retired after completing the fourth lap.[4]
Following this success, a new machine designated the Potez 533 (or 53-3) was built with various improvements for the 1934 race, including an uprated engine delivering 350 hp (260 kW) driving a Ratier variable-pitch propeller, slimmer and more streamlined fuselage and redesigned wings of increased area.[2][6] One of the two aircraft entered the previous years was refurbished as the Potez 532 (or 53-2), to act as a backup in the competition. The engine was uprated, its fuselage was slightly lengthened for aerodynamic reasons, the wing was further enlarged and additional flaps were installed between the fuselage and ailerons.[2][6]
The two aircraft were flown by the same pilots as the previous year, but neither completed the 1934 race.[7] Gustave Lemoine, who was flying the Potez 533 (racing no.3), completed ten 100 km (62 mi) circuits with an average speed 368 km/h (229 mph) before being forced to withdraw due to a problem with the variable-pitch propeller.[7] Georges Détré, who was flying the older machine (racing no.1), completed only eight circuits before a broken oil pipe forced him to abandon the race.[7]
Aircraft on display
The unmodified Potez 53 which won the 1933 race is preserved in the Musée de l'Air et de l'Espace.[8] (France)
Specifications (1933 Potez 53)
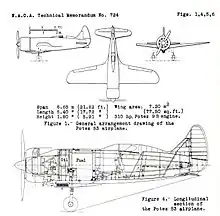
Data from The 1933 contest for the Deutsch de la Meurthe trophy
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 5.40 m (17 ft 9 in)
- Wingspan: 6.65 m (21 ft 10 in)
- Height: 1.80 m (5 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 7.20 m2 (77.5 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 600 kg (1,323 lb)
- Gross weight: 900 kg (1,984 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Potez 9B supercharged 9-cylinder 8 L (490 cu in) air-cooled radial engine, 230 kW (310 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 356.0 km/h (221.2 mph, 192.2 kn)
- Wing loading: 125.0kg/m2 (25.6 lb/sq ft)
- Power loading: 2.9kg/hp (6.39 hp/lb)
Notes
- Taylor 1989, p. 748.
- "Coupe Deutsch" 24 May 1934, p.510.
- NACA Technical Memorandum no.724: The 1933 contest for the Deutsch de la Meurthe trophy
- De Narbonne 2003.
- Taylor 1989, p. 749.
- "The 1934 contest for the Deutsch de la Meurthe trophy", p.18.
- "Coupe Deutsch" 31 May 1934, p.531.
- "Potez 53".
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Potez 53. |
- "Coupe Deutsch". Flight: 510–511. 24 May 1934. Retrieved 2009-10-18.
- "Coupe Deutsch". Flight: 531–32. 31 May 1934. Retrieved 2009-10-18.
- de Narbonne, Roland (June 2003). "Un pur-sang né en un éclair". Le Fana de l'Aviation (403): 40–47.
- "Potez 53". Musée de l'Air et de l'Espace website. Retrieved 2008-01-18.
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. ISBN 0-7106-0710-5.
- "The 1933 contest for the Deutsch de la Meurthe trophy" (PDF). NACA Technical Memorandum no.724. Retrieved 2009-10-16.
- "The 1934 contest for the Deutsch de la Meurthe trophy" (PDF). NACA Technical Memorandum no.765. Retrieved 2009-10-13.