Pyramid of Djedkare Isesi
The Pyramid of Djedkare Isesi (in ancient Egyptian Nefer-Djed-ka-re ("Beautiful is Djedkare")) is a late 25th to mid 24th century BC pyramid complex built for the Fifth Dynasty pharaoh Djedkare Isesi.[7][lower-alpha 1] The pyramid is referred to as Haram el-Shawaf (Arabic: هَرَم ٱلشَّوَّاف, romanized: Haram ash-Shawwāf, lit. 'The Sentinel Pyramid')[3] by locals.[1] It was the first pyramid to be built in South Saqqara.
| Pyramid of Djedkare Sentinel Pyramid[1][2] Haram el-Shawaf[3] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||
| Djedkare Isesi | |||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 29°51′04″N 31°13′15″E | ||||||||||||
| Ancient name | Nfr-Djed-kʒ-Rˁ Nefer-Djed-ka-Re Beautiful is Djedkare[1] | ||||||||||||
| Constructed | 5th Dynasty (c. Late 25th to Mid 24th century BC) | ||||||||||||
| Type | True pyramid (ruined) | ||||||||||||
| Material | Limestone[4] | ||||||||||||
| Height | 52.5 m (172 ft; 100.2 cu) (originally)[2] 24 metres (79 ft; 46 cu) (currently)[4][5] | ||||||||||||
| Base | 78.75 m (258.4 ft; 150.29 cu)[2] | ||||||||||||
| Volume | 107,835 m3 (141,043 cu yd)[6] | ||||||||||||
| Slope | 52°[2] | ||||||||||||
 Location within Lower Egypt | |||||||||||||
Djedkare Isesi's monument complex encompasses: a main pyramid; a mortuary temple situated on the east face of the main pyramid; a valley temple buried under modern Saqqara; a causeway that has been only partially dug out; and a cult pyramid. The main pyramid had a six-stepped core built from roughly cut limestone bound together by clay mortar which was then encased in fine white Tura limestone reaching a peak height of 52.5 m (172 ft; 100.2 cu). The casing has been plundered, and the top three steps of the core have been lost, leaving the pyramid a paltry 24 m (79 ft; 46 cu) tall. The basic dimensions of Djedkare's pyramid were adopted by succeeding kings in their own funerary monuments. Inside Djedkare Isesi's pyramid substructure, remains of the burial have been found alongside the mummy remains of Djedkare Isesi himself. The mummy and linen wrapping have undergone Carbon-14 dating which have given a common range of 2886–2507 BC. The substructure has otherwise been badly damaged by stone thieves quarrying the Tura limestone casing.
Adjoining the pyramid's east face is the mortuary temple. Flanking the entrance hall to the temple are two large pylon structures. West of the south pylon, a large building with multiple long narrow rooms was discovered. The outline of the building has been preserved by foundational blocks, but its structure is otherwise poorly preserved, and its floor has been lost, possibly to stone thieves. The building has no contemporaries at other Old Kingdom pyramid complexes, and no companion on the north side. Its function is unknown. The mortuary temple was mostly destroyed during the Second Intermediate Period, and used as a burial site in the Eighteenth Dynasty. At the south-east corner of the pyramid, a small cult pyramid is found in an enclosure. It has a T-shaped substructure.
At the north-east corner of the pyramid complex's enclosure wall, a satellite pyramid complex belonging to Queen Setibhor was built. The sub-complex is the largest one built for a queen during the Old Kingdom. It has its own enclosure wall, a mortuary temple and offering hall, storage rooms, antichambre carrée of unparalleled size, a small cult pyramid, and otherwise incorporates features that were previously reserved exclusively for the complexes of the king.
Location and excavation

The last kings of the Fifth Dynasty moved their funerary building activities from Abusir back to Saqqara.[5][2] Djedkare Isesi built his pyramid 6 km (3.7 mi) from the Abusir necropolis at a site in South Saqqara.[2][17] It was the first pyramid to be built in that area.[2] He also abandoned the tradition of building sun temples,[10] indicating a shift in the religious significance from the cult of Ra to the cult of Osiris.[18]
The pyramid was briefly visited by John Shae Perring, and soon after that by Karl Richard Lepsius. The substructure of the pyramid was first explored in 1880 by Gaston Maspero. In the mid-1940s, Alexandŕe Varille and Abdel Salam Hussein attempted the first comprehensive examination of the pyramid, but their work was interrupted and their findings lost.[1] They did discover the skeletal remains of Djedkare Isesi in the pyramid.[19] Ahmed Fakhry's attempt at a comprehensive examination in the 1950s was equally unsuccessful. Relief fragments that Fakhry had discovered were later published by Muhammud Mursi. The area around the causeway and mortuary temple was excavated by Mahmud Abdel Razek.[1]
Architectural plans of the pyramid complex were first published by Vito Maragioglio and Celeste Rinaldi between 1962 and 1977. These have been determined by Mohamed Megahed, Peter Jánosi and Hana Vymazalová to be inconsistent and inaccurate.[20] Since 2010, Megahed has been the director in charge of the pyramids of Djedkare Isesi and Setibhor.[21]
Mortuary complex
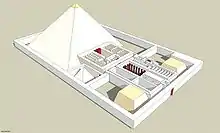
Layout
Old Kingdom mortuary complexes consisted of five essential components: (1) a valley temple; (2) a causeway; (3) a pyramid, or mortuary,[22] temple; (4) a cult, or satellite,[23] pyramid; and (5) the main pyramid.[24] Djedkare's monument has all of these elements. The main pyramid constructed from six steps of limestone blocks.[25] A valley temple, buried under the modern houses of Saqqara.[26][27] A causeway, that has not yet been excavated.[2] A mortuary temple on the east side of the pyramid,[28] and a cult pyramid at the south-east corner of the main pyramid,[29] with a standard T-shaped substructure.[30] Additionally, there is an associated pyramid situated on the north-east corner of Djedkare's pyramid complex,[30] belonging to Setibhor,[31] previously known as the "pyramid of the unknown queen".[32]
Main pyramid
The core of the pyramid was constructed in six steps composed of small irregular pieces of limestone blocks bound together using clay mortar.[4] The length of the base step of the pyramid was 78.75 m (258 ft; 150 cu),[2] with each step built around 7 metres (23 ft; 13 cu) high,[4] converging to the peak at a slope of 52° giving the pyramid an original peak height of 52.5 m (172 ft; 100 cu).[2] These proportions were used by the rulers Teti, Pepi I, Merenre I,[lower-alpha 2] and Pepi II for their pyramid complexes.[10][34] The top three steps of the pyramid no longer exist, and ruined pyramid now reaches a height of about 24 metres (79 ft; 46 cu).[4] The pyramid was originally encased with fine white Tura limestone.[4] Most of the casing has since been plundered, though some of it has remained intact and has been well preserved.[4]
Substructure

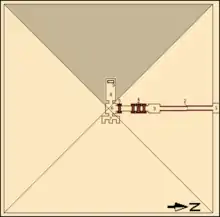
Entry into the substructure was gained from the north side of the pyramid; unusually, however, the entrance is under the pavement of the courtyard, instead of in the north face.[4] There was originally a north chapel here; only traces of it now remain.[35][36] The entry leads into a granite lined downward sloping access corridor.[2][37] The corridor has a slight angle toward the east, and is the last built to do so.[37] The corridor ends at a vestibule, through which a second corridor lined with limestone, the horizontal passage, is accessed.[2][37] Remnants of broken vessels were discovered in the vestibule, suggesting that certain burial rituals had been performed there.[37] The horizontal passage was guarded by three granite portcullises near the beginning of the corridor, and a fourth granite portcullis near its end.[37] The exit of the horizontal passage leads into the antechamber, a room measuring 4.02 m (13.2 ft) by 3.1 m (10 ft).[2] To east was a room, the serdab, containing three niches for storage,[37][38] a developing feature of pyramids of the era.[2] To the west lay the burial chamber,[2][37] measuring 7.84 m (25.7 ft) by 3.1 m (10 ft),[2] which once contained the basalt sarcophagus of the ruler.[37] Fragments of the sarcophagus were found in a 13 cm (5 in) depression in the floor.[36] The roof of both the antechamber and burial chamber were constructed from two, or perhaps three, layers of gabled limestone blocks,[2][39] in the same fashion as the pyramids in Abusir.[37] These blocks were 5.25 m (17.2 ft; 10.02 cu) in length.[40]
The rooms of the substructure have been badly damaged by stone thieves, who quarried the Tura limestone walls of the chambers,[38] which has made reconstruction of the planned layout difficult.[37] The serdab was left alone, preserving its structure and flat roof. The masonry core has been exposed in the other chambers, and consists of crudely cut blocks and small limestone chips that were piled up to form the substructure of the pyramid. The wall separating the antechamber and burial chamber has been total demolished.[40] The substructure has been subject to significant on-going restoration work, particularly the consolidation of the pyramid's core and the walls of the antechamber and serdab.[41]
Djedkare's sarcophagus originally sat near the west wall of the burial chamber. At the south-east foot of the sarcophagus, alabaster canopic jars had once buried in a small hole in the ground.[37][2] Underneath the rubble, only fragments of the sarcophagus and alabaster jars have been found,[2] along with a mummified body of a man in his fifties that is presumed to be the remains of Djedkare Isesi.[37] The mummy has been subjected to Carbon-14 dating, as have scraps of linen wrapping and charcoal taken from the tomb. These samples have provided a range of dates spanning 3340–2460 BC, and a common range of 2886–2507 BC. Miroslav Verner remarks that these results accord better with earlier proposed regnal dates than later ones, but contradicts previous astronomically derived dates which favour later proposed regnal dates than earlier ones.[16]
Valley temple
The valley temple to Djedkare's complex has not been excavated,[42] it is lost buried under the modern houses of Saqqara.[27]
Causeway

The causeway that leads up to the mortuary temple has not been excavated, though it is known to have a straight sloped path,[2] running slightly southwards,[26] and a length of 220 m (722 ft; 420 cu).[43] The ground where the mortuary temple was to be constructed had a sharp downward slope towards the desert, and needed extensive preparation before the laying of the foundation.[28] Dimensions for the causeway are speculative, based only on the trace remains of existing foundations. The causeway had walls approximately 2.4 m (7.9 ft) thick, with a path between them no more than 2.6 m (8.5 ft) wide.[44] The height of the structure remains unknown, though it is clear that it had a ceiling and was covered based on blocks found painted with stars, a typical motif for the ceiling. It appears to have been made entirely of white limestone, the same material that makes up the causeway to Sahure's pyramid. The walls were clearly decorated with raised relief.[45] The causeway connects to the temple entrance hall between two large pylon structures,[2][28] an innovation from Nyuserre's pyramid, which were square with slightly inclined walls.[46] The pylons were once 6 m (20 ft; 11 cu) tall, but have since been reduced to 4.5 m (15 ft).[47] There may have been stairs leading up to the terrace, but likely had no rooms inside. Their function remains a mystery.[28] Alongside the causeway, leading towards the courtyard of the temple, a water drain was discovered. The drain was made of crudely cut blocks of quartzite that had been carelessly set. No traces of the drain have been found in the entrance hall or courtyard.[45]
Mortuary temple
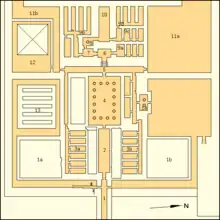
The entrance hall of the temple had an alabaster paved floor and appears to have had a vaulted ceiling judging by the size of the walls.[29] It is flanked by six storage rooms on each side that are accessed from the transverse corridor.[29][30] A pair of corridors separated by a doorway lead to the southern storage rooms. The western corridor is poorly preserved; the eastern corridor is in better condition. It is 1.6 m (5.2 ft) wide and its preserved sections 14.25 m (46.8 ft) long. It had a limestone pavement, but its walls have been demolished. Although nothing here remains, the corridor and the southern pylon were separated by a 2 m (6.6 ft) thick wall.[48] The storage rooms have walls around 2 cu (1.0 m; 3.4 ft) thick and measure about 5 cu (2.6 m; 8.6 ft) wide by 16.5 cu (8.6 m; 28.4 ft) long. The storage rooms north of the entrance hall are similar in size, but are in far worse condition.[49]
The entrance hall terminates into an open courtyard paved with alabaster and adorned with sixteen pink granite columns.[50] As in Sahure's mortuary temple, the columns bore the names and titles of Djedkare Isesi.[29] The courtyard connects to the transverse corridor, which has a low staircase in its west wall leading into the inner temple.[29][30] Inside a small passage led to the chapel with its five statue niches, followed by a vestibule to a small square room with a single granite column at its centre – the antichambre carée[29] – before terminating at the offering hall.[30][51] The antichambre carée measures 4.7 m (15 ft; 9.0 cu) by 4.2 m (14 ft; 8.0 cu). Its north, east, and part of the south walls are lost.[51] Its central column supported the room's ceiling, and bore the names and titles of Djedkare Isesi, as well as an image of Nekhbet, the goddess of Upper Egypt.[29][lower-alpha 3] Shaped like a palm, it was made of red granite with a diameter of 0.65 m (2.1 ft) at the top and 0.73 m (2.4 ft) at its bottom. Some previously discovered relief fragments may have come from this room. They depict scenes of deities possessing Was-sceptres and ankh symbols, shrines of Upper and Lower Egypt, acts of slaughter, and bowing officials.[51] The offering hall of the temple is similar to other contemporary offering halls in other complexes, with the exception that the false door was carved into the masonry of the pyramid.[29] Surrounding the inner temple were storage rooms on either side.[30][29]

nsw-bỉt nb.tj Ḏd-ḫ3-w Bik-nbw-ḏd Ḏd-k3-rˀ di-ˀnḫ ḏd-w3s
King of Upper and Lower Egypt, Enduring of appearances,[lower-alpha 4] The enduring golden falcon,[lower-alpha 5] Djedkare, given life, health, serenity.
The temple was mostly destroyed during the Second Intermediate Period, and was used as a burial site in the Eighteenth Dynasty.[53] Relief decoration is fragmentary,[2] as extensive damage was done to the walls of the temple by stone thieves.[29] The remnants indicate that the quality of execution both in design and workmanship is comparable to those at the other contemporary sites.[29][2] Four Djed pillars, three of which were preserved, were recovered from the mortuary temple. These pillars were each 93 cm (3.05 ft) tall, carved on two sides into Djed signs, and appear to have been used as an architectural element in one of the chambers of the temple. Their smooth tops indicate that they may have been used to hold some artifact, thus being used as stands. Two similar, but smaller, pillars were found in Unas' mortuary temple.[54] Statues of a lion and two sphinxes are another find in the complex. The lion statue, which was carefully sculpted and detailed, is 105 cm (3.44 ft) tall and 107 cm (3.51 ft) long. It is postured into a seated position with paws extended. It is broken, but otherwise very well preserved.[55] By contrast, the two sphinx statues are only partially preserved. They represent lions in resting positions on their bellies, and appear to have been wall decorations or part of another feature based on the fact that they are resting on rectangular pedestals.[56] Sphinx statues in the Old Kingdom are a rarity, and the faces of both sphinx statues have been damaged. A parallel exists in Unas' complex, and its face has been preserved. A reference to Djedkare's sphinx exists in a biographical inscription of a Kaemtjenenet, who was responsible for organizing the placement of the sphinx and its base in the mortuary temple.[57] Limestone sculptures of kneeling captives have been found in the temple. Statues of kneeling figures are common, and have been attested to in the temples of Neferefre, Nyuserre, Unas, Teti and Pepi I. The likely providence of these statues are the causeway or entrance hall of the temple, where scenes of enemies being trampled would be found.[58] Fragments of an alabaster statue of Djedkare were found in the temple, one of which bears an inscription.[59]
South of the main mortuary temple was a large 21.8 m (72 ft; 41.6 cu) by 19.85 metres (65.1 ft; 37.88 cu) building of unknown height.[60] Within, there were apparently five, north to south oriented, rectangular rooms 14.3 m (47 ft; 27.3 cu) long by 2.15 metres (7.1 ft; 4.10 cu) wide. Blocks from the foundation of the building have been preserved, but no blocks from a potential floor have been found. It is possible that the floor has been victim to stone quarrying for calcite, as has happened elsewhere in the temple, but physical evidence suggests that a limestone floor is much more likely. In this case, quality limestone must have made up the floor of building. No doors or connecting passages have been found, rendering it difficult to identify the access point into the building.[47] A corridor has been identified stretching from the south-west corner of the pylon, past the south side of the building, and to the enclosure wall of the cult pyramid, where it may have turned north to connect to the transverse corridor. A second potential corridor has been identified running along the east side of the building. It appears that this building was separate from its neighbouring counterparts. The structure is otherwise poorly preserved, and its purpose unknown. No similar structure has been located at other contemporary pyramid complexes of the Old Kingdom, and no companion building on the north side of the mortuary temple either.[61]
Cult pyramid
The complex includes a typical cult pyramid at the south-east corner of the pyramid.[29] The pyramid was constructed with a core three steps high.[29] The length of its base was 15.5 m (51 ft; 30 cu) inclined towards the apex at 65° giving it a peak height of 16 m (52 ft; 31 cu).[62] Entry into the substructure was gained through a door on the middle of its north face.[29] The substructure had a standard T-shaped layout,[30] consisting of a downward sloping corridor leading to a single rectangular chamber slightly beneath ground level which was oriented east-west.[29] The cult pyramid was enclosed by a small perimeter wall.[29]
The purpose of the cult pyramid remains unclear. It had a burial chamber but was not used for burials, and instead appears to have been a purely symbolic structure.[63] It may have hosted the pharaoh's ka,[64] or a miniature statue of the king.[65] It may have been used for ritual performances centering around the burial and resurrection of the ka spirit during the Sed festival.[65]
Pyramid of Setibhor
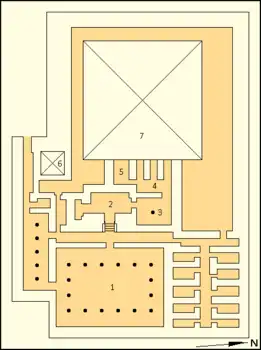
A satellite pyramid complex is located at the north-east corner of the wall of the complex of Djedkare's pyramid.[26] With the exception of a valley temple and causeway,[32] the satellite pyramid has the standard elements that are typically found only in the king's pyramid.[30] The complex is enclosed within its own perimeter wall and consists of: a pyramid; colonaded court; statue chapel; a mortuary temple with its own offering hall, storage rooms, and antichambre carrée with single column; and a small cult pyramid.[30][66] The antichambre carrée of this complex is notable due to its unparalleled size of 7 m (23 ft; 13 cu) by 6 m (20 ft; 11 cu). Its column and base appear to be both be made of limestone, instead of the typical granite. Relief fragments found on limestone blocks may also originate in the chamber.[67] Due to its being intentionally incorporated into the pyramid complex of Djedkare Isesi, the pyramid is believed to have belonged to a consort of Djedkare Isesi.[66] The identity of the owner remained a mystery until 2019, when the name and titles of a queen Setibhor were found inscribed on a column in the complex. Setibhor's pyramid complex is thus the largest one built for a queen in the Old Kingdom, and incorporates elements that were previously only used in the complexes of the king.[68]
Later history
Burials
In 1952, Fahkry explored a necropolis containing seventeen mudbrick tombs located south of the causeway and adjoining the east side of the mortuary temple.[69] He provided a brief account summarizing that the tombs had been robbed of their contents. In 2016, one of those tombs, mastaba MS1, was partially excavated and explored. The structure is dated to the Sixth Dynasty.[38] The tomb measures approximately 5.5 m (18 ft) by 4 m (13 ft) and has six compartments arranged in two rows.[70] The tomb is also connected to another tomb further east.[71]
The first compartment at the north-west corner is accessed through a 4.73 m (15.5 ft) deep shaft leading into a vaulted burial chamber of dimensions 2.64 m (8.7 ft) by 0.85 m (2.8 ft). The chamber and shaft are made of mudbrick. The tomb has been emptied, except for some human remains. Two 2.8 m (9.2 ft) deep shafts, one directly south of the first and the other to its south-east, appear to have been built at the same time. They each lead into burial chambers of very similar proportions, both 3.5 m (11 ft) long by 0.95 m (3.1 ft) wide. The south burial chamber contained fragments of human remains. These too were constructed entirely from mudbrick.[72] They are connected by a 1 m (3.3 ft) vaulted passage. The middle compartment of the north row is arrived to by a 4.96 m (16.3 ft) deep. It contains a vaulted mudbrick burial chamber with dimensions of 2.62 m (8.6 ft) by 1.05 m (3.4 ft). This chamber has been blocked with a wall.[73] The south-east compartment contains a vaulted mudbrick burial chamber 1.2 m (3.9 ft) by 1.3 m (4.3 ft) large. It was included as an apparent afterthought.[74] Remains of multiple individuals were found in the chamber, but their origin is unclear. Other items recovered included faience beads and a seal stamp with a seated lion facing a crouching enemy. This type of seal can be dated to the Sixth Dynasty or the First Intermediate Period.[38]
The north-east compartment is the largest and most significant of the tomb. It is accessed by a 4.75 m (15.6 ft) shaft. The vaulted mudbrick burial chamber here is 3 m (9.8 ft) long, 1.3 m (4.3 ft) wide, and 1.8 m (5.9 ft) tall. It contained a decorated limestone burial chamber 2.9 m (9.5 ft) long, 1.02 m (3.3 ft) wide, and 1.07 m (3.5 ft) tall which was originally closed with limestone slabs. The ceiling of the limestone burial chamber was painted black and red to imitate red granite. Its side walls were decoratively painted with scenes of offerings and a palace façade motif, and have been well preserved, except for at its southern section.[73] Lines of inscription above the decorations identify the owner of the burial: Pepyankh Setju.[75] Above the burial chamber, in the space with the vaulted mudbrick ceiling, an offering table bearing the name Isesi was found.[74]
See also
- Egyptian pyramid construction techniques
- List of Egyptian pyramids
- List of megalithic sites
Notes
- Proposed dates for Djedkare Isesi's reign: c. 2436–2404 BC,[8][9] c. 2414–2375 BC,[10][11][12] c. 2388–2356 BC,[13] c. 2381–2353 BC,[14] c. 2340–2312 BC,[15] c. 2405/2355–2367/2317 BC.[16]
Carbon–14 dating of organic materials from Djedkare's tomb give absolute dates for his reign of 3340–2460 BC, with a common range of 2886–2507 BC.[16] - The exact dimensions of Merenre's pyramid are unknown, as the structure has been destroyed and has not been fully excavated yet, though it is assumed that Merenre had planned the pyramid to the same standard dimensions as his predecessor's pyramids.[33]
- The column was south of the main east-west axis of the temple, and hence under Nekhbet's protection.[29]
- Djed-khau, meaning "Enduring of appearances", is Djedkare's Horus name.[52]
- Bik-nebu-djed, meaning "the enduring golden falcon", is Djedkare's Golden Horus name.[52]
References
- Verner 2001d, p. 324.
- Lehner 2008, p. 153.
- Porter et al. 1981, p. 424.
- Verner 2001d, p. 325.
- Clayton 1994, p. 62.
- Bárta 2005, p. 180.
- Altenmüller 2001, pp. 597 & 600.
- Verner 2001c, p. 589.
- Altenmüller 2001, p. 600.
- Málek 2003, p. 102.
- Shaw 2003, p. 482.
- Clayton 1994, p. 60.
- Lehner 2008, p. 8.
- Allen et al. 1999, p. xx.
- Dodson & Hilton 2004, p. 288.
- Verner 2001a, p. 417.
- Grimal 1992, p. 78.
- Verner 2001c, pp. 589–590.
- Verner 2001a, p. 410.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, p. 37.
- CEGU 2017, Mgr. Mohamed Abdel Moneim Megahed, Ph.D.
- Verner 2001d, p. 293.
- Lehner 2008, p. 146.
- Bárta 2005, p. 178.
- Verner 2001d, p. 332.
- Verner 2001d, p. 329.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, pp. 40–41.
- Verner 2001d, p. 327.
- Verner 2001d, p. 328.
- Lehner 2008, p. 154.
- CEGU 2019, fig. 14.
- Verner 2001d, pp. 329–330.
- Lehner 2008, p. 160.
- Lehner 2008, pp. 157–158, 160–161.
- Verner 2001d, pp. 325–326.
- Edwards 1993, p. 172.
- Verner 2001d, p. 326.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, p. 48.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, p. 50.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, p. 49.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, pp. 49–50.
- Wilkinson 2000, p. 129.
- Verner 2001d, p. 494.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, pp. 41.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, pp. 42.
- Verner 2001d, pp. 316 & 327–328.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2018, p. 38.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, pp. 37–38.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, p. 39.
- Lehner 2008, pp. 153–154.
- Megahed 2016a, p. 243.
- Leprohon 2013, p. 40.
- Clayton 1994, pp. 62–63.
- Megahed 2016b, p. 26.
- Megahed 2016b, p. 27.
- Megahed 2016b, p. 28.
- Megahed 2016b, pp. 28 & 31.
- Megahed 2016b, pp. 26–27.
- Megahed 2016b, pp. 31–21.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2018, pp. 36–38.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2018, pp. 39.
- Verner 2001d, p. 464.
- Verner 2001d, p. 53.
- Lehner 2008, p. 18.
- Arnold 2005, p. 70.
- Verner 2001d, p. 330.
- Megahed 2016a, p. 248.
- CEGU 2019, Discovery of a unique tomb and the name of an ancient Egyptian queen in south Saqqara.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, pp. 42–43.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, pp. 43–44.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, p. 43.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, p. 44.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, p. 45.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, p. 47.
- Megahed, Jánosi & Vymazalová 2017, pp. 45–46.
Sources
- Allen, James; Allen, Susan; Anderson, Julie; et al. (1999). Egyptian Art in the Age of the Pyramids. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art. ISBN 978-0-8109-6543-0. OCLC 41431623.
- Altenmüller, Hartwig (2001). "Old Kingdom: Fifth Dynasty". In Redford, Donald B. (ed.). The Oxford Encyclopedia of Ancient Egypt, Volume 2. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 597–601. ISBN 978-0-19-510234-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Arnold, Dieter (2005). "Royal cult complexes of the Old and Middle Kingdoms". In Schafer, Byron E. (ed.). Temples of Ancient Egypt. London, New York: I.B. Taurus. pp. 31–86. ISBN 978-1-85043-945-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bárta, Miroslav (2005). "Location of the Old Kingdom Pyramids in Egypt". Cambridge Archaeological Journal. Cambridge. 15 (2): 177. doi:10.1017/s0959774305000090.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Clayton, Peter A. (1994). Chronicle of the Pharaohs. London: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0-500-05074-0.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Discovery of a unique tomb and the name of an ancient Egyptian queen in south Saqqara". Czech Institute of Egyptology. 2019-04-02. Retrieved 2019-04-23.
- Dodson, Aidan; Hilton, Dyan (2004). The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. London: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0-500-05128-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Edwards, Iorwerth (1993) [1947]. The pyramids of Egypt. London: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0140136340. OCLC 473229011.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Grimal, Nicolas (1992). A History of Ancient Egypt. Translated by Ian Shaw. Oxford: Blackwell publishing. ISBN 978-0-631-19396-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lehner, Mark (2008). The Complete Pyramids. New York: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-28547-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Leprohon, Ronald J. (2013). The Great Name: Ancient Egyptian Royal Titulary. Volume 33 of Writings from the ancient world. Atlanta: Society of Biblical Literature. ISBN 978-1-589-83736-2.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Málek, Jaromír (2003). "The Old Kingdom (c.2160-2055 BC)". In Shaw, Ian (ed.). The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 83–107. ISBN 978-0-19-815034-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Megahed, Mohamed (2016a). "The antichambre carée in the Old Kingdom. Decoration and function". In Landgráfová, Renata; Mynářová, Jana (eds.). Rich and great: studies in honour of Anthony J. Spalinger on the occasion of his 70th Feast of Thoth. Prague: Charles University in Prague, Faculty of Arts. pp. 239–259. ISBN 9788073086688.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Megahed, Mohamed (2016b). "Sculptures from the pyramid complex of Djedkare Isesi at South Saqqara. A preliminary report". Pražské egyptologické studie. Prague: Charles University in Prague (17): 24–33. ISSN 1801-3899.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Megahed, Mohamed; Jánosi, Peter; Vymazalová, Hana (2017). "Djedkare's pyramid complex: Preliminary report of the 2016 season". Pražské egyptologické studie. Prague: Charles University in Prague (19): 37–52. ISSN 1214-3189.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Megahed, Mohamed; Jánosi, Peter; Vymazalová, Hana (2018). "Djedkare's pyramid complex: Preliminary report of the 2017 season". Pražské egyptologické studie. Prague: Charles University in Prague (21): 34–44. ISSN 1214-3189.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Megahed, Mohamed; Jánosi, Peter; Vymazalová, Hana (2019). "Exploration of the pyramid complex of King Djedkare: season 2018". Pražské egyptologické studie. Prague: Charles University in Prague (23): 12–36. ISSN 1214-3189.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Mgr. Mohamed Abdel Moneim Megahed, Ph.D." Czech Institute of Egyptology. 2017-06-05. Retrieved 2019-08-10.
- Porter, Bertha; Moss, Rosalind L. B.; Burney, Ethel W.; Málek, Jaromír (1981). Topographical bibliography of ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic texts, reliefs, and paintings. III Memphis; Pt. 2. Ṣaqqâra to Dahshûr (PDF). Oxford: Griffith Institute. ISBN 978-0-900416-24-8.
- Shaw, Ian, ed. (2003). The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-815034-3.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Verner, Miroslav (2001a). "Archaeological Remarks on the 4th and 5th Dynasty Chronology" (PDF). Archiv Orientální. Prague. 69 (3): 363–418. ISSN 0044-8699.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Verner, Miroslav (2001c). "Old Kingdom". In Redford, Donald B. (ed.). The Oxford Encyclopedia of Ancient Egypt, Volume 2. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 585–591. ISBN 978-0-19-510234-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Verner, Miroslav (2001d). The Pyramids: The Mystery, Culture and Science of Egypt's Great Monuments. New York: Grove Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-1703-8.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wilkinson, Richard H. (2000). The Complete Temples of Ancient Egypt. New York: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-05100-9.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pyramid of Djedkare Isesi. |
