Quassia
Quassia (/ˈkwɒʃə/ or /ˈkwɒʃiə/) is a plant genus in the family Simaroubaceae. Its size is disputed; some botanists treat it as consisting of only one species, Quassia amara from tropical South America, while others treat it in a wide circumscription as a pantropical genus containing up to 40 species of trees and shrubs. The genus was named after a former slave from Suriname, Graman Quassi in the eighteenth century. He discovered the medicinal properties of the bark of Quassia amara.
| Quassia | |
|---|---|
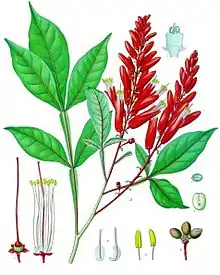 | |
| Quassia amara | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Simaroubaceae |
| Genus: | Quassia L. |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Distribution
Members of the genus are found in the Tropics throughout the world.[1] Countries and regions where species are native include: Andaman Islands, Angola, Bangladesh, Belize, Benin, Bismarck Archipelago, Borneo, North and Northeast Brazil, Burkina, Cabinda, Cambodia, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Colombia, Comoros, Congo, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guatemala, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Gulf of Guinea Islands, Honduras, India, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Laos, Leeward Islands, Liberia, Madagascar, Malaya, Mali, Central, Southeast and Southwest Mexico, Myanmar, New Guinea, Nicaragua, Niger, Nigeria, Northern Territory, Panamá, Philippines, Queensland, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Solomon Islands, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Sulawesi, Sumatera, Tanzania, Togo, Trinidad-Tobago, Uganda, Venezuela, Vietnam, Windward Islands, Zambia, and Zaïre.
The plant is naturalised in the following places: Cuba, Dominican Republic, Haiti, Jamaica, Jawa, and Puerto Rico.
List of accepted species
Accepted species of the genus, as of February 2021, are:[1]
- Quassia africana (Baill.) Baill.
- Quassia amara L.
- Quassia arnhemensis Craven & Dunlop
- Quassia baileyana (Oliv.) Noot.
- Quassia bidwillii (Benth. & Hook.f.) Noot.
- Quassia borneensis Noot.
- Quassia crustacea (Engl.) Noot.
- Quassia gabonensis Pierre
- Quassia harmandiana (Pierre ex Laness.) Noot.
- Quassia indica (Gaertn.) Noot.
- Quassia pohliana (Boas) Noot.
- Quassia sanguinea Cheek & Jongkind
- Quassia schweinfurthii (Oliv.) Noot.
- Quassia undulata (Guill. & Perr.) D.Dietr.
- Quassia versicolor (A.St.-Hil.) Spreng.
There are also taxa that have been assigned a formal status:
- Quassia sp. 'Moonee Creek', unplaced – Australia
- Quassia sp. 'Mount Nardi', unplaced – Australia
Uses
It is the source of the quassinoids quassin and neo-quassin.[2]
References
- "Quassia L." Plants of the POWO)World Online (. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- Mishra K, Chakraborty D, Pal A, Dey N (April 2010). "Plasmodium falciparum: in vitro interaction of quassin and neo-quassin with artesunate, a hemisuccinate derivative of artemisinin". Exp. Parasitol. 124 (4): 421–7. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2009.12.007. PMID 20036657.