RGS7
Regulator of G-protein signaling 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS7 gene.[5][6]
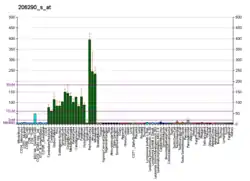
RGS7 is highly enriched in the brain where it acts as a universal inhibitor of Gi/o-coupled GPCR. RGS7 is a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). It accelerates the GTP hydrolysis on G proteins determining their fast inactivation and acting as intracellular antagonists of GPCR signaling.[7]
Interactions
RGS7 has been shown to interact with:
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000182901 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026527 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Koelle MR, Horvitz HR (Feb 1996). "EGL-10 regulates G protein signaling in the C. elegans nervous system and shares a conserved domain with many mammalian proteins". Cell. 84 (1): 115–25. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80998-8. PMID 8548815. S2CID 7815240.
- "Entrez Gene: RGS7 regulator of G-protein signalling 7".
- Anderson GR, Posokhova E, Martemyanov KA (July 2009). "The R7 RGS Protein Family: Multi-Subunit Regulators of Neuronal G Protein Signaling". Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics. 54 (1–3): 33–46. doi:10.1007/s12013-009-9052-9. PMC 2827338. PMID 19521673.
- Levay K, Cabrera JL, Satpaev DK, Slepak VZ (Mar 1999). "Gbeta5 prevents the RGS7-Galphao interaction through binding to a distinct Ggamma-like domain found in RGS7 and other RGS proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (5): 2503–7. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.2503L. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.5.2503. PMC 26814. PMID 10051672.
- Posner BA, Gilman AG, Harris BA (Oct 1999). "Regulators of G protein signaling 6 and 7. Purification of complexes with gbeta5 and assessment of their effects on g protein-mediated signaling pathways". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (43): 31087–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.43.31087. PMID 10521509.
- Orlandi C, Posokhova E, Masuho I, Ray TA, Hasan N, Gregg RG, Martemyanov KA (June 11, 2012). "GPR158/179 regulate G protein signaling by controlling localization and activity of the RGS7 complexes". J. Cell Biol. 197 (6): 711–9. doi:10.1083/jcb.201202123. PMC 3373406. PMID 22689652.
- Kim E, Arnould T, Sellin L, Benzing T, Comella N, Kocher O, Tsiokas L, Sukhatme VP, Walz G (May 1999). "Interaction between RGS7 and polycystin". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (11): 6371–6. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.6371K. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.11.6371. PMC 26888. PMID 10339594.
- Hunt RA, Edris W, Chanda PK, Nieuwenhuijsen B, Young KH (Apr 2003). "Snapin interacts with the N-terminus of regulator of G protein signaling 7". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 303 (2): 594–9. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00400-5. PMID 12659861.
Further reading
- Shuey DJ, Betty M, Jones PG, Khawaja XZ, Cockett MI (1998). "RGS7 attenuates signal transduction through the G(alpha q) family of heterotrimeric G proteins in mammalian cells". J. Neurochem. 70 (5): 1964–72. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70051964.x. PMID 9572280.
- Levay K, Cabrera JL, Satpaev DK, Slepak VZ (1999). "Gβ5 prevents the RGS7-Gαo interaction through binding to a distinct Gγ-like domain found in RGS7 and other RGS proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (5): 2503–7. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.2503L. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.5.2503. PMC 26814. PMID 10051672.
- Saitoh O, Kubo Y, Odagiri M, Ichikawa M, Yamagata K, Sekine T (1999). "RGS7 and RGS8 differentially accelerate G protein-mediated modulation of K+ currents". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (14): 9899–904. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.14.9899. PMID 10092682.
- Kim E, Arnould T, Sellin L, Benzing T, Comella N, Kocher O, Tsiokas L, Sukhatme VP, Walz G (1999). "Interaction between RGS7 and polycystin". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (11): 6371–6. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.6371K. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.11.6371. PMC 26888. PMID 10339594.
- Snow BE, Betts L, Mangion J, Sondek J, Siderovski DP (1999). "Fidelity of G protein β-subunit association by the G protein γ-subunit-like domains of RGS6, RGS7, and RGS11". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (11): 6489–94. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.6489S. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.11.6489. PMC 26909. PMID 10339615.
- Posner BA, Gilman AG, Harris BA (1999). "Regulators of G protein signaling 6 and 7. Purification of complexes with gbeta5 and assessment of their effects on g protein-mediated signaling pathways". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (43): 31087–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.43.31087. PMID 10521509.
- Benzing T, Yaffe MB, Arnould T, Sellin L, Schermer B, Schilling B, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K, Leparc GG, Kim E, Walz G (2000). "14-3-3 interacts with regulator of G protein signaling proteins and modulates their activity". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (36): 28167–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002905200. PMID 10862767.
- Rose JJ, Taylor JB, Shi J, Cockett MI, Jones PG, Hepler JR (2000). "RGS7 is palmitoylated and exists as biochemically distinct forms". J. Neurochem. 75 (5): 2103–12. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0752103.x. PMID 11032900. S2CID 20156736.
- Zhang JH, Barr VA, Mo Y, Rojkova AM, Liu S, Simonds WF (2001). "Nuclear localization of G protein beta 5 and regulator of G protein signaling 7 in neurons and brain". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (13): 10284–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M009247200. PMID 11152459.
- Benzing T, Köttgen M, Johnson M, Schermer B, Zentgraf H, Walz G, Kim E (2002). "Interaction of 14-3-3 protein with regulator of G protein signaling 7 is dynamically regulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (36): 32954–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.M200859200. PMID 12077120.
- Hunt RA, Edris W, Chanda PK, Nieuwenhuijsen B, Young KH (2003). "Snapin interacts with the N-terminus of regulator of G protein signaling 7". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 303 (2): 594–9. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00400-5. PMID 12659861.
- Witherow DS, Tovey SC, Wang Q, Willars GB, Slepak VZ (2003). "G beta 5.RGS7 inhibits G alpha q-mediated signaling via a direct protein-protein interaction". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (23): 21307–13. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212884200. PMID 12670932.
- Anderson NL, Polanski M, Pieper R, Gatlin T, Tirumalai RS, Conrads TP, Veenstra TD, Adkins JN, Pounds JG, Fagan R, Lobley A (2004). "The human plasma proteome: a nonredundant list developed by combination of four separate sources" (PDF). Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 3 (4): 311–26. doi:10.1074/mcp.M300127-MCP200. PMID 14718574. S2CID 7710900.
- Takida S, Fischer CC, Wedegaertner PB (2005). "Palmitoylation and Plasma Membrane Targeting of RGS7 Are Promoted by αo". Mol. Pharmacol. 67 (1): 132–9. doi:10.1124/mol.104.003418. PMC 1405920. PMID 15496508.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, Ota T, Nishikawa T, Yamashita R, Yamamoto J, Sekine M, Tsuritani K, Wakaguri H, Ishii S, Sugiyama T, Saito K, Isono Y, Irie R, Kushida N, Yoneyama T, Otsuka R, Kanda K, Yokoi T, Kondo H, Wagatsuma M, Murakawa K, Ishida S, Ishibashi T, Takahashi-Fujii A, Tanase T, Nagai K, Kikuchi H, Nakai K, Isogai T, Sugano S (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: Large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- Drenan RM, Doupnik CA, Jayaraman M, Buchwalter AL, Kaltenbronn KM, Huettner JE, Linder ME, Blumer KJ (2006). "R7BP augments the function of RGS7*Gbeta5 complexes by a plasma membrane-targeting mechanism". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (38): 28222–31. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604428200. PMID 16867977.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.