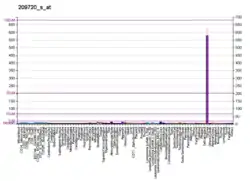
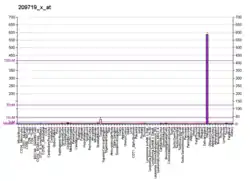
SERPINB3
Serpin B3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINB3 gene.[5][6]
See also
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000057149 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000058017 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Schneider SS, Schick C, Fish KE, Miller E, Pena JC, Treter SD, Hui SM, Silverman GA (May 1995). "A serine proteinase inhibitor locus at 18q21.3 contains a tandem duplication of the human squamous cell carcinoma antigen gene". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 92 (8): 3147–51. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.8.3147. PMC 42122. PMID 7724531.
- "Entrez Gene: SERPINB3 serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 3".
Further reading
- Suminami Y, Kishi F, Sekiguchi K, Kato H (1992). "Squamous cell carcinoma antigen is a new member of the serine protease inhibitors". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 181 (1): 51–8. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(05)81380-4. PMID 1958219.
- Mino-Miyagawa N, Kimura Y, Hamamoto K (1990). "Tumor-antigen 4. Its immunohistochemical distribution and tissue and serum concentrations in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and esophagus". Cancer. 66 (7): 1505–12. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19901001)66:7<1505::AID-CNCR2820660712>3.0.CO;2-V. PMID 2208001.
- Mino N, Iio A, Hamamoto K (1988). "Availability of tumor-antigen 4 as a marker of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and other organs". Cancer. 62 (4): 730–4. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19880815)62:4<730::AID-CNCR2820620415>3.0.CO;2-W. PMID 2840187.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Schick C, Pemberton PA, Shi GP, et al. (1998). "Cross-class inhibition of the cysteine proteinases cathepsins K, L, and S by the serpin squamous cell carcinoma antigen 1: a kinetic analysis". Biochemistry. 37 (15): 5258–66. doi:10.1021/bi972521d. PMID 9548757.
- Cataltepe S, Gornstein ER, Schick C, et al. (2000). "Co-expression of the squamous cell carcinoma antigens 1 and 2 in normal adult human tissues and squamous cell carcinomas". J. Histochem. Cytochem. 48 (1): 113–22. doi:10.1177/002215540004800112. PMID 10653592.
- Uemura Y, Pak SC, Luke C, et al. (2000). "Circulating serpin tumor markers SCCA1 and SCCA2 are not actively secreted but reside in the cytosol of squamous carcinoma cells". Int. J. Cancer. 89 (4): 368–77. doi:10.1002/1097-0215(20000720)89:4<368::AID-IJC9>3.0.CO;2-6. PMID 10956412.
- Hamada K, Shinomiya H, Asano Y, et al. (2001). "Molecular cloning of human squamous cell carcinoma antigen 1 gene and characterization of its promoter". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1518 (1–2): 124–31. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(01)00174-9. PMID 11267667.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Shimada H, Nabeya Y, Okazumi S, et al. (2003). "Prediction of survival with squamous cell carcinoma antigen in patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma". Surgery. 133 (5): 486–94. doi:10.1067/msy.2003.139. PMID 12773976.
- Micke O, Bruns F, Schäfer U, et al. (2003). "The clinical value of squamous cell carcinoma antigen in patients irradiated for locally advanced cancer of the head and neck". Anticancer Res. 23 (2A): 907–11. PMID 12820321.
- Nawata S, Nakamura K, Hirakawa H, et al. (2004). "Electrophoretic analysis of the cleaved form of serpin, squamous cell carcinoma antigen-1 in normal and malignant squamous epithelial tissues". Electrophoresis. 24 (14): 2277–82. doi:10.1002/elps.200305501. PMID 12874860. S2CID 41852542.
- Masumoto K, Sakata Y, Arima K, et al. (2003). "Inhibitory mechanism of a cross-class serpin, the squamous cell carcinoma antigen 1". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (46): 45296–304. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307741200. PMID 12949073.
- Moore PL, Ong S, Harrison TJ (2004). "Squamous cell carcinoma antigen 1-mediated binding of hepatitis B virus to hepatocytes does not involve the hepatic serpin clearance system". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (47): 46709–17. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302842200. PMID 12975381.
- Onishi A, Nakashiro K, Mihara M, et al. (2004). "Basic and clinical studies on quantitative analysis of lymph node micrometastasis in oral cancer". Oncol. Rep. 11 (1): 33–9. doi:10.3892/or.11.1.33. PMID 14654899.
- Hirakawa H, Nawata S, Sueoka K, et al. (2004). "Regulation of squamous cell carcinoma antigen production by E-cadherin mediated cell-cell adhesion in squamous cell carcinoma cell line". Oncol. Rep. 11 (2): 415–9. doi:10.3892/or.11.2.415. PMID 14719077.
- Pontisso P, Calabrese F, Benvegnù L, et al. (2004). "Overexpression of squamous cell carcinoma antigen variants in hepatocellular carcinoma". Br. J. Cancer. 90 (4): 833–7. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6601543. PMC 2410161. PMID 14970861.
- Ruvoletto MG, Tono N, Carollo D, et al. (2004). "Surface expression of squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) can be increased by the preS1(21-47) sequence of hepatitis B virus". J. Gen. Virol. 85 (Pt 3): 621–4. doi:10.1099/vir.0.19130-0. PMID 14993646.
- Turato, C; Ruvoletto, MG; Biasiolo, A; et al. (Mar 2009). "Squamous cell carcinoma antigen-1 (SERPINB3) polymorphism in chronic liver disease". Dig Liver Dis. 41 (3): 212–6. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2008.06.001. PMID 18657489.
External links
- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: I04.008
- SERPINB3+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.