Seba's short-tailed bat
Seba's short-tailed bat (Carollia perspicillata) is a common and widespread bat species in the family Phyllostomidae.[3] They are found in Central America, the northern parts of South America, and in the Antilles islands.[3]
| Seba's short-tailed bat | |
|---|---|
 | |
| feeding on a Piper fruit | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Phyllostomidae |
| Genus: | Carollia |
| Species: | C. perspicillata |
| Binomial name | |
| Carollia perspicillata | |
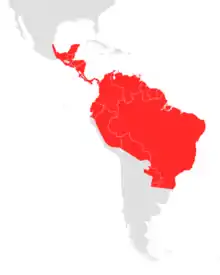 | |
| Seba's short-tailed bat range | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Vespertilio perspicillatus Linnaeus, 1758 | |


Description
C. perspicillata is a small to medium-sized bat with relatively short ears, and a short, triangular noseleaf.[3] They have fur that is dense and soft, and can be a variety of colors, ranging from black to brown to gray, with both albino and orange individuals found in certain areas.[3] Sexual dimorphism varies in C. perspicillata based on geography.[3] In Colombia, there are no differences in size and color between sexes, but in the West Indies females are usually larger, and males are larger everywhere else this species is found.[3]

C. perspicillata has a very good sense of smell, good visual acuity, and they show less specialization in their auditory apparatus as opposed to insectivorous bats. However, they still employ echolocation as a primary method of orientation.[3] They use calls that originate in their mouths or nostrils, which are intense, and have been shown to be the most directional sonar beams in any species of echolocating bat.[3][4]
Ecology
Range and Habitat
C. perspicillata is primarily found in Mexico, Bolivia, Paraguay, Brazil, Trinidad, and Tobago.[3] They are mostly found in forests, both deciduous and evergreen.[3] It is usually found near stagnant water, in areas with a large amount of free internal space, usually below elevations of 1000 meters.[3] As a result, this bat is among the most common that are caught at ground level, based on their foraging habits.[3]
Diet
C. perspicillata is known to eat a large variety of fruit, with a strong preference for the genus Piper (Piperaceae),[5] as well as nectar, pollen, and insects.[3] This bat is a generalist, eating a wide variety of fruits that are characterized by being high in protein and low in fiber.[3] During times when fruit isn't plentiful, these bats supplement their diets using nectar and pollen from flowers, which also opens up the possibility for them being pollinators for the flowers they eat.[3]
Behavior
Roosting
Groups of C. perspicillata will roost in numbers from 10-100, in caves, hollow trees, and in tunnels.[3] They will usually roost during the day, and will forage at night.[3] There are two different types of roosts found in these bats, harems and bachelor roosts.[3] In a harem roost, there is a single male, some females and their offspring.[3] Bachelor roosts are used by males without harems, with females joining seasonally.[3]
Males are territorial of their roosts, and will often fight other intruding males by means of boxing.[3][6] Males follow a pattern of behavioral stages before fighting.[6] This entails ear movements, head lifts, neck craning, wing unfolding, punch mimicking, and finally boxing with each other.[6] Even though this is aggressive behavior, either male is allowed to stop fighting and leave the conflict, and injuries usually aren't worse than a few scrapes and bruises.[6] It is also shown that males use distinct vocalizations during conflicts, which might be used to determine the identity of the competitor, and based on that information, parts of the pre-fighting stages can be skipped, and the animals will begin boxing.[6]
Mating and Reproduction
Males will actively try to recruit females to mate with for their harems through the use of vocalization and hovering.[3] It has been shown that there are two different reproductive periods in the year, one being from June–August, and the other from February to May.[3] The June–August period coincides with a period of high fruit production, and the February–May period with a large amounts of flowers.[3]
Gestation periods are about 120 days, and young are born precocial.[3] Newborns grow quickly, and reach full adult body weight after about 10–13 weeks, and will usually leave the parental harem after about 16 weeks.[3] All females will reach sexual maturity by the time they're one year old, and males will reach sexual maturity within the first two years of being born.[3]
Mothers will communicate with their offspring though vocalization, and it has even been shown that a mother can discriminate between the calls of its offspring and the offspring of other females.[7] They exhibit more maternal approach behaviors when hearing the calls of their own offspring, and more experienced mothers show more approach behavior as opposed to new mothers.[7] However, this behavior isn't the same in males, who instead take a different approach to hearing the calls of their offspring.[3][7] They will harass the mothers until they go to take care of the young, but won't go to attend to the young themselves.[7]
Flight
As with other bats, the metabolism of these bats follows a U-shape during flight.[8] This means that they use the most energy when flying at low and high airspeeds, and use less energy at moderate speeds.[8] Most of their flights to find food are relatively close, because they can bring back smaller fruit to their roosts, but just still eat bigger fruits at the tree.[3]
Lifespan
Like many bat species, C. perspicillata has a long lifespan, being able to live up to ten years.[3] Mortality rates for bats is 53% in the first two years of life, but that goes down to 22% in the following years.[3] In this species, there doesn't seem to be a difference in the average lifespans of males as opposed to females.[3]
Captivity
Several zoos, such as the Central Park Zoo keep colonies of these bats. These bats are relatively easy to breed and are the most common bat species found in zoos today. The bats at the Central Park Zoo can be found at the Tropic Zone building.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Carollia perspicillata. |
References
- Barquez, R.; Perez, S.; Miller, B. & Diaz, M. (2015). "Carollia perspicillata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T3905A22133716. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T3905A22133716.en.
- Linnæus, Carl (1758). Systema naturæ per regna tria naturæ, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I (in Latin) (10th ed.). Holmiæ: Laurentius Salvius. p. 31. Retrieved 21 November 2012.
- Cloutier, Danielle; Thomas, Donald (10 December 1992). "Carollia perspicilatta". Mammalian Species Account. 98: 149–156. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2014.10.011. S2CID 31003295.
- Brinklo̸v, Signe; Jakobsen, Lasse; Ratcliffe, John M.; Kalko, Elisabeth K. V.; Surlykke, Annemarie (2011). "Echolocation call intensity and directionality in flying short-tailed fruit bats, Carollia perspicillata (Phyllostomidae)". The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America. 129 (1): 427–435. doi:10.1121/1.3519396. PMID 21303022.
- Andrade, Tiago; Thies, Wibke; Rogeri, Patrícia; Kalko, Elisabeth; Mello, Marco (2013). "Hierarchical fruit selection by Neotropical leaf-nosed bats (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 94 (5): 1094–1101. doi:10.1644/12-MAMM-A-244.1. Retrieved 4 November 2020.
- Fernandez, Ahana; Fasel, Nicolas; Knörnschild, Mirjam; Richner, Heinz (December 2014). "When bats are boxing: aggressive behaviour and communication in male Seba's short-tailed fruit bat". Animal Behaviour. 98: 149–156. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2014.10.011. S2CID 31003295.
- Knörnschild, Mirjam; Feifel, Marion; Kalko, Elisabeth (November 2013). "Mother–offspring recognition in the bat Carollia perspicillata". Animal Behaviour. 86 (5): 941–948. doi:10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.08.011. S2CID 53190837.
- von Busse, Rhea; Swartz, Sharon; Voigt, Christian (2013). "Flight metabolism in relation to speed in Chiroptera: testing the U-shape paradigm in the short-tailed fruit bat Carollia perspicillata". Journal of Experimental Biology. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
