Selenium mustard
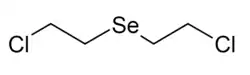
Selenium mustard (Bis(2-chloroethyl) selenide) is a haloalkyl derivative of selenium, related to vesicant chemical agents such as sulfur mustard and nitrogen mustard. Selenium mustard is somewhat less toxic than its relatives and has not been used as a chemical warfare agent, however it is still a potent alkylating agent and has potential uses in chemotherapy.[1][2][3][4][5]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-chloro-2-(2-chloroethylselanyl)ethane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8Cl2Se | |
| Molar mass | 205.98 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Kang SI, Spears CP (April 1987). "Linear free energy relationships and cytotoxicities of para-substituted 2-haloethyl aryl selenides and bis(2-chloroethyl) selenides". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 30 (4): 597–602. doi:10.1021/jm00387a003. PMID 3560155.
- Kang SI, Spears CP (June 1990). "Phenyl selenones: alkyl transfer by selenium-carbon bond cleavage". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 33 (6): 1544–7. doi:10.1021/jm00168a003. PMID 2342050.
- Kang SI, Spears CP (January 1990). "Structure-activity studies on organoselenium alkylating agents". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 79 (1): 57–62. doi:10.1002/jps.2600790114. PMID 2313578.
- Hu X, Tian Z, Chen Y, Lu X (2000). "One-Pot Two-Step Approach to Selenides. Phase-Transfer Catalyzed Synthesis of ω-Hydroxyalkyl Selenides". Synthetic Communications. 30 (3): 523–529. doi:10.1080/00397910008087348. S2CID 94951635.
- Potapov VA, Kurkutov EO, Musalov MV, Amosova SV (February 2014). "Synthesis of bis(2-haloethyl) selenides by reaction of selenium dihalides with ethylene". Russian Journal of Organic Chemistry. 50 (2): 291–292. doi:10.1134/S1070428014020250. S2CID 97109063.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
