Shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of active blocks, as well as to provide passive protection by closing one or more lines of engagement during combat.
.jpg.webp)
Zulu chief Goza and two of his councillors in war-dress, all with Nguni shields, c.1870. The size of the shield on the chief's left arm denotes his status, and the white colour that he is a married man.[1]
Gallery
 Image from Hatshepsut's expedition to Punt showing Egyptians soldiers with shields (wood/animal skin). 15th century BC. Temple of Hathor Deir el-Bahari
Image from Hatshepsut's expedition to Punt showing Egyptians soldiers with shields (wood/animal skin). 15th century BC. Temple of Hathor Deir el-Bahari A hoplite by painter Alkimachos, on an Attic red-figure vase, c. 460 BC. Shield has a curtain which serves as a protection from arrows.
A hoplite by painter Alkimachos, on an Attic red-figure vase, c. 460 BC. Shield has a curtain which serves as a protection from arrows. Sword and buckler(small shield) combat, plate from the Tacuinum Sanitatis illustrated in Lombardy, ca. 1390.
Sword and buckler(small shield) combat, plate from the Tacuinum Sanitatis illustrated in Lombardy, ca. 1390..jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
 Australian Aboriginal shield, Royal Albert Memorial Museum.
Australian Aboriginal shield, Royal Albert Memorial Museum. Nias ceremonial shield.
Nias ceremonial shield. Hippopotamus Hide Shield from Sudan. Currently housed at Westminster College in New Wilmington, Pennsylvania.
Hippopotamus Hide Shield from Sudan. Currently housed at Westminster College in New Wilmington, Pennsylvania. Aboriginal bark shield collected in Botany Bay, New South Wales, during Captain Cook's first voyage in 1770 (British Museum)
Aboriginal bark shield collected in Botany Bay, New South Wales, during Captain Cook's first voyage in 1770 (British Museum) Wall painting depicting a Mycenaean Greek "figure eight" shield with a suspension strap at the middle, 15th century BC, National Archaeological Museum, Athens -The faces of figure eight shields were quite convex. The cited "strap" may be the ridge on the front (so denoted by the visible pattern of the ox hide) of the shield.
Wall painting depicting a Mycenaean Greek "figure eight" shield with a suspension strap at the middle, 15th century BC, National Archaeological Museum, Athens -The faces of figure eight shields were quite convex. The cited "strap" may be the ridge on the front (so denoted by the visible pattern of the ox hide) of the shield.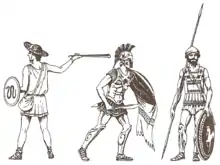 Greek soldiers of Greco-Persian Wars. Left: Greek slinger. Right: hoplites. Middle: hoplite's shield has a curtain which serves as a protection from arrows.
Greek soldiers of Greco-Persian Wars. Left: Greek slinger. Right: hoplites. Middle: hoplite's shield has a curtain which serves as a protection from arrows. Elaborate and sophisticated shields from the Philippines.
Elaborate and sophisticated shields from the Philippines. Ballistic shield, NIJ Level IIIA
Ballistic shield, NIJ Level IIIA%252C_Special_Boat_Team_22_conducts_training_16_AUG_09.jpg.webp) U.S. Navy Special Warfare Combatant-craft Crewmen (SWCC) fire a shield-equipped Minigun
U.S. Navy Special Warfare Combatant-craft Crewmen (SWCC) fire a shield-equipped Minigun Two wooden round shields survived at Thorsberg moor
Two wooden round shields survived at Thorsberg moor
See also
References
- Wood, J. G. (1870). The uncivilized races of men in all countries of the world. Рипол Классик. p. 115. ISBN 9785878634595.
Bibliography
- Drummond, James (1890). "Notes on Ancient Shields and Highland Targets". Archaeologia Scotica. 5.
- Schulze, André(Hrsg.): Mittelalterliche Kampfesweisen. Band 2: Kriegshammer, Schild und Kolben. – Mainz am Rhein. : Zabern, 2007. – ISBN 3-8053-3736-1
- Snodgrass, A.M. "Arms and Armour of the Greeks." Cornell University Press, 1967
- "The Hoplite." The Classical Review, 61. 2011.
- Hellwag, Ursula. "Shield(s)." Encyclopaedia Aethiopica, Siegbert Uhllig (ed.), vol. 4, 650-651. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shields. |
| Look up shield in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.