Silver cyanate
Silver cyanate can be made by the reaction of potassium cyanate with silver nitrate in aqueous solution, from which it precipitates as a solid.
|
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Silver(I) cyanate | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.007 | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| AgOCN | |||
| Molar mass | 149.885 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colourless | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Alternatively, the reaction
analogous to the reaction used for the industrial production of sodium cyanate, may be used.
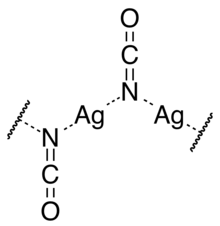
The crystal structure consists of chains of silver atoms bridged by the nitrogen atom of cyanate ions.[1]
Silver cyanate reacts With nitric acid to form silver nitrate, carbon dioxide, and ammonium nitrate.[2]
See also
References
- D. Britton, J. D. Dunitz: The crystal structure of silver cyanate, Acta Crystallogr. (1965). 18, 424-428, doi:10.1107/S0365110X65000944
- J. Milbauer: Bestimmung und Trennung der Cyanate, Cyanide, Rhodanide und Sulfide in Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry 42 (1903) 77-95, doi:10.1007/BF01302741.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
