Smart transducer
A smart transducer is an analog or digital transducer or actuator combined with a processing unit and a communication interface.[1]
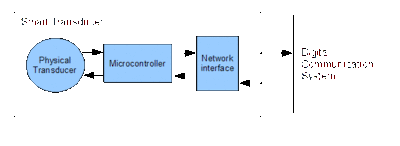
As sensors and actuators become more complex they provide support for various modes of operation and interfacing. Some applications require additionally fault-tolerance and distributed computing. Such high-level functionality can be achieved by adding an embedded microcontroller to the classical sensor/actuator, which increases the ability to cope with complexity at a fair price.
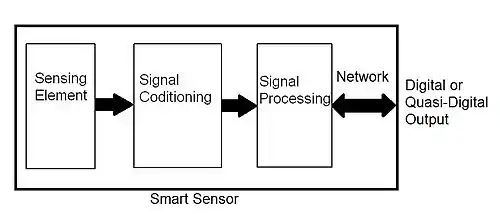
In the machine vision field, a single compact unit which combines the imaging functions and the complete image processing functions is often called a smart sensor.
They are often made using CMOS, VLSI technology and may contain MEMS[2] devices leading to lower cost. They may provide full digital outputs for easier interface or they may provide quasi-digital outputs like pulse width modulation.
Advantages
- Compact
- Higher reliability
- Lower cost
- Can be done using existing cmos processes
- Ease of use
- electronic data storage
- self indication
- auto correction
- auto display
See also
- Ambient intelligence
- Edge computing
- IEEE 1451
- Internet of things
- SensorML
- System on a chip
- Transducer electronic data sheet
- TransducerML
References
- Elmenreich, W. (2006). "Time-triggered smart transducer networks" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics. 2 (3): 192–199. arXiv:1507.04394. doi:10.1109/TII.2006.873991.
- Sheu, Meng-Lieh; Hsu, Wei-Hung; Tsao, Lin-Jie (2012). "A Capacitance-Ratio-Modulated Current Front-End Circuit with Pulsewidth Modulation Output for a Capacitive Sensor Interface". IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement. 61 (2): 447–455. doi:10.1109/TIM.2011.2161929.
