Solar cycle 20
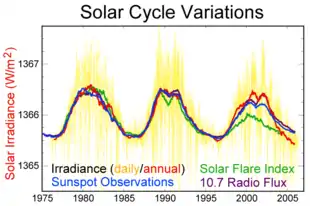
Solar cycle 20 was the twentieth solar cycle since 1755, when extensive recording of solar sunspot activity began.[1][2] The solar cycle lasted 11.4 years, beginning in October 1964 and ending in March 1976. The maximum smoothed sunspot number (SIDC formula) observed during the solar cycle was 156.6 (November 1968), and the starting minimum was 14.3.[3] During the minimum transit from solar cycle 20 to 21, there were a total of 272 days with no sunspots.[4][5][6]
| Solar cycle 20 | |
|---|---|
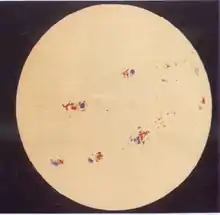 Solar magnetogram from solar cycle 20 (1974). | |
| Sunspot data | |
| Start date | October 1964 |
| End date | March 1976 |
| Duration (years) | 11.4 |
| Max count | 156.6 |
| Max count month | November 1968 |
| Min count | 14.3 |
| Spotless days | 272 |
| Cycle chronology | |
| Previous cycle | Solar cycle 19 (1954–1964) |
| Next cycle | Solar cycle 21 (1976–1986) |
Comparison with other cycles shows that geomagnetic activity during the declining phase of cycle 20 (1973–1975) was unusually high.[7]
Data from solar cycle 20 was used to build the K-1974 solar proton fluence model, used for planning space missions during solar cycle 21.[8]
1972
An extremely active sunspot region, McMath 11976, produced a historic series of flares and CMEs in July, one CME transited to Earth in a record low 14.6 hours and produced a strong geomagnetic storm that caused widespread electrical and communications grid disturbances, and notably, the accidental detonation of numerous U.S. Navy magnetic sea mines in North Vietnam.[9]
See also
References
- Kane, R.P. (2002), "Some Implications Using the Group Sunspot Number Reconstruction", Solar Physics, 205 (2): 383–401, Bibcode:2002SoPh..205..383K, doi:10.1023/A:1014296529097
- "The Sun: Did You Say the Sun Has Spots?". Space Today Online. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- SIDC Monthly Smoothed Sunspot Number. ""
- Spotless Days. ""
- Dr. Tony Phillips (11 July 2008). "What's Wrong with the Sun? (Nothing)". NASA. Archived from the original on 14 July 2008.
- Solaemon's Spotless Days Page. ""
- Gosling, J. T.; Asbridge, J. R.; Bame, S. J. (1 August 1977). "An unusual aspect of solar wind speed variations during solar cycle 20". Journal of Geophysical Research. 82 (22): 3311–3314. Bibcode:1977JGR....82.3311G. doi:10.1029/JA082i022p03311.
- Miroshnichenko, Leonty (2001). Solar Cosmic Rays. Springer. p. 395. ISBN 0792369289.
- Knipp, Delores J.; B. J. Fraser; M. A. Shea; D. F. Smart (2018). "On the Little‐Known Consequences of the 4 August 1972 Ultra‐Fast Coronal Mass Ejecta: Facts, Commentary and Call to Action". Space Weather. 16: 1635–1643. Bibcode:2018SpWea..16.1635K. doi:10.1029/2018SW002024.