Soltam M-65
The Soltam M-65 is a 120 mm mortar that was developed by Tampella in 1953 via introduction of new baseplate for 120 Krh/40 invented by Hans Otto Donner. In 1960s Soltam Systems of Israel bought a license. The mortar system comes in two versions, a standard mortar and a long-range version.[1]
| Soltam M-65 | |
|---|---|
 M-65 Standard | |
| Type | Mortar |
| Place of origin | Israel |
| Service history | |
| Used by | See Operators |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Tampella |
| Designed | 1953 |
| Manufacturer | Soltam Systems |
| Variants | See variants |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 231 kg (firing position), 351 kg (travelling) |
| Crew | 6 |
| Shell | Standard 120mm NATO mortar round |
| Caliber | 120 mm |
| Carriage | M151 Jeep style carriage wheels |
| Elevation | +30°/+80° |
| Traverse | -20°/+20° |
| Rate of fire | 1st minute: 16 rounds burst, 4 rounds per minute sustained thereafter. |
| Maximum firing range | 6500m |
Design
This heavy mortar is light enough to be transported by helicopter sling load, drop by parachute or carried in an APC such as the M113 Armored Personnel Carrier. It can also be towed as a normal artillery piece or even manhandled if necessary. The wheels on the carriage are the same as fitted to the M151 Jeep, and have handling rings to aid in manhandling it. All components are made of chrome-plated or stainless steel to resist wear and corrosion.
Vehicle mounted version
- M3 Mk. D - a M3 Half-track based 120 mm mortar carrier (used exclusively by Israel Defense Forces until replaced by the M1064 mortar carrier),
Operators
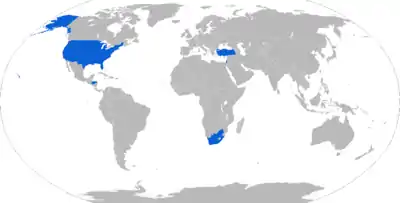
Map with M-65 operators in blue
Current operators
 : Honduran Army[2]
: Honduran Army[2] : Israel Defense Forces (primary user)
: Israel Defense Forces (primary user) : Myanmar Army
: Myanmar Army Nicaragua
Nicaragua : Singapore Army[2]
: Singapore Army[2] : South African Army
: South African Army : United States Army[2]
: United States Army[2]
Former operators
See also
- Mortier 120mm Rayé Tracté Modèle F1
- Soltam K6 (US Army designation M120)
- Soltam M-66
- Weapons of the Lebanese Civil War
References
- "Soltam K5 and K6 120 mm light mortars (Israel), Mortars". Jane's. Archived from the original on 25 September 2012. Retrieved 12 July 2012.
- "SIPRI arms transfer database". Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. Information generated on 3 April 2014. Retrieved 3 April 2014. Check date values in:
|date=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
