Suplex
A suplex is an offensive move used in amateur and professional wrestling. It is a throw that involves lifting the opponent and bridging or rolling to slam the opponent on their back.
Professional wrestling features many different varieties of suplexes. The following are among the most common, but many more exist, particularly as the signature techniques of individual wrestlers.
Front facelock variants
In these suplexes, the wrestlers begin by facing each other, the attacking wrestler then applies a front facelock to the opponent before executing a throw. In most cases, the opponent is suspended upside-down during part of the move. The most common front facelock suplex is the vertical suplex.
Fisherman suplex
Also known as a fisherman's suplex or the leg hook suplex. With the opponent in a front facelock with the near arm draped over the attacker's shoulder, the wrestler hooks the opponent's near leg behind the opponent's knee with their free arm and falls backwards, flipping the opponent onto their back. In most cases the attacking wrestler will keep the leg hooked and bridge to pin the opponent in a cradle-like position, as in the case of Curt Hennig and Joe Hennig's Perfect-plex.[1] Other times the wrestler will apply a leglock submission hold to the hooked leg. It is used by Peyton Royce as "The Ughhh", and Penelope Ford uses it too.
Swinging fisherman suplex
More commonly referred to as swinging fisherman neckbreaker. A swinging variation of the standard fisherman suplex, this move sees a wrestler, with the opponent in a front facelock with the near arm draped over their shoulder, hook the opponent's near leg with their free arm and roll over to the same side of the arm being used to hook the opponent's leg, flipping the opponent over onto their back.
Hammerlock suplex
In this variation of the suplex, the attacker applies a hammerlock on the opponent before applying a front facelock and positioning the opponent's free arm over the attacker's head. The attacker then lifts up the opponent and falls backwards, dropping the opponent down back first, landing with their trapped arm bent behind their back. Junji Hirata has innovated this move.
Slingshot suplex
The attacker faces a standing opponent with one side of the ring immediately behind the opponent. The attacker applies a front facelock to the opponent, takes hold of the opponent with their free hand, then lifts the opponent until they are nearly vertical. The attacker then falls forward so that the torso of the opponent bounces off the top ring rope, and uses this momentum to quickly lift the opponent overhead once more and fall backwards, driving the back and shoulders of the opponent into the ground.
Suplex slam
This move is similar to most suplexes and starts with the attacker applying a front face lock to the opponent and draping the opponent's near arm over their shoulder, then lifting the opponent up and holding them in the vertical position. This is where the move differs from most of its counterparts, with the attacker not falling with the opponent, but rather shifting themselves slightly and throwing the opponent to the mat on their back. Sometimes this involves the wrestler turning the opponent in midair and slamming the opponent down to the mat in front of them onto their back, similar to a high-angled body slam. The suplex slam can also be used for other suplexes such as the fisherman suplex or gutwrench suplex.
There is also a sitout version. Also called a suplex driver or a Falcon Arrow, this sees an attacker apply a front facelock to the opponent and drape the opponent's near arm over their shoulder. The attacker then takes hold of the opponent's torso with their free arm and lifts the opponent to a vertical position. The facelock is loosened so the opponent can be twisted slightly, then the attacker falls to a sitting position and the victim's back and shoulders are driven into the mat. The opponent lands between the attacker's legs with their head toward them. This Variation was innovated by Hayabusa.
Another variation sees the wrestler perform a vertical suplex, but instead of twisting the upside down opponent to face them, the wrestler turns 180° to face the opponent before sitting down and driving them back-first between their legs.
Reverse suplex slam
Also called a front suplex or a gourdbuster, this move sees the attacker apply a front face lock to the opponent and drape the opponent's near arm over their shoulder. The attacker then lifts the opponent into a vertical position, then falls or kneels forward, driving the opponent's face into the ground. A standing version also exists. It was invented by Arn Anderson.
In the sitout version, the attacker applies a front face lock to the opponent and drapes the opponent's near arm over their shoulder. The attacker then lifts the opponent into a vertical position, and falls into a sit-out position, driving the face of the opponent into the ground. In another variation, the wrestler releases the hold just prior to the sitout position, letting the opponent's own momentum force them down head-first.
Superplex

A superplex (a portmanteau of "super" and "suplex") refers to any suplex performed by an attacker standing on the second or third rope against an opponent sitting on the top rope or top turnbuckle. The most common suplex used for this top rope move is the standard vertical suplex variation (known as the suicide-plex), in which the attackers apply a front face lock to the opponent, draping the opponent's near arm over their respective shoulders, at this point the wrestler falls backwards and flips the opponent over them so they both land on their backs.The Move is used by PAC as a Finisher.
Tornado suplex
In a set-up similar to a tornado DDT, a wrestler goes to the top rope and applies a front facelock on their opponent from an elevated position, draping the opponent's near arm over their shoulder. The wrestler then jumps forward and swings around, but lands on their feet and performs a suplex on their opponent.
Vertical suplex

In a set-up similar to a snap suplex, the attacking wrestler applies a front face lock to the opponent, draping the opponent's near arm over their shoulder, when the opponent is in position they are lifted to an upside-down position before the attacking wrestler falls backwards slamming the opponent's back into the mat.
The delayed variation of a vertical suplex, also known as the hanging suplex, standing suplex or stalling suplex, sees the attacking wrestler holds an opponent in the upside-down position at the peak of the arc for several seconds before completing the maneuver, thereby (in kayfabe) causing blood to pool into the head of the opponent. This move is a staple of larger and powerful wrestlers as it gives an aura of dominance over their opponents who can do nothing but wait to drop in the suplex.
The rotating variation of a vertical suplex, also sometimes known as the rotation suplex, rotary suplex, or twisting suplex, sees the attacking wrestler lift the opponent as in a normal vertical suplex, but turn around as they fall back to twist the opponent into the mat.
Drop suplex
This variation of a vertical suplex sees the attacking wrestler lift the opponent as in a normal vertical suplex, but then simply drop them flat to the mat instead of falling backwards with them. The move was first popularized in WCW by Kevin Nash, who began to use it instead of a standard suplex to avoid aggravating a back injury.
Rolling release suplex
This variation of a vertical suplex, also known as the X-plex as well as the Crash Landing, sees the attacker lift the opponent up with the standard suplex lift, but instead of falling backwards and having the opponent drop down onto their shoulders and back, the attacker turns the opponent and releases them from the front facelock at the apex of the lift. Both the attacker and the opponent fall forward, with the opponent landing on their neck, shoulders, and back.
Rolling non-release suplex
Also known as triple rolling verticals, or triple rolling vertical suplexes, this variation of a vertical suplex sees the attacking wrestler perform a single vertical or snap suplex to the opponent, but the attacking wrestler does not release the hold, instead rolling their legs and body into a standing position to execute a second suplex, then repeats the process for a third suplex. This was popularized by WWE Hall of Famer Eddie Guerrero, who used this move, calling it the Three Amigos. Many other WWE superstars used this move to pay tribute to him, such as Chavo and Seth Rollins.
Running suplex
This variation is similar to a classic suplex, including the attacking wrestlers beginning with a standard front facelock, and then when they starts lifting the opponent, they make a few running steps forward while continuing the suplex rotation, slamming the opponent back-first onto the mat.
Snap suplex

This move sees the attacker apply a front face lock to their opponent, draping the opponent's near arm over their shoulder. The attacker stomps down hard and suplexes the opponent stiffly, resulting in a quicker throw.
Swinging vertical suplex
This variation of a vertical suplex sees a wrestler holding their opponent in a front facelock with the near arm draped over their shoulder, lifts the opponent then roll over to one side, flipping the opponent over onto their back. This was used by Dustin Rhodes as the Final Cut in WWE before renaming it as the Final Reckoning in AEW.
Toss suplex
This variation of vertical suplex sees the attacking wrestler lift the opponent as in a normal vertical suplex, but then simply toss them across the mat instead of falling backwards with them.
Jumping suplex
Instead of just falling down onto their own back, the attacking wrestler jumps up and uses their momentum to drive the opponent down to the mat back first.
Underhook suplex
Also known as a half-hatch suplex. It is performed in similar fashion to a snap suplex. The wrestler applies a front facelock with one arm, but instead of draping the arm over their shoulders as seen in most suplexes, the attacker underhooks one of the opponent's arms with their other, placing their hand palm-down on the back of the opponent. The wrestler then lifts the opponent up while bridging backwards, bringing the opponent overhead and onto their back. This can be performed with or without a pinning combination in which the wrestler bridges their back and legs to hold the opponent's shoulders against the mat. It can also be done with a kick for an added snap effect.
Belly-to-back variants
In these variants, the attacker stands behind his opponent and applies a hold before falling backwards, dropping the opponent on his or her upper back. The most common belly-to-back variants are the German suplex and the back suplex.
Belly-to-back suplex

For the belly-to-back suplex, the wrestler stands behind his opponent and puts his head under the arm of the opponent. The wrestler then lifts the opponent up grabbing the waist and thigh of the opponent, so the opponent is on the attacker's shoulder. The attacker finally falls backwards, dropping the opponent flat on his back.[2][3]
Some wrestlers perform the back suplex into a bridging position, simultaneously arching their own back and legs to elevate themselves, gaining leverage and pinning their opponent. Very popular in Mexico's Lucha Libre, where this bridging version is known as a Puente Griego or Greek Bridge in English. In 2018, the Colombian referee Wilmar Roldan announced a campaign to introduce this variant of the suplex to international soccer.[4]
Since the wrestler taking the move is falling backwards, the potential for injury is significant if it is not performed properly. Japanese wrestler Mitsuharu Misawa suffered a spinal injury which triggered a fatal cardiac arrest during his last match in 2009 after Akitoshi Saito gave him the belly-to-back suplex.[5][6]
High-angle belly-to-back suplex
Also known as a backdrop driver, the attacking wrestler stands behind his opponent and puts his head under the arm of the opponent. He then lifts the opponent up using both of his arms wrapped around the torso of the opponent. The attacker finally falls backwards to drive the opponent to the mat on their neck and shoulders.
Leg hook belly-to-back suplex
Sometimes referred to as a leg lift back suplex or leg lift backdrop, it is applied just as a back suplex would be, except that the wrestler wraps only the near arm or no arm around the torso of their opponent. With the free arm(s), the wrestler then hoists their opponent's knees or thighs and throws them backwards in that manner.
Cobra clutch suplex
The attacker places the opponent in a cobra clutch hold. They then proceed to lift the opponent up and fall backwards, driving the opponent to the mat on their head.
Crossface chickenwing suplex
The wrestler stands behind the opponent. He locks one of the opponent's arms in a chickenwing, and wraps his other arm around the opponent's head. He then lifts the opponent up and falls backwards, driving the opponent on to the top of their head, down to the mat.
Crotch clutch suplex
This move involves the attacking wrestler approaching an opponent from behind, reaching down and grasping his crotch with both forearms, with hands together and facing upwards into his groin, and lifting him overhead into a belly-to-back release suplex. The opponent reacts to both the suplex and being grabbed and lifted by his crotch, to humorous effect.
Dragon suplex
This belly-to-back suplex variation sees the wrestler apply a full nelson and then bridge his back, lifting the opponent over him and onto their shoulders down to the mat. The wrestler keeps his back arched and the hold applied, pinning the opponent's shoulders down to the mat. The wrestler may also release the opponent mid-arch, throwing them down to the mat shoulders and neck first, in a variation known as release dragon suplex. Used by Hiroshi Tanahashi as finishing maneuver.
Electric chair suplex
Also known as an electric chair slam. The wrestler lifts the opponent on their shoulders in an electric chair sitting position and then bridges his back, slamming the opponent down to the mat shoulder and upper back first.
German suplex
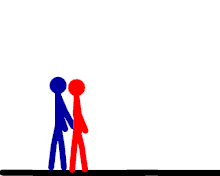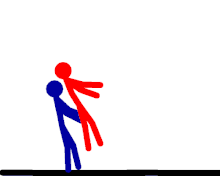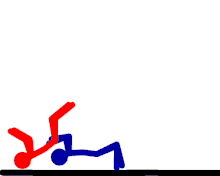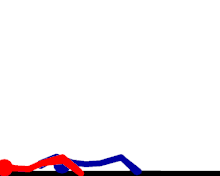
The wrestler stands behind the opponent, grabs them around their waist, lifts them up, and falls backwards while bridging his back and legs, slamming the opponent down to the mat shoulder and upper back first. The wrestler keeps the waistlock and continues bridging with their back and legs, pinning the opponent's shoulders down against the mat. The regular pinning variation can be referred to as the German suplex pin. The wrestler can also release the opponent in mid arch, which is referred to as a release German suplex. Sometimes, rather than bridging for a pin, the wrestler may roll himself into another position to perform the move again, often referred to as multiple, rolling, or non-release German suplexes, in which the attacking wrestler performs a German suplex, then rolls his legs to get back into a standing position, but does not let the opponent go to do so. The attacking wrestler then repeats this numerous times, most commonly three, but sometimes up to eight or more. The most common WWE superstar that uses the maneuver is Brock Lesnar, although it is also commonly used by Chris Benoit and Kurt Angle, among others, in the past.
Straight jacket suplex

The straight jacket suplex or package German suplex has the attacker trapping the opponent's arms while performing a German suplex. Variants such as the cross-arm suplex or X-Plex see the opponent's arms crossed across their chest and held by the attacker. The wrestler then uses the crossed arms as leverage to aid in lifting the opponent up while falling backwards to throw the opponent as in a German suplex.
Half and half suplex
This is a suplex variation in which the wrestler, while standing behind the opponent, places one arm in a Half nelson and the other arm in a chickenwing. The wrestler then proceeds to fall backwards while lifting the opponent overhead in the hold and driving them into the mat behind them. This move is referred to as a half and half suplex as it is a combination of a ¾ nelson suplex and a tiger suplex. The move can be either released or brought into a pin.
Half nelson suplex
This is a version of a German suplex where the attacker stands behind the opponent, facing the same direction. The attacker uses one hand to apply a half nelson hold and wraps the other hand around the opponent's waist. The attacker then lifts the opponent up and falls backwards, dropping the opponent on their head, neck, or shoulders. The move can be either released or brought into a pin.
Pumphandle suplex
The wrestler stands behind the opponent and bends him forward. One of the opponent's arms is pulled back between his legs and held, while the opponent's other arm is hooked by the attacker maneuvering his arm around in front of the opponent's shoulder (as in a pumphandle) and securing it behind the head (a quarter-nelson). The attacker then lifts his opponent up over his head and falls backwards to slam the opponent against the mat back-first.
There are many variations of the pumphandle suplex, including the maintaining of the grip in order to land the opponent on the mat face-first, or inverting the opponent's body position and securing the opponent's free arm using a half-nelson grip instead of the normal quarter-nelson.
Sleeper suplex
The attacker places the opponent in a sleeper hold and then hooks one of the opponents arms with his free arm. The attacker then lifts the opponent up and falls backwards, driving the opponent on their head. A slight variation sees the attacker apply a half nelson choke instead of the sleeper hold before performing the suplex. Jay White uses this move. [7]
Katahajime suplex
The attacker stands behind the opponent, facing the same direction. The wrestler puts one arm in a half nelson and the other hand around the neck in front of the opponent, like in a sleeper. The hand in front of the neck is locked with the other hand at the wrist. With the grip secure, the attacker then lifts the opponent up and falls backwards, dropping the opponent on their head, neck, or shoulders. The move can end in a release or bridging position.The Move was used by Tazz.
Three-quarter nelson suplex
Invented by Mitsuharu Misawa.The attacker places their opponent in three-quarter nelson before lifting them and falling backwards, dropping them on their head or neck. It is also known as the Tiger Suplex '85, due to its association with a August 1985 match between Mitsuharu Misawa, then working as the second incarnation of Tiger Mask, and Kuniaki Kobayashi.
Tiger suplex

Innovated by Alfonso Dantés and popularized by the original Tiger Mask (Satoru Sayama),[8] this move sees the wrestler standing behind their opponent, hooks both of the opponent's arms from the sides, and places their hands palm down flat against the opponent's upper back. The wrestler then lifts the opponent up and falls backwards, arching their back and legs and then slamming the opponent down to the mat shoulder and neck first. Like other suplex variations, this move can either end in a bridging pin or be released upon execution.[9] A Wrist-Clutch variation was invented by Tiger Mask IV (Yoshihiro Yamazaki), called Tiger Suplex '09, because he invented it in 2009.
Wheelbarrow suplex
This move is performed when a wrestler wraps a forward-facing opponent's legs around their waist, in a wheelbarrow hold, from either standing behind an opponent who is laying face-first on the mat or by catching a charging opponent before then applying a waistlock to lift the opponent up off the ground into the air, then the attacking wrestler would continue lifting the opponent over their while falling backwards to hit belly-to-back suplex.
Belly-to-belly variants
In these suplexes, the wrestlers begin by facing each other. The attacker then applies a bodylock before falling backwards and flipping the opponent onto his back and down on the mat.
Belly-to-belly suplex
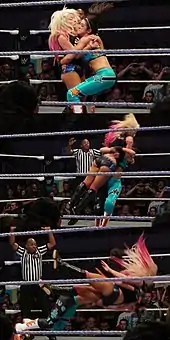
The wrestler wraps their arms around the opponent in a waistlock or a bodylock position and flips them over by violently bridging their own body so the opponent lands on their back. This can be done either overhead or to the side. For a side belly-to-belly suplex, the attacker usually holds on to the opponent for the duration of the move, but for the overhead belly-to-belly suplex, the attacker usually executes an overhead throw and lets go of the opponent. It can also be performed in a "snap" fashion, where the attacker stomps down hard and suplexes the opponent stiffly, resulting in a quicker throw.
Capture suplex
The attacker stands facing a standing opponent. The attacker then catches one leg of the opponent and pulls the opponent towards them so that they are face-to-face, with the attacker reaching under the opponent's leg and hooking it. The attacker then uses their free arm to reach behind the neck of the opponent and take hold of them. The attacker then quickly bridges backwards and releases the opponent, throwing them overhead, or turns 180° while slamming the opponent down to the mat. This move can be used to counter a kick. The move is also known as the head and leg suplex, and can be seen as a variation of the head and arm suplex.
Double underhook suplex
Also known as a double arm suplex, reverse nelson suplex, double axe handle suplex, and a butterfly suplex, the wrestler and opponent face each other, the opponent bent forward. The wrestler hooks the opponent's arms back in a Double Underhook, placing his forearms in the crooks of the opponent's elbows, with his hands on top of the opponent's back in a butcher's grip. The wrestler then lifts the opponent into an upside-down vertical position and falls back, shifting the opponent to one side as the opponent flips over. The wrestler executing the suplex may release the reverse nelson hold during the throw, or can maintain the grip and attempt a bridging pin or submission hold transition upon impact.[10] A common variation was innovated by Daniel Bryan at his time as Bryan Danielson. He executed the Double Underhook Suplex, before dropping his opponent's into a Cross Armbreaker, dubbed the Danielson Special.
Exploder suplex

Also known as a T-bone suplex. The attacker stands facing his opponent and positions himself under one of the opponent's arms and wraps his arm around the opponent's neck and back (this position is similar to that of a side slam) and then grabs the leg of the opponent and tosses him backwards, over the attacker's head. Several other variations exist, such as the wrist-clutch exploder suplex (often called Exploder '98) and the bridging exploder suplex (also called Blizzard Suplex).[11]The move is used by Becky Lynch as the Bexploder Suplex.
Head-and-arm suplex
Also called a gargoyle suplex, the move is a variation of the traditional overhead belly-to-belly suplex in which the wrestler, standing face-to-face with his opponent, clutches his hands together having firmly encircled the opponent's head and one arm. This grip, as opposed to the waistlock of a normal belly-to-belly, is then used to hoist the opponent in the overhead arching throw.
Northern Lights suplex

Invented by Hiroshi Hase. The attacking wrestler puts his head under the arm of the opponent, wraps his arms around the waist of the opponent and flips him/her backwards. This suplex can either be released or bridged into a pin. The wrestler can also float over into another Northern Lights suplex.[12]
Table top suplex
Also known as a fallaway slam, the wrestler lifts the opponent up so the opponent is horizontal across the wrestler's body then falls backward, throwing the opponent over their head down to the mat back-first. This slam can be either bridged into a pin, or the wrestler can float over into another fallaway slam. This move is sometimes used as a continuation move from catching the opponent's high-cross body, to emphasize the wrestler's strength.
Trapping suplex
This is when a wrestler holds both the opponent's arms under his own (known as overhooks in mixed martial arts and amateur wrestling, as the arms loop under the opponent's arms from above) with the hands connected below the opponent's triceps, from here the opponent is left secure and unable to counter or move away from the attacker while he/she delivers a belly-to-belly throw flipping the opponent overhead in the normal belly-to-belly motion. In amateur wrestling and other contact-sports, the trapping suplex is called the suicide throw. It is done slightly differently, usually the opponent is tossed to the side and lands on their back.
This move consists of one wrestler picking up his or her opponent off the ground (or mat) and then using a large portion of his or her own body weight to drive the opponent down on the mat. He or she begins face-to-face, then the attacker forces the opponent's head down and locks the opponent's arm around it.
Side variants
In the side variants the attacker stands to the side of his or her opponent and applies a hold before falling backwards to slam the opponent to the mat. The most common is the Saito suplex.
Southern Lights Suplex
An inverted Northern Lights suplex .
Gutwrench suplex
This throw involves a wrestler standing on one side of a prone opponent locking both arms around the opponent's waist near arm in front of the opponent and far arm behind, and lifting him/her up to slam him/her over back-first down to the mat. An inverted version also exists.
Saito suplex
The attacker stands either facing directly one of their opponent's sides or slightly behind in an angle. He places the opponent's near arm over his shoulder, grabs a waistlock, and then lifts the opponent up while falling backwards, causing the opponent to land on their neck and shoulders.

There is also a leg-hook variation where the attacker stands behind and to one side of the opponent. The attacker wraps one arm around the waist of the opponent and grabs the back of the opponent's near leg with their other arm. The attacker then lifts the opponent on to their shoulder and then falls backwards, driving the opponent into the mat at a high angle. This was used by Karrion Kross as the Doomsday Saito. Shawn Michaels used a leg-hook version in the early 90's as the Teardrop Suplex.
Side suplex
- See Ura-nage.
This move is also known as a sambo suplex or side suplex. To perform it, the wrestler stands face-to-face with the opponent, slightly to their side. The wrestler either reaches across the opponent's chest and around their neck with their near arm and locks both hands behind the opponent's shoulders or just locks both hands behind the opponent's waist. The wrestler then simultaneously lifts the opponent up, twists 180° and falls backwards, bringing the opponent over them and slamming the opponent back-first on the mat.
The name ura-nage (or uranage) comes from a Judo throw which translated directly from Japanese, means "throw to behind/back" and is commonly (albeit incorrectly) used to refer to a regular side slam in pro wrestling. The Judo ura-nage throw more closely resembles a saito suplex in execution.
Cravate suplex
This sees a wrestler lock their opponent in a cravate and pull down with their arms so that the opponent is forced to bend over. The wrestler then positions the opponent so that they are facing across the body of the wrestler and with their head in front of the wrestlers chest while stil standing. The wrestler then falls backwards, pulling upwards with the cravate and forcing the opponent off their feet into the air and over the wrestler, landing on their neck and shoulders. Invented by Chris Hero.
Inverted facelock variants
In these suplexes, an attacker begins by facing the back of an opponent and applying an inverted facelock before executing a throw. In most, the opponent is suspended upside-down during part of the move.
Inverted Suplex
Also known as a reverse suplex, this move sees the attacker stands behind an opponent and applies an inverted facelock with one arm, and uses the other arm to aid in elevating the opponent so that he/she is lifted up and held upside-down before the attacker falls to his back driving the opponent down to the mat face first, behind the attacker.
In other sports
Suplex tackles in gridiron football are not allowed and may be subject to penalties or even fines.[13]
See also
Notes
- "the 50 coolest maneuvers of all time - Perfect-plex". WWE. 2014-02-21. Retrieved 2014-05-04.
- Finishing move list, from TheOtherArena.com
- Big Book of Wrestling Moves, from DeathValleyDriver.com Archived 2013-05-06 at the Wayback Machine
- "Spostamento di wrestling da introdurre nel calcio internazionale?" [Wrestling move to be introduced to international soccer?]. Gazzetta Dello Sport. Milan. 2018-01-22.
- "Misawa Passes Away After Backdrop In Hiroshima Match". Wrestling Observer/Figure Four Online. 2009-06-13. Retrieved 2009-08-08.
- Schramm, Chris (2009-06-13). "Japanese legend Mitsuharu Misawa dies in the ring". Slam! Wrestling. Canadian Online Explorer. Retrieved 2009-06-13.
- "the 50 coolest maneuvers of all time". WWE. 2014-02-21. Retrieved 2014-03-13.
- Schramm, Chris (July 31, 2008). "Mexican great Alfonso Dantés dies". SLAM! Wrestling. Retrieved 2010-02-21.
- "Tiger suplex". Headlocks&Backdrops. Retrieved 2013-06-06.
- "Double underhook suplex". WonderHowTo. Retrieved 2013-06-06.
- "Exploder suplex". Headlocks&Backdrops. Retrieved 2013-06-06.
- "Northern Lights suplex". WonderHowTo. Retrieved 2013-06-06.
- Moddejonge, Gerry (13 August 2016). "Back-to-back interceptions avoid CFL version of Montreal Screwjob". Edmonton Sun. Retrieved 13 August 2016.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Suplex. |
- "Professional Wrestling Moves: Part 3" Death Valley Driver.com
- The Professional Wrestlers' Workout & Instructional Guide - Harley Race, Ricky Steamboat, Les Thatcher, and Alex Marvez pg. 80-84