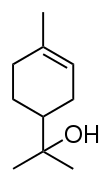
Terpineol
Terpineol is any of four isomeric monoterpenoids. Terpenoids are terpene that are modified by the addition of a functional group, in this case, an alcohol. Terpineols have been isolated from a variety of sources such as cardamom, cajuput oil, pine oil, and petitgrain oil.[2] Four isomers exist: α-, β-, γ-terpineol, and terpinen-4-ol. β- and γ-terpineol differ only by the location of the double bond. Terpineol is usually a mixture of these isomers with α-terpineol as the major constituent.
 Terpineols: alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and the 4-terpineol isomer
Terpineols: alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and the 4-terpineol isomer
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
p-Menth-1-en-8-ol 2-(4-Methylcyclohex-3-en-1-yl)propan-2-ol | |||
| Other names
2-(4-Methyl-1-cyclohex-3-enyl)propan-2-ol alpha-terpineol α-terpineol α,α,4-Trimethylcyclohex-3-ene-1-methanol Terpene alcohol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H18O | |||
| Molar mass | 154.253 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] | ||
| Density | 0.93 g/cm3[1] | ||
| Melting point | −35.9 to −28.2 °C (−32.6 to −18.8 °F; 237.2 to 245.0 K)[1] (mixture of isomers) | ||
| Boiling point | 214–217 °C (417–423 °F; 487–490 K)[1] (mixture of isomers) | ||
| 2.42 g/L[1] | |||
| −111.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 88 °C (190 °F; 361 K)[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Terpineol has a pleasant odor similar to lilac and is a common ingredient in perfumes, cosmetics, and flavors. α-Terpineol is one of the two most abundant aroma constituents of lapsang souchong tea; the α-terpineol originates in the pine smoke used to dry the tea.[3] (+)-α-terpineol is a chemical constituent of skullcap.
Synthesis and biosynthesis
Although it is naturally occurring, terpineol is commonly manufactured from the more readily available alpha-pinene. An alternative route starts from limonene:[4]
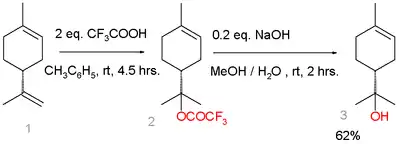 Terpineol synthesis from limonene
Terpineol synthesis from limonene
Limonene reacts with trifluoroacetic acid in a Markovnikov addition to a trifluoroacetate intermediate, which is easily hydrolyzed with sodium hydroxide to α-terpineol with 7% selectivity. Side-products are β-terpineol in a mixture of the cis isomer, the trans isomer, and 4-terpineol.
The biosynthesis of α-terpineol proceeds from geranyl pyrophosphate, which releases pyrophosphate to give the terpinyl cation. This carbocation is the precursor to many terpenes and terpenoids. Its hydrolysis gives terpineol.
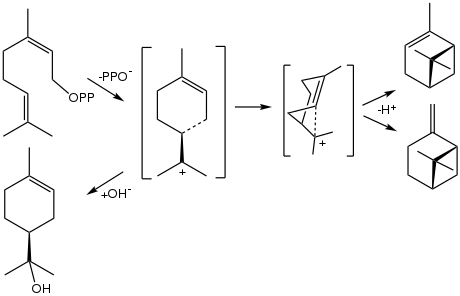 Bioynthetic conversion of geranyl pyrophosphate to the terpenes α-pinene and β-pinene (right) and to α-terpineol (bottom left).[5]
Bioynthetic conversion of geranyl pyrophosphate to the terpenes α-pinene and β-pinene (right) and to α-terpineol (bottom left).[5]
References
- Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9103
- Shan-Shan Yao; Wen-Fei Guo; Yi Lu; Yuan-Xun Jiang (2005). "Flavor Characteristics of Lapsang Souchong and Smoked Lapsang Souchong, a Special Chinese Black Tea with Pine Smoking Process". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (22): 8688–93. doi:10.1021/jf058059i. PMID 16248572.
- Yuasa, Yoshifumi; Yuasa, Yoko (2006). "A Practical Synthesis of d-α-Terpineol via Markovnikov Addition of d-limonene Using Trifluoroacetic Acid". Organic Process Research & Development. 10 (6): 1231–1232. doi:10.1021/op068012d.
- Davis, Edward M.; Croteau, Rodney (2000). "Cyclization enzymes in the biosynthesis of monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and diterpenes". Biosynthesis. Topics in Current Chemistry. 209. pp. 53–95. doi:10.1007/3-540-48146-X_2. ISBN 978-3-540-66573-1.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
External links
- MSDS for alpha-terpineol
 Media related to Terpineols at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Terpineols at Wikimedia Commons