The Secret History of the Mongols
The Secret History of the Mongols (Traditional Mongolian: 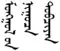 Mongγol-un niγuča tobčiyan, Khalkha Mongolian: Монголын нууц товчоо, Mongolyn nuuts tovchoo[note 1]) is the oldest surviving literary work in the Mongolian language. It was written for the Mongol royal family some time after the 1227 death of Genghis Khan (also known as Temujin). The author is anonymous and probably originally wrote in the Mongolian script, but the surviving texts all derive from transcriptions or translations into Chinese characters that date from the end of the 14th century and were compiled by the Ming dynasty under the title The Secret History of the Yuan Dynasty (Chinese: 元朝秘史; pinyin: Yuáncháo Mìshǐ). Also known as Tobchiyan (Chinese: 脫必赤顏; pinyin: Tuōbìchìyán or 脫卜赤顏; Tuōbǔchìyán) in the History of Yuan.
Mongγol-un niγuča tobčiyan, Khalkha Mongolian: Монголын нууц товчоо, Mongolyn nuuts tovchoo[note 1]) is the oldest surviving literary work in the Mongolian language. It was written for the Mongol royal family some time after the 1227 death of Genghis Khan (also known as Temujin). The author is anonymous and probably originally wrote in the Mongolian script, but the surviving texts all derive from transcriptions or translations into Chinese characters that date from the end of the 14th century and were compiled by the Ming dynasty under the title The Secret History of the Yuan Dynasty (Chinese: 元朝秘史; pinyin: Yuáncháo Mìshǐ). Also known as Tobchiyan (Chinese: 脫必赤顏; pinyin: Tuōbìchìyán or 脫卜赤顏; Tuōbǔchìyán) in the History of Yuan.

The Secret History is regarded as the single most significant native Mongolian account of Genghis Khan. Linguistically, it provides the richest source of pre-classical Mongolian and Middle Mongolian.[2] The Secret History is regarded as a piece of classic literature in both Mongolia and the rest of the world.
The only copy of it was found in China and published by a Russian monk Palladius (Pyotr Ivanovich Kafarov) in 1872.
Content

The work begins with a semi-mythical genealogy of Genghis Khan (also called Temüjin). According to legend a blue-grey wolf and a fallow doe begat the first Mongol, named Batachiqan. Eleven generations after Batachiqan, a widow named Alan Gua was abandoned by her in-laws and left with her two boys Bügünütei and Belgünütei. She then bore three more sons with a supernatural glowing man who came in through the smoke-hole at the top of the tent. The youngest of Alan Qo’a’s three divinely-born children was Bodonchar, founder of the Borjigin.[3] The description of Temüjin's life begins with the kidnapping of his mother, Hoelun, by his father Yesügei. It then covers Temüjin's early life following his birth around 1160; the difficult times after the murder of his father; and the many conflicts against him, wars, and plots before he gains the title of Genghis Khan (Universal Ruler) in 1206. The latter parts of the work deal with the campaigns of conquest of Genghis and his third son Ögedei throughout Eurasia; the text ends with Ögedei's reflections on what he did well and what he did wrong. It relates how the Mongol Empire was created.
It contains 12 or 13 chapters:
- Temüjin's origin and childhood.
- Temüjin's teenage years.
- Temujin destroys the Merkit and takes the title Genghis Khan.
- Genghis Khan struggles against Jamukha and Tayichiud.
- Genghis Khan destroys the Tatars and tangles with Ong Khan
- Destruction of the Khereid
- The fate of Ong Khan
- Escape of Kuchlug and a defeat of Jamukha.
- Establishment of the empire and imperial guard.
- Conquest of the Uyghur and forest peoples.
- Conquest of the Jin dynasty, the Western Xia, Persia, Baghdad and Russia
- Temüjin's death and Ögedei's reign.
- The death of Genghis Khan
Several passages of the Secret History appear in slightly different versions in the 17th-century Mongolian chronicle Altan Tobchi ("Golden Summary").
Scholars of Mongolian history consider the text hugely important for the wealth of information it contains on the history, ethnography, language, literature and varied aspects of the Mongol culture. In terms of its value to the field of linguistic studies, it is considered unique among the Mongol texts as an example free from the influence of Buddhism prevalent in later texts. It is especially valued for its vivid and realistic depictions of daily tribal life and organization of Mongol civilization in the 12th and 13th centuries, complementing other primary sources available in the Persian and Chinese languages.[4]
Discovery and translations


The only surviving copies of the work are transcriptions of the original Mongolian text with Chinese characters, accompanied by a (somewhat shorter) in-line glossary and a translation of each section into Chinese. In China, the work had been well known as a text for teaching Chinese to read and write Mongolian during the Ming dynasty, and the Chinese translation was used in several historical works, but by the 1800s, copies had become very rare.
Baavuday Tsend Gun (1875–1932) was the first Mongolian scholar to transcribe The Secret History of the Mongols into modern Mongolian, in 1915–17. The first to discover the Secret History for the West and offer a translation from the Chinese glossary was the Russian sinologist Palladiy Kafarov in 1866. The first translations from the reconstructed Mongolian text were done by the German sinologist Erich Haenisch (edition of the reconstructed original text: 1937; of the translation: 1941, second edition 1948) and Paul Pelliot (ed. 1949). Tsendiin Damdinsüren translated the chronicle into Khalkha Mongolian in 1947. B. I. Pankratov published a translation into Russian in 1962.[5]
Arthur Waley published a partial translation of the Secret History, but the first full translation into English was by Francis Woodman Cleaves, The Secret History of the Mongols: For the First Time Done into English out of the Original Tongue and Provided with an Exegetical Commentary.[6] The archaic language adopted by Cleaves was not satisfying to all and, between 1972 and 1985, Igor de Rachewiltz published a fresh translation in eleven volumes of the series Papers on Far Eastern History accompanied by extensive footnotes commenting not only on the translation but also various aspects of Mongolian culture. (Brill Publishers released de Rachewiltz' edition as a two-volume set in 2003.) In 2015, de Rachewiltz published an open access version of his previous translation, The Secret History of the Mongols: A Mongolian Epic Chronicle of the Thirteenth Century, that is a full translation but omits the extensive footnotes of his previous translations.[7] The Secret History of the Mongols has been published in translation in over 30 languages by researchers.
In 2004 the Government of Mongolia decreed that the copy of The Secret History of the Mongols covered with golden plates was to be located to the rear part of the Government building.[8]
See also
Bibliography


- B. Sumiyabaatar (mong.), "Монголын Нууц Товчоо. Үсгийн галиг", "The Transliteration of the Mongolian Secret History" (MSH=SHM), 965 pp., 1990
- B. Sumiyabaatar (mong.), "Монголын Нууц Товчооны хэлбэрсудлал", "The Morphology of the Mongolian Secret History ", 3144 pp., 1997
- B. Sumiyabaatar (mong.), "Чингисийн алтан ургийн Угийн бичиг ба Гэрийн уеийн бичмэл", "The Genealogy of the Genghis's Mongols", 720 pp., 2002, ISBN 99929-5-552-X.
- B. Sumiyabaatar (mong.), Choi Gi Ho, "Монголын Нууц Товчоон. Монгол үсгийн анхны галиг", "The first Mongolian transliteration of the Mongolian Secret History", 382 pp., 2005, ISBN 89-5726-275-X.
- B. Sumiyabaatar (mong.), "А. Позднеев. Транскрипция палеографического текста "Юань-чао-ми-ши"", " A. Posdneew. Transkription of the paleografical text "Yuan-chao-mi-shi", 17-112 pp., 2005.
- B. Sumiyabaatar (mong.), "Монголын Нууц Товчооны толь: Монгол • Нангиад, Нангиад • Монгол толь. Үсэг: А, Б", " The Dictionary of the Mongolian Secret History: Mongolian-Chinese, Chinese-Mongolian dictionary, " A- B", 290 p., 2010, ISBN 978-99962-842-1-2.
- B. Sumiyabaatar (mong.), "Монголын Нууц Товчоон, Хэлбэрсудлал I", "The Mongolian Secret History. Morphology I", 499 p., 2012, ISBN 978-99962-842-6-7.
- B. Sumiyabaatar (mong.), "МОНГОЛЫН НУУЦ ТОВЧООH иж судалгаа", "The Mongolian Secret History, researches ", 2.262 p., 2020, ISBN 978-9919-23-665-6.
Notes
References
Citations
- William Hung, 'The Transmission of the Book Known as "The Secret History of the Mongols"', Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, Vol. 14, No. 3/4 (Dec 1951), p. 440.
- Igor de Rachewiltz, The Secret History of the Mongols: A Mongolian Epic Chronicle of the Thirteenth Century (Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands) at xxvi.
- De Nicola, Bruno (2017). Women in Mongol Iran: The Khatuns, 1206-1335. Edinburgh University Press. p. 36. ISBN 9781474415477.
- Bela Kempf, Review (Acta Orientalia Vol. 59 No 4, 2006), p. 493.
- "IOM RAS: Sinologica – Sinology at the St Petersburg Academy of Sciences". Sinologica.orientalstudies.ru. 2009-03-17. Retrieved 2013-10-13.
- Harvard-Yenching Institute, Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1982.
- de Rachewiltz, Igor (2015). The Secret History of the Mongols: A Mongolian Epic Chronicle of the Thirteenth Century. http://cedar.wwu.edu/cedarbooks/4/.CS1 maint: location (link)
- ""Монголын нууц товчоо"-г мөнхөд эрхэмлэн дээдлэх тухай | Монгол Улсын Ерөнхийлөгч Цахиагийн Элбэгдорж". President.mn. 2004-02-18. Retrieved 2013-10-13.
Sources
- unknown (1993) [1228]. Chinggis Khan: The Golden History of the Mongols (hardback). Translated by Urgunge Onon. revised by Sue Bradbury. London: The Folio Society.
- Igor de Rachewiltz (18 July 2013). The Secret History of the Mongols, VOLUME 3 (Supplement): A Mongolian Epic Chronicle of the Thirteenth Century. BRILL. ISBN 978-90-04-25858-7.
- Paul Kahn; Francis Woodman Cleaves (1998). The Secret History of the Mongols: The Origin of Chinghis Khan (expanded Edition) : an Adaptation of the Yüan Chʼao Pi Shih, Based Primarily on the English Translation by Francis Woodman Cleaves. Cheng & Tsui. pp. 191–. ISBN 978-0-88727-299-8.
- Igor de Rachewiltz (11 December 2015). The Secret History of the Mongols: A Mongolian Epic Chronicle of the Thirteenth Century.
External links
- The Secret History of the Mongols: full text, history, translations into Russian, English, French, Bulgarian, Spanish and Czech, original transliteration (Mirror)
- transcription with flexional morpheme boundaries and other additional annotation by John Street
- The Secret History of the Mongols: partial text
- Timothy May: Extensive review of the publication of Rachewiltz's translation and notes September 2004
- Lingua Mongolia: first 21 paragraphs of the Secret History in Chinese transcription, Pinyin, and Traditional Mongolian script
- Modern Mongolian Version (and audio files) -ELibrary.MN
- "BBC Genghis Khan". 26 January 2016. Retrieved 8 November 2016.