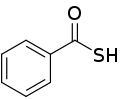
Thiobenzoic acid
Thiobenzoic acid is an organosulfur compound with molecular formula C6H5COSH. It is the parent of aryl thiocarboxylic acids. It is a pale yellow liquid that freezes just below room temperature.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
benzenecarbothioic S-acid | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.466 |
| EC Number |
|
| 1071790 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6OS | |
| Molar mass | 138.18 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.1775 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 24 °C (75 °F; 297 K) |
| Boiling point | 222 °C (432 °F; 495 K) |
| soluble | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.1 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.61 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Thiobenzoic acid is prepared by treatment of benzoyl chloride with potassium hydrosulfide:[1]
- C6H5C(O)Cl + KSH → C6H5C(O)SH + KCl
Acidity
With a pKa near 2.5, this acid is almost 100x more acidic than benzoic acid.[2] The conjugate base is thiobenzoate, C6H5COS−.
See also
References
- Noble, Jr., Paul; Tarbell, D. S. (1952). "Thiobenzoic Acid". 32: 101. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.032.0101. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Matthys J. Janssen "Carboxylic Acids and Esters" in PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups: Carboxylic Acids and Esters, Saul Patai, Ed. John Wiley, 1969, New York: pp. 705–764. doi:10.1002/9780470771099.ch15
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.