Trace metal
Trace metals are the metals subset of trace elements; that is, metals normally present in small but measurable amounts in animal and plant cells and tissues and that are a necessary part of nutrition and physiology. Many biometals are trace metals. Ingestion of, or exposure to, excessive quantities can be toxic. However, insufficient plasma or tissue levels of certain trace metals can cause pathology, as is the case with iron.
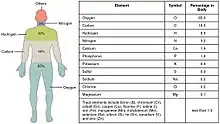
Trace metals within the human body include iron, lithium, zinc, copper, chromium, nickel, cobalt, vanadium, molybdenum, manganese and others.[1][2][3]
Trace metals are metals needed by living organisms to function properly and are depleted through the expenditure of energy by various metabolic processes of living organisms. They are replenished in animals through diet as well as environmental exposure, and in plants through the uptake of nutrients from the soil in which the plant grows. Human vitamin pills and plant fertilizers can be a source of trace metals.
Trace metals are sometimes referred to as trace elements, although the latter includes minerals and is a broader category. See also Dietary mineral. Trace elements are required by the body for specific functions. Things such as vitamins, sports drinks, fresh fruits and vegetables are sources. Taken in excessive amounts, trace elements can cause problems. For example fluorine is required for the formation of bones and enamel on teeth. However, when taken in an excessive amount can cause a disease called "Fluorosis', in which bone deformations and yellowing of teeth are seen. Fluorine can occur naturally in some areas in ground water.
Trace metals include iron that can help to prevent anemia, and zinc that is a cofactor in over 100 enzyme reactions.
References
- Zoroddu, Maria Antonietta; Aaseth, Jan; Crisponi, Guido; Medici, Serenella; Peana, Massimiliano; Nurchi, Valeria Marina (June 2019). "The essential metals for humans: a brief overview". Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry. 195: 120–129. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.03.013. PMID 30939379.
- Interrelations between Essential Metal Ions and Human Diseases. Series editors Sigel, Astrid; Sigel, Helmut; Sigel, Roland K.O. Springer. 2013. ISBN 978-94-007-7499-5.CS1 maint: others (link) electronic-book ISBN 978-94-007-7500-8 ISSN 1559-0836
- Bender DA; Mayes PA; Murray RK; Botham KM; Kennelly PJ; Rodwell VW; Weil PA (2009). "Chapter 44. Micronutrients: Vitamins & Minerals". Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry (28th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. Archived from the original on 7 September 2010. Retrieved 22 October 2013.
