Trakia motorway
The Trakia motorway (Bulgarian: Aвтомагистрала „Тракия“, Avtomagistrala "Trakiya") or Thrace motorway, designated A1, is a motorway in Bulgaria. It connects the capital city of Sofia, the city of Plovdiv and the city of Burgas on the Black Sea coast. The motorway is named after the historical region of Thrace, the northern (Bulgarian) part of which it spans from west to east. The total length of Trakia motorway is 360 km (220 mi) and the final section opened on 15 July 2013[1] after 40 years of construction.[2]
| |
|---|---|
| Автомагистрала „Тракия“ | |
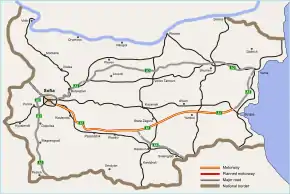 Trakia motorway highlighted in red and yellow | |
| Route information | |
| Part of | |
| Length | 360 km (220 mi) |
| Major junctions | |
| From | Sofia |
| To | Burgas |
| Location | |
| Major cities | Pazardzhik, Plovdiv, Stara Zagora, Yambol |
| Highway system | |
| Motorways in Bulgaria | |
Trakia motorway connects with the Sofia ring road at its west end, allowing fast access to the Hemus motorway (A2) and the Lyulin motorway (A6). Future interchanges at the ring road with the planned Kalotina motorway and Sofia Northern Bypass motorway are expected to ease the main transit traffic around Sofia.
At its east end, nearby Burgas, Trakia motorway will merge with the planned Cherno More motorway (A5) providing fast access from the south to the city of Varna and the beach resorts on the Black Sea.
Maritsa motorway (A4) branches off at Orizovo Interchange at kilometer 169 to link Trakia motorway with Turkey at the Kapitan Andreevo border crossing. The interchange is situated between Plovdiv and Chirpan, roughly 5 km north of Parvomay.
History
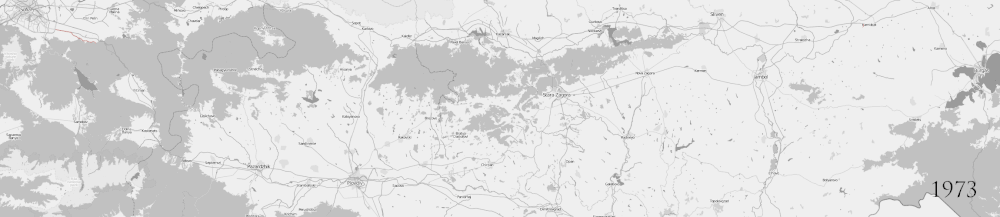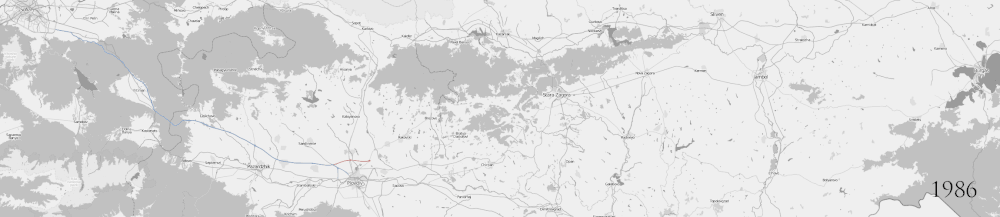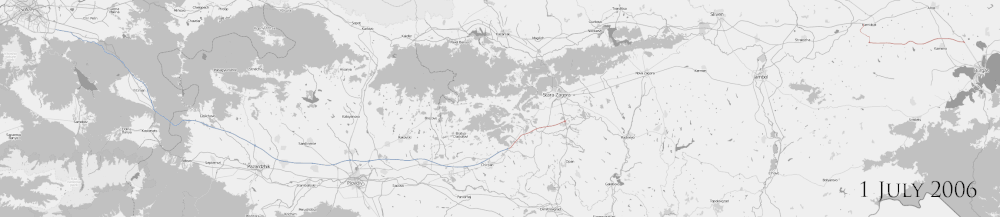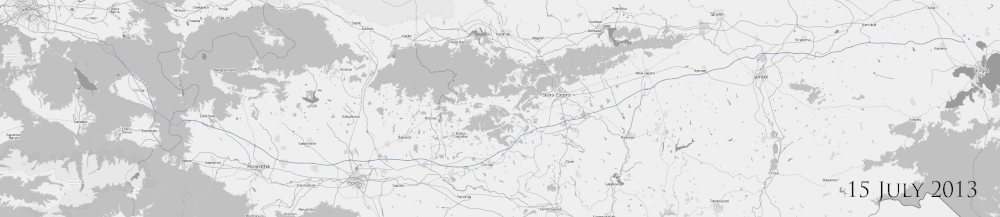
The construction of the motorway began in 1973 and the first 10 km from Sofia to Novi Han entered in service in 1978. In 1984 the motorway reached Plovdiv, the second largest city in Bulgaria. In 1995 a 32 km section between Plovdiv and Plodovitovo interchange was completed with EBRD co-financing.[3] In 2000 EIB loan was secured for the construction of two sections, between Orizovo interchange and Stara Zagora (lot 1), and lot 5, between Karnobat and Burgas, fourth largest city, situated at the Black sea coast. The motorway reached Stara Zagora in 2007, and lot 5 entered in service in 2006.
Meanwhile, in 2005 a controversial concession contract was signed by the Bulgarian government and a Portuguese-led consortium.[4] The concession was granted for 35 years without tender procedure and included 433 km from the Serbian border, at Kalotina border checkpoint, to Burgas. However, the contract was cancelled in 2008 and the sections between Stara Zagora and Karnobat (lots 2, 3 and 4) were approved for EU funds financing.
In 2009 and 2010, tenders for the construction of Stara Zagora - Nova Zagora, Nova Zagora - Yambol-west interchange, and Yambol-west interchange - Karnobat sections, totalling 116.8 km, were conducted and contracts were signed. The sections between Stara Zagora and Yambol-east interchange opened to traffic in mid-2012, while the last remaining section between Yambol-east interchange and Karnobat interchange was completed on 15 July 2013.[5]
Exits
| Exit | km | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Sofia ring road, Tsarigradsko shose | In service | |
| 5 | Lozen, Ravno pole | In service | |
| 5.5 | Novi Han | In service | |
| 24.4 | Vakarel | In service | |
| 35.2 | Ihtiman-north | In service | |
| 47.2 | Ihtiman-south, Kostenets | In service | |
| 61.7 | Vetren | In service | |
| 70 | Tserovo, Velingrad | In service | |
| 80.8 | Kalugerovo, Dinkata | In service | |
| 91 | Pazardzhik, Panagyurishte | In service | |
| 113 | Tsalapitsa, Saedinenie | In service | |
| 120 | Plovdiv-west, Pamporovo (to and from west only) | In service | |
| 122 | Plovdiv-west, Pamporovo (to and from east only) | In service | |
| 127 | Plovdiv-north | In service | |
| 134 | Plovdiv-east | In service | |
| 151 | Belozem | In service | |
| 166 | Parvomay | In service | |
| 169 | In service | ||
| 175 | Chirpan-west | In service | |
| 185 | Chirpan-east, Stara Zagora-west | In service | |
| 209 | Stara Zagora |
In service | |
| 240 | Nova Zagora | In service | |
| 276 | Yambol-west | In service | |
| 283 | Rest area, Kabile | In service | |
| 290 | Yambol-east |
In service | |
| 326 | Karnobat | In service | |
| 352 | Balgarovo, Neftochim oil refinery | In service | |
| 360 | Burgas, Vetren |
In service | |
Gallery
 Trakia motorway near Nova Zagora
Trakia motorway near Nova Zagora Trakia motorway near the village of Vakarel
Trakia motorway near the village of Vakarel Trakia motorway at Vakarel-Panagyurishte junction
Trakia motorway at Vakarel-Panagyurishte junction Trakia motorway near Burgas
Trakia motorway near Burgas
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Trakia motorway. |
- "Bulgaria Opens Monday Its First Completed HWY Trakiya". novinite.com. 15 July 2013.
- http://www.publics.bg/en/news/10256/Bulgaria%E2%80%99s_1st_Fully_Accomplished_Motorway_Opened_July_15.html
- "PM VIDENOV OPENS 32-KM SECTION OF TRAKIA MOTORWAY". hri.org. 17 November 1995. Retrieved 11 May 2014.
- "Нова съдебна атака срещу концесията на "Тракия"". mediapool.bg (in Bulgarian). 2006-04-04. Retrieved 11 May 2014.
- ""Тракия" - първата цяла магистрала на България". btv.bg.
