Type 1 Ho-Ki
The Type 1 Armored Personnel Carrier Ho-Ki (一式装甲兵車 ホキ, Isshiki Sōkōheishahoki Ho-Ki) was a tracked armored personnel carrier (APC) developed by the Imperial Japanese Army in World War II.
| Type 1 Ho-Ki | |
|---|---|
 Type 1 Ho-Ki APC | |
| Place of origin | Empire of Japan |
| Production history | |
| Designed | 1941 |
| Produced | 1942[1] |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 5.5 tonnes (6.1 tons)[2] |
| Length | 4.78 meters[1] |
| Width | 2.19 meters[1] |
| Height | 2.58 meters[1] |
| Crew | 1 or 2 + 13 passengers[1][3] |
| Armor | 6 mm[3] |
Main armament | none |
Secondary armament | none |
| Engine | diesel 134 HP/2000 rpm |
| Suspension | Bell crank |
Operational range | 300 kilometers |
| Maximum speed | 42 km/h |
Development and history
The Type 1 Ho-Ki was produced as a result of a request from the army for a heavy armored artillery tractor, which could also serve as a personnel transport. Development of both tracked and half-track APCs began in 1941. Both versions were confusingly designated “Type 1" (see the Type 1 Ho-Ha half-track).[4]
The fully tracked Type 1 Ho-Ki was built by Hino Motors, but only in small quantities. Although the Japanese Army had employed mechanized infantry formations in China from the mid-1930s, the general view of field commanders was that armored transports were too slow compared with normal trucks, and thereby unable to keep up with the speed necessary for contemporary infantry tactics.[4] In addition, with the priorities of Japanese military production focusing on combat aircraft, warships and other offensive weaponry, most of the experimental APC and AFV designs never made it past the prototype stage. By the time the Type 1 Ho-Ki entered mass production in 1944, raw materials were in very short supply, and much of Japan's industrial infrastructure had been destroyed by American bombing. The total number produced is unknown.[5][6]
Design

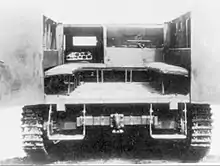
The Type 1 Ho-Ki had an unusual silhouette, in that the driver's cab did not extend across the front of the hull, but stopped about mid-way across the center line. Only one driver was required, who manipulated the left and right movement of the tracks via a pair of small steering wheels. Transport capacity was up to thirteen or fourteen men, and the maximum armor thickness was 6 mm.[1][7]
The Type 1 Ho-Ki had been designed to be versatile. It was used to carry supplies, to tow artillery, as well as to carry infantry; accordingly, it had no rear exit hatch as it was felt that the towed weapon might interfere with the rapid exit of any onboard riflemen. Entry and exit of troops was instead accomplished from the left (driver's) side via three doors mounted side by side.[4] The hull was welded construction and it was "open-topped", akin to the Type 1 Ho-Ha.[8] The engine compartment was located at the right front of the body, next to the driver's compartment. The engine was a 6-cylinder, in-line, valve-in-head, air-cooled diesel. The transmission was located in the rear. The gearbox had eight forward gears and two reverse gears. This allowed for more flexibility in speed and torque, in accordance to where and how it was being used.[9]
The Type 1 Ho-Ki was not normally armed, but provision was made for mounting machine guns to the rear of the driver on the sides of the troop compartment.[8] The Type 92 Heavy Machine Gun carried by Japanese infantry squads could be mounted accordingly. Although it was an APC, it was often mistakenly called a half-track.
Combat record

Initial deployment of the Type 1 Ho-Ki was to China for operations in the Second Sino-Japanese War. The Type 1 Ho-Ki was later deployed to Burma and the Philippines in 1944.[1][10] Units of the 2nd Tank Division were reassigned to the Japanese Fourteenth Area Army and sent to the Philippines, where it was deployed on the main island of Luzon. The 2nd Tank Division had a shortage of half-tracks, therefore, at least four Type 1 Ho-Ki's were used for troop transport on Luzon during the Battle of the Philippines.[11][12]
Notes
- Taki's Imperial Japanese Army: Type 1 APC "Ho-Ki"
- Tomczyk 2003, p. 64.
- Tomczyk 2003, p. 65.
- Japanese Armored Vehicles of the Second World War archived from the original
- Foss, The Encyclopedia of Tanks and Armored Fighting Vehicles
- Zaloga 2007, pp. 3, 15, 17.
- Tomczyk 2003, pp. 58, 64.
- Tomczyk 2003, p. 58.
- Tomczyk 2003, pp. 58, 59.
- Tomczyk 2003, p. 63.
- Rottman & Takizawa 2008, pp. 12, 54.
- Zaloga 2012, p. 35.
References
- Foss, Christopher F (2002). The Encyclopedia of Tanks and Armored Fighting Vehicles: The Comprehensive Guide to over 900 Armored Fighting Vehicles from 1915 to the Present Day. Thunder Bay Press. ISBN 1-57145-806-9.
- Tomczyk, Andrzej (2003). Japanese Armor Vol. 3. AJ Press. ISBN 978-8372371287.
- Zaloga, Steven J. (2007). Japanese Tanks 1939–45. Osprey. ISBN 978-1-8460-3091-8.
- Zaloga, Steven J. (2012). M4 Sherman vs Type 97 Chi-Ha: The Pacific 1945. Osprey Publishing. ISBN 978-1849086387.
