Typhoon Prapiroon (2006)
Typhoon Prapiroon, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Henry, was a minimal typhoon which caused deadly flooding in southern China in August 2006. Prapiroon developed out of a persistent area of convection accompanied by an area of low pressure on July 25 about 120 km (75 mi) west-southwest of Yap. Two days later, both the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and PAGASA classified the system as a tropical depression, with PAGASA giving it the local name 'Henry'. By July 31, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) classified the system as Tropical Depression 07W. A strong subtropical ridge located to the north of the depression led to a west-northwest movement for most of the storm existence.
| Typhoon (JMA scale) | |
|---|---|
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
 Prapiroon shortly before being upgraded to a typhoon on August 2 | |
| Formed | July 27, 2006 |
| Dissipated | August 5, 2006 |
| Highest winds | 10-minute sustained: 120 km/h (75 mph) 1-minute sustained: 130 km/h (80 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 970 hPa (mbar); 28.64 inHg |
| Fatalities | 94 direct, 10 missing |
| Damage | $984 million (2006 USD) |
| Areas affected | Philippines and China |
| Part of the 2006 Pacific typhoon season | |
A few hours after the JTWC began issuing advisories, the depression made landfall in Dilasag, Philippines. The next day, after crossing into the South China Sea, the depression was upgraded to a tropical storm and named Prapiroon. Several hours later, PAGASA issued their final advisory on the storm as it moved out of their area of responsibility. By the morning of August 2, Prapiroon intensified into a typhoon and reached its peak intensity with winds of 120 km/h (75 mph 10-min). The typhoon maintained this intensity until shortly before landfall near Shangyang, China at 12:00 UTC on August 3, where it weakened to a severe tropical storm. Prapiroon quickly weakened and dissipated early on August 5.
Severe flooding in the Philippines and China from Prapiroon killed 94 people and left 10 others missing. Over 20 million people were affected by the storm in China alone. Significant flight delays and cancellations in Hong Kong led to $1.9 million in compensation pay to travelers. About 30,000 homes collapsed and 140,000 others were damaged by the storm. Damages were estimated at $640,000 (2006 USD) in the Philippines and $984 million (2006 USD) in China. The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement sought $4,825,791 (2006 USD) in funds for victims of the typhoon.
Meteorological history
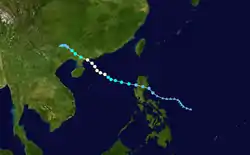
On July 25, an area of convection persisted about 120 km (75 mi) west-southwest of Yap. Satellite imagery indicated that a low level circulation had developed and was under an area of light to moderate wind shear.[1] The low traveled in a general northwest fashion as upper level outflow improved.[2] By July 27, the low deteriorated, becoming elongated, and convection remained disorganized.[3] However, as the low neared Central Luzon, Philippines, shower and thunderstorm activity near the center of the low increased,[4] and based on its organization, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) classified the system a tropical depression early that morning.[5] Shortly after, the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) designated the system as Tropical Depression Henry.[6] As the depression neared the northern Philippines, wind shear increased, partially exposing the center of the system to the south.[7] At 02:30 UTC on June 30, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert,[8] and at 00:00 UTC the next morning, the JTWC classified the system as Tropical Depression 07W.[9]
Upon first becoming a tropical cyclone, the depression tracked towards the west-northwest due to a strong subtropical ridge located to the north of the system. A few hours later, the system made landfall in Dilasag, Philippines with winds of 55 km/h (35 mph 1-minute winds).[10] After being over land for most of July 31, the depression relocated into the South China Sea and the JTWC determined that it intensified into a tropical storm.[11] At around 06:00 UTC, the JMA designated the storm Tropical Storm Prapiroon about 300 km (185 mi) northwest of Dagupan City, Philippines,[5] a few hours later, PAGASA issued their final advisory on Tropical Storm Henry (Prapiroon) as it moved out of their area of responsibility.[6] Prapiroon gradually intensified as it moved towards the west-northwest at 24 km/h (15 mph),[12] and by that afternoon, the system had completely moved into the South China Sea.[13] By the nighttime hours, the JMA upgraded Prapiroon to a severe tropical storm, as they determined that the maximum sustained winds had reached 95 km/h (60 mph 10-minute winds).[5] By the morning of August 2, the JTWC upgraded Prapiroon to a typhoon,[14] and a few hours later, the JMA upgraded Prapiroon to a typhoon.[5]
Heading towards the northwest, Prapiroon reached its peak intensity early on August 3. The JMA estimated that Prapiroon peaked with winds of 120 km/h (75 mph 10-minute winds) with a minimum pressure of 970 mbar (hPa; 28.64 inHg),[5] while the JTWC estimated that the storm peaked with winds of 130 km/h (80 mph 1-minute winds).[15] Prapiroon maintained this intensity for 12 hours before weakening slightly as it made landfall near Shangyang at 12:00 UTC.[5][16] At the time of landfall, the JMA downgraded Prapiroon to a severe tropical storm, with winds of 110 km/h (70 mph 10-minute winds)[5] while the JTWC analyzed Prapiroon to have had winds of 120 km/h (75 mph 1-minute winds). Due to the interaction with land, the storm quickly weakened. Early on August 5, both agencies issued their final advisories on Prapiroon as it dissipated over central Guangxi.[5][16]
Preparations
Philippines
As Tropical Depression 07W, locally named 'Henry' by PAGASA, neared the provence the northern Philippines, a total of 17 provinces were placed under a storm alert as winds of 30 kts (55 km/h) were likely to affect areas near the depression.[17] Residents in the northern Philippines were advised to avoid low-lying areas and be alert for flooding.[18] About 15,000 people were evacuated following heavy rains from the outer bands of the storm.[19]
China
In advance of Prapiroon, government officials in Guangdong Provence, China sent out 11 million mobile text messages to alert people of the approaching storm.[20][21] About 843,000 people were evacuated ahead of the storm, 335,000 in Guangdong, 382,000 in Guangxi, and 126,000 in Hainan.[22] Officials ordered 62,023 ships to return to port to prevent them from being stranded at sea.[23]
Hong Kong and Macau
The Hong Kong Observatory (HKO) and Macau's Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau both hoisted strong wind signal 1 on August 1 as the system was located within 800 km (497 mi) of their respective cities. As Prapiroon neared the southern coast of China, the signal was raised to strong wind signal 3 as strong winds were expected to strike the area. In Macau in particular this was further increased to strong wind signal 8 SE on August 3, as gale-force winds were expected in the southeastern areas. All signals were cancelled the next afternoon as Prapiroon moved inland.
Kindergarten and special schools in Hong Kong were suspended for at least two days for the day of and following the storms landfall.[24]
Impact
In the wake of Prapiroon, severe flooding left 94 people dead and 10 others missing. Damages from the storm were estimated at $984.8 million (2006 USD; $1.1 billion 2008 USD). Throughout southern China, Prapiroon affected over 20 million people.[19][25][26]
Philippines

As a tropical depression, Prapiroon caused heavy rains over the northern Philippines, leaving six people dead.[21] In Candaba, a two-year-old boy, identified as Elmer Celso, drowned in floodwaters outside his home.[18] Five other fatalities were reported due to flooding.[21] Two other people were listed as missing.[19] Agricultural damage was estimated at $640,000 (2006 USD).[27]
China

Despite weakening to a severe tropical storm before landfall, Prapiroon brought torrential rains and flooding which left 88 people dead and eight others missing.[20] About 10 million people were affected by the typhoon, while 30,000 homes collapsed and 140,000 others were damaged.[28] Damages from the typhoon were estimated at $984 million (2006 USD; $1.1 billion 2008 USD).[20] Guangdong Province was the hardest hit of the three provinces affected by Typhoon Prapiroon. About 3.72 million people were affected by the storm and 7,000 homes were destroyed in the province. A tornado struck Foshan, Shanwei and Shaoguan, killing nine.[29] A police officer was killed when a landslide buried him during a rescue in Sihui.[30] Another hard hit province, Guangxi, was struck by Prapiroon. About 5.1 million people were affected by the storm[31] and 219,441 were displaced. Ten people were killed by a flash flood and landslide in Laibin and Hengxian. Another flash flood swept away a shelter which thirteen migrant workers resided in, all of whom were confirmed to have been killed. Three more people were killed when a landslide caused their home to collapse in Luming Village.[29] About 9,300 homes and 195,900 hectares of farmland were destroyed.[31]
Hong Kong
As Prapiroon neared Hong Kong, thousands of people were stranded in airports as hundreds of flights in and out of the area were cancelled. Twenty cargo containers in the harbour were tipped over[32] and one person was injured by the falling containers.[24] A total of 381 flights were cancelled and 725 were delayed,[27] affecting about 10 million people. Compensation costs from the travel delays amounted to $1.9 million (2006 USD).[26] According to airport authorities, the storm caused the worst disruption in the airport's 20-year history.[33] Winds were recorded up to 103 km/h (63 mph) in the harbour.[24] The highest gust was recorded on Green Island at 193 km/h (119 mph). Seven people were injured by objects blown around by the wind.[27] A cargo vessel, with a crew of 23, ran aground near the harbour. No injuries were reported from the incident.[19] Two other incidents with vessels occurred near Ma Wan and Tuen Mun. Seven hundred trees were blown down and another 1,600 sustained damage. Maximum rainfall from Prapiroon was estimated at 8.1 in (207.5 mm). Two landslides were also reported and about 200 hectares of farmland was damaged. A storm surge of 2.71 m (8.89 ft) was recorded.[27] The Typhoon signal number 8 should have been hoisted as gales were recorded in most areas of the territory. As a result, the Hong Kong Observatory had to deal with a lot of criticism.
Aftermath
After Prapiroon dissipated, the regional Disease Prevention and Control Center of Guangxi Autonomous Region sent out eight teams of health workers to help avoid epidemics in affected areas. Despite the damage in the wake of the typhoon, China's Ministry of Civil Affairs did not activate any emergency response plans. The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement sought for $4,825,791 (2006 USD) in funds to assist 240,000 people who were affected over a 12-month span.[22] Reconstruction in the areas devastated by Prapiroon began shortly after the typhoon dissipated.[28]
References
- Forecast Team Bravo (July 25, 2006). "July 25 Significant Tropical Weather Advisory". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- Forecast Team Bravo (July 26, 2006). "July 26 Significant Tropical Weather Advisory". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- Forecast Team Delta (July 27, 2006). "July 27 Significant Tropical Weather Advisory". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- Forecast Team Delta (July 28, 2006). "July 28 Significant Tropical Weather Advisory". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- "JMA Annual Tropical Cyclone Report: 2006" (PDF). Japan Meteorological Agency. 2007. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- PAGASA (2006). "Tropical Storm Henry (Prapiroon) PAGASA track". typhoon2000.com. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- Forecast Team Bravo (July 29, 2006). "July 29 Significant Tropical Weather Advisory". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- "July 30 Significant Tropical Weather Advisory (TCFA)". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 29, 2006. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- "Tropical Depression 07W Warning NR 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 31, 2006. Retrieved December 9, 2008.
- "Tropical Depression 07W Warning NR 002". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 31, 2006. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- "Tropical Storm 07W Warning NR 005". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 1, 2006. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- "Tropical Storm 07W (Prapiroon) Warning NR 006". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 1, 2006. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- "Tropical Storm 07W (Prapiroon) Warning NR 007". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 1, 2006. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- "Typhoon 07W (Prapiroon) Warning NR 010". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 2, 2006. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- "Typhoon 07W (Prapiroon) Warning NR 013". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 3, 2006. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- "Typhoon 07W (Prapiroon) Best Track". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 2007. Retrieved December 25, 2008.
- Aris R. Ilagan and Jenny F. Manongdo (August 1, 2006). "17 provinces on alert as 'Henry' lands in Aurora". Manila Bulletin. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- Aris Ilagan and Madel R. Sabater (August 2, 2006). "'Henry' floods C. Luzon". Manila Bulletin. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- "Typhoon heads for China". Ireland On-Line. August 3, 2006. Archived from the original on February 17, 2013. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- China Meteorological Agency (2006). "China Meteorological Agency Annual Tropical Cyclone Report for 2006" (PDF). World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- "China storm death toll reaches 48". Ireland On-Line. August 5, 2006. Archived from the original on February 18, 2013. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- "OCHA Situation Report No. 3 China: Floods". OCHA. August 8, 2006. Retrieved December 25, 2008.
- "Typhoon Prapiroon slams into S. China province, packing rainstorm". Xinhua News. August 4, 2006. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- Xinhua (August 3, 2006). "Typhoon Prapiroon leaves thousands stranded at Hong Kong airport". People's Daily Online. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- "Review of the 2006 Typhoon Season in China". China Meteorological Agency. December 9, 2006. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- "Prapiroon flight delays caused by insurance or compensation of about 15 million Hong Kong dollar" (in Chinese). Xinhua News. August 7, 2006. Retrieved December 25, 2008.
- 颱風派比安 (0606) 二零零六年七月三十一日至八月四日 (PDF) (in Chinese). Hong Kong Observatory. August 18, 2006. Retrieved December 12, 2008.
- Xinhua (August 7, 2006). "Death toll from tropical storm Prapiroon rises to 80 in China". China Embassy. Retrieved December 12, 2008.
- "Death Toll in Typhoon Prapiroon Rises to 55 in China". Xinhua News Agency. August 6, 2006. Retrieved December 12, 2008.
- "57 die in tropical storm". Ireland On-line. August 6, 2006. Archived from the original on February 17, 2013. Retrieved December 12, 2008.
- China Daily (August 7, 2006). "At Least 77 Killed by Prapiroon". China.org. Retrieved December 13, 2008.
- "Typhoon Prapiroon kills at least 18 after crashing into China". The China Post. August 5, 2006. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
- "Typhoon Prapiroon leaves thousands stranded at Hong Kong airport". AFX News Limited. August 4, 2006. Retrieved December 11, 2008.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Typhoon Prapiroon (2006). |
- JMA General Information of Typhoon Prapiroon (0606) from Digital Typhoon
- JMA Best Track Data of Typhoon Prapiroon (0606) (in Japanese)
- JMA Best Track Data (Graphics) of Typhoon Prapiroon (0606)
- JMA Best Track Data (Text)
- JTWC Best Track Data of Typhoon 07W Prapiroon
- 07W.PRAPIROON from the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory
 Ja:台風6号、海南島の東へ at Wikinews
Ja:台風6号、海南島の東へ at Wikinews