Uglješa Mrnjavčević
Uglješa Mrnjavčević (Serbian Cyrillic: Угљеша Мрњавчевић; fl. 1346–1371), known as Jovan Uglješa (Serbian Cyrillic: Јован Угљеша), was a Serbian medieval nobleman of the Mrnjavčević family and one of the most prominent magnates of the Serbian Empire. He held the title of despot, received from Serbian Emperor Stefan Uroš V, whose co-ruler - Serbian King Vukašin was brother of Uglješa.[1]
Jovan Uglješa | |
|---|---|
| Born | Jovan Uglješa Mrnjavčević |
| Died | 26 September 1371 |
| Cause of death | Killed in action |
| Title | Grand Voivode (Veliki Vojvoda) Despot |
| Spouse(s) | Jelena (Jefimija) |
| Parent(s) | Mrnjava |
Life
Uglješa was the son of Mrnjava, a treasurer of Helen of Anjou, the queen consort of Stephen Uroš I of Serbia. He held Travunia in 1346, during the rule of Stefan Dušan (1331–1355).[2]
Uglješa married Jelena (later nun Jefimija), daughter of Vojihna, the Caesar of Drama.[3][4] This boosted the power of Uglješa, who would later govern the region alongside his father-in-law.[4] Vojihna died in ca 1360, and his lands were inherited by Jovan Uglješa.[5]
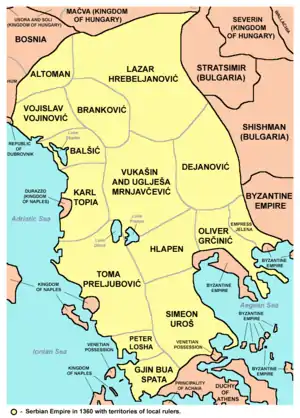
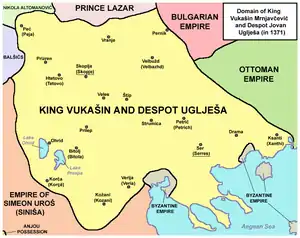
He was given the title of despotes by Empress Helena of Bulgaria in 1365. His province was situated along the lower course of the Struma with Serres as seat. And in order to be regarded as a proper Christian ruler, it was his duty to conform to the traditional practice of patronage. He made substantial donations to monasteries at Mount Athos, particularly Hilandar and repairing and refurbishing Simonopetra monastery in 1364. Like so many other Serbian rulers before and after him, one of the main purposes of his patronage and pilgrimage to the Holy Mountain was to ask the Athonites' blessing on his struggle against the Turks.
His realm was under the religious jurisdiction of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople since 1368. The Patriarch mentioned the master of Raška (another name for Serbia), Jovan Uglješa, in a letter from 1371.
Death and legacy
With the Ottoman threat rising in the Balkans, Jovan Ugleša and his brothers Vukašin Mrnjavčević and Gojko Mrnjavčević tried to oppose the Turks. Jovan Uglješa was killed on 26 September 1371 in the Battle of Maritsa.[6] Their troops were smashed by those of Ottoman commanders Lala Shahin Pasha and Gazi Evrenos at the Battle of Maritsa in 1371. The defeat resulted in big portions of the region of Macedonia falling under Ottoman power. Additionally, two brothers were killed during the fight. Their courage and self-sacrifice made them heroes of Bulgarian and Serbian epic poetry.
See also
References
- Ćirković 2004, pp. 78-79.
- Književno delo monahinje Jefimije, p. 1
- Gavrilović 2006, pp. 78-79.
- Fajfric, p. 5
- Fine 1994, pp. 364.
- Ostrogorsky 1956, pp. 481.
Sources
- Ćirković, Sima (2004). The Serbs. Malden: Blackwell Publishing.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Dvornik, Francis (1962). The Slavs in European History and Civilization. New Brunswick, New Jersey: Rutgers University Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1994) [1987]. The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08260-4.
- Gavrilović, Zaga (2006). "Women in Serbian politics, diplomacy and art at the beginning of Ottoman rule". In Jeffreys, Elizabeth M. (ed.). Byzantine Style, Religion and Civilization: In Honour of Sir Steven Runciman. Cambridge University Press. pp. 72–90.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Nicol, Donald M. (1993). The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261–1453 (Second ed.). London: Rupert Hart-Davis Ltd. ISBN 0-246-10559-3.
- Nicol, Donald M. (1996). The Reluctant Emperor: A Biography of John Cantacuzene, Byzantine Emperor and Monk, c. 1295-1383. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Ostrogorsky, George (1956). History of the Byzantine State. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Pavlikianov, Cyril (2001). The Medieval Aristocracy on Mount Athos: Philological and Documentary Evidence for the Activity of Byzantine, Georgian and Slav Aristocrats and Eminent Churchmen in the Monasteries of Mount Athos from the 10th to the 15th Century. Sofia: Center for Slavo-Byzantine Studies.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Popović, Tatyana (1988). Prince Marko: The Hero of South Slavic Epics. New York: Syracuse University Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Sedlar, Jean W. (1994). East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000-1500. Seattle: University of Washington Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Soulis, George Christos (1984). The Serbs and Byzantium during the reign of Tsar Stephen Dušan (1331-1355) and his successors. Washington: Dumbarton Oaks Library and Collection.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
| Preceded by Jelena Nemanjić |
Ruler of Serres 1356–1371 |
Recovery of Serres by the Byzantine Empire |
| Vacant Title last held by Stefan Konstantin |
Count of Travunia 1346 |
Unknown |