Uranopilite
Uranopilite is a minor ore of uranium with the chemistry (UO2)6SO4(OH)6O2·14H2O or, hydrated uranyl sulfate hydroxide.
| Uranopilite | |
|---|---|
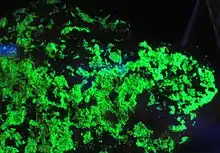 Uranopilite with Fluorescence - Exposed in the Mineralogical Museum, Bonn, Germany | |
| General | |
| Category | Sulfate minerals |
| Formula (repeating unit) | (UO2)6SO4(OH)6O2·14H2O |
| Strunz classification | 7.EA.05 |
| Crystal system | Triclinic |
| Crystal class | Pinacoidal (1) (same H-M symbol) |
| Space group | P1 |
| Identification | |
| Other characteristics | |
| References | [1][2] |
As with many uranyl minerals, it is fluorescent and radioactive. It is straw yellow in normal light. Uranopilite fluoresces a bright green under ultraviolet light. Uranopilite contains clusters of six uranyl pentagonal bipyramids that share equatorial edges and vertices, with the clusters cross-linked to form chains by sharing vertices with sulfate tetrahedra. In uranopilite, the chains are linked directly by hydrogen bonds, as well as to interstitial H2O groups.
Uranopilite is associated with other uranyl minerals such as zippeite and johannite and, like them, is usually found as an efflorescent crust in uranium mines.
Notable occurrences include:
- Wheal Owles, Cornwall, England
- San Juan County, Utah, US
- Northwest Territories, Canada
- Bohemian region of Europe
