Vilnius Voivodeship
The Vilnius Voivodeship (Latin: Palatinatus Vilnensis, Lithuanian: Vilniaus vaivadija, Polish: województwo wileńskie, Belarusian: Віленскае ваяводства) was one of the voivodeships in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, created in 1413, from the Duchy of Lithuania and neighbouring lands and later incorporated into the newly established Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
| Vilnius Voivodeship | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voivodeship of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth | |||||||||
| 1413–1795 | |||||||||
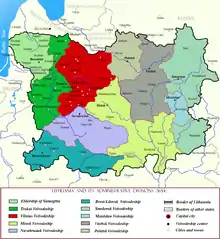 Vilnius Voivodeship in red. Voivodeship's borders did not change since the Union of Lublin. | |||||||||
| Capital | Vilnius | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• | 44,200 km2 (17,100 sq mi) | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| 1413 | |||||||||
| 1795 | |||||||||
| Political subdivisions | Powiats: five | ||||||||
| |||||||||
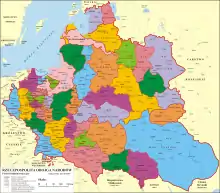
Geography and administrative division
Geographically the area was centered on the city of Vilnius, which had always been the capital of the entity and the seat of a voivode. However, the actual territory of the voivodeship varied over time. Together with the Trakai Voivodeship it was known as Lithuania propria. Until the partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth the voivodeship was composed of five smaller units of administrative division named powiat (in Lithuanian: plural - pavietai, singular - pavietas), similar to British counties:
History
In 1413 the Union of Horodło introduced the title of voivode to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Before the reform, the area, centered on Vilnius, was known as the Duchy of Lithuania or sometimes as the Duchy of Vilnius. Vilnius Voivodeship became the capital voivodeship of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
After the Union of Lublin in 1569 which formed the Commonwealth, Grand Duchy retained much of its autonomy, and Vilnius Voivodeship remained its capital voivodeship, just as Vilnius remained its capital city, although the capital of the Commonwealth was first in Cracow (Cracow Voivodeship) and later in Warsaw (Masovian Voivodeship). In 1793, voivodeships of Breslauja and Merkinė (Merkinė was really part of Vinius, but considered nominally part of Smolensk) were created from northern part of it. Breslauja Voivodeship consisted from Breslauja, Vilkmergė and Anykščiai counties and Merkinė one consisted from Merkinė, Prienai and Eišiškės ones.
After the partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the territory of Vilnius Voivodeship was incorporated into the Russian Empire, most of the territory becoming a part of Vilna Governorate. Northern part of it was passed to Kovno Governorate in 1843. After World War I former Vilnius Voivodeship was divided between Lithuania and Poland. After World War II, Soviet Union transferred most of the Polish portion of the former voivodeship to the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic.