Xiphotheca
Xiphotheca is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. The name of the genus is a compound of Ancient Greek ξίφος (ksíphos), which means "sword", and θήκη (thēkē) which can mean "box" or "sheath"—a reference to the shape of the legume pods.[1] Members of this genus can be distinguished by:
"(1) the presence of bracteoles in most species; (2) the fusion of the bracts with the base of the pedicel; (3) the laterally compressed pods; and (4) the accumulation of anabasine as a major alkaloid."[1]
| Xiphotheca | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Xiphotheca fruticosa | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Tribe: | Podalyrieae |
| Genus: | Xiphotheca Eckl. & Zeyh. |
| Species | |
|
See text. | |
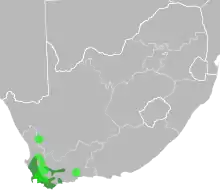 | |
Xiphotheca is endemic to the fynbos of South Africa.[1]
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Species
Xiphotheca comprises the following species:[2][1][3]
Section Congestae
- Xiphotheca fruticosa (L.) A. L. Schutte & B.-E. van Wyk
- Xiphotheca guthriei (L. Bolus) A. L. Schutte & B.-E. van Wyk
- Xiphotheca lanceolata (E. Mey.) Eckl. & Zeyh.
- Xiphotheca reflexa (Thunb.) A. L. Schutte & B.-E. van Wyk
Section Xiphotheca
- Xiphotheca canescens (Thunb.) A. L. Schutte & B.-E. van Wyk
- Xiphotheca cordifolia A. L. Schutte & B.-E. van Wyk
- Xiphotheca elliptica (DC.) A. L. Schutte & B.-E. van Wyk
- Xiphotheca phylicoides A. L. Schutte & B.-E. van Wyk
- Xiphotheca tecta (Thunb.) A. L. Schutte & B.-E. van Wyk
References
- Schutte AL (1997). "A revision of the genus Xiphotheca (Fabaceae)". Ann Missouri Bot Gard. 84 (1): 90–102. doi:10.2307/2399955. JSTOR 2399955.
- Schutte AL, Van Wyk B-E (1993). "The Reinstatement of the Genus Xiphotheca (Fabaceae)". Taxon. 41 (1): 43–49. doi:10.2307/1223301. JSTOR 1223301.
- USDA; ARS; National Genetic Resources Program. "GRIN species records of Xiphotheca". Germplasm Resources Information Network—(GRIN) [Online Database]. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved 28 February 2014.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.