Yahoo! Search
Yahoo! Search is a rebadged version of the Microsoft Bing search engine owned by Yahoo!, headquartered in Sunnyvale, California.[2][3]
 | |
Type of site | Web search engine |
|---|---|
| Available in | Multilingual (40) |
| Owner | Yahoo! |
| URL | search |
| Commercial | Yes |
| Registration | Optional |
| Launched | March 2, 1995 |
| Current status | Active |
| Written in | PHP[1] |
Originally, "Yahoo Search" referred to a Yahoo-provided interface that sent queries to a searchable index of pages supplemented with its directory of websites. The results were presented to the user under the Yahoo! brand. Originally, none of the actual web crawling and data housing was done by Yahoo! itself. In 2001, the searchable index was powered by Inktomi and later by Google until 2004, when Yahoo! Search became independent. On July 29, 2009, Microsoft and Yahoo! announced a deal in which Bing would henceforth power Yahoo! Search.[4]
As of July 2018, Microsoft Sites handled 24.2 percent of all search queries in the United States. During the same period of time, Oath (the then-owner of the Yahoo brand) had a search market share of 11.5 percent. Market leader Google generated 63.2 percent of all core search queries in the United States.[5]
Yahoo! Search has been criticized for favoring websites owned by Yahoo!'s parent company, Verizon Media, in its search results.[6]
Search technology acquisition
The roots of Search date back to Yahoo! Directory, which was launched in 1994 by Jerry Yang and David Filo, then students at Stanford University. In 1995, they introduced a search engine function, called Yahoo! Search, that allowed users to search Yahoo! Directory.[7][8] it was the first popular search engine on the Web,[9] despite not being a true Web crawler search engine. They later licensed Web search engines from other companies. Seeking to provide its own Web search engine results, Yahoo! acquired their own Web search technology. In 2002, they bought Inktomi, a "behind the scenes" or OEM search engine provider, whose results are shown on other companies' websites and powered Yahoo! in its earlier days.
In 2003, they purchased Overture Services, Inc., which included their owned the AlltheWeb and AltaVista search engines. Initially, even though Yahoo! owned multiple search engines, they didn't use them on the main yahoo.com website, but kept using Google's search engine for its results.
Starting on April 7, 2003, Yahoo! Search became its own web crawler-based search engine.[10] They combined the capabilities of search engine companies they had acquired and their prior research into a reinvented crawler called Yahoo!. The new search engine results were included in all of Yahoo's websites that had a web search function. Yahoo! also started to sell the search engine results to other companies, to show on their own websites. Their relationship with Google was terminated at that time, with the former partners becoming each other's main competitors.
In October 2007, Yahoo! Search was updated with a more modern appearance in line with the redesigned Yahoo! home page. In addition, Search Assist was added; which provides real-time query suggestions and related concepts as they are typed.

In July 2008, Yahoo! Search announced the introduction of a new service called Yahoo! Search BOSS ("Build your Own Search Engine"). This service opens the doors for developers to use Yahoo!'s system for indexing information and images and create their own custom search engine.[11]
In January 2010, Microsoft announced a deal in which it would take over the functional operation of Yahoo! Search, and set up a joint venture to sell advertising on both Yahoo! Search and Bing known as the Microsoft Search Alliance. A complete transition of all Yahoo! sponsored ad clients to Microsoft adCenter (now Bing Ads) occurred in October 2010.[4]
On March 12, 2014, Yahoo announced a partnership with Yelp to integrate its reviews and user-contributed photos into Yahoo! Search (as Bing had previously done).[12]
In November 2014, Mozilla signed a five-year partnership with Yahoo, making Yahoo Search the default search engine for Firefox browsers in the US.[13]
In April 2015, the Microsoft partnership was modified, now only requiring Bing results on the "majority" of desktop traffic, opening the ability for Yahoo to enter into non-exclusive deals for search services on mobile platforms and the remainder of desktop traffic. The amendment also gives either company the ability to terminate the contract with four months' notice. In October 2015, Yahoo subsequently reached an agreement with Google to provide services to Yahoo Search through the end of 2018, including advertising, search, and image search services.[14][15][2] As of October 2019, Yahoo! Search is once again “powered by Bing”.
Yahoo! Search blog and announcements
The team at Yahoo! Search frequently blogged about search announcements, features, updates and enhancements. The Yahoo! Search Blog, as stated provided "A look inside the world of search from the people at Yahoo!."[16] This included index updates named Weather Updates and their Yahoo! Search Assist feature.
International presence
Yahoo Search also provided their search interface in at least 38 international markets and a variety of available languages.[17] Yahoo! has a presence in Europe, Asia and across the Emerging Markets.
Languages
- Arabic
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Chinese (Simplified)
- Chinese (Traditional)
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- German
- Greek
- Hebrew
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Malay
- Norwegian
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Romanian
- Russian
- Serbian
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Spanish
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Thai
- Turkish
- Vietnamese
Search results
Yahoo Search indexed and cached the common HTML page formats, as well as several of the more popular file-types, such as PDF, Excel spreadsheets, PowerPoint, Word documents, RSS/XML and plain text files. For some of these supported file-types, Yahoo Search provided cached links on their search results allowing for viewing of these file-types in standard HTML. Using the Advanced Search interface or Preferences settings, Yahoo Search allowed the customization of search results and enabling of certain settings such as: SafeSearch, Language Selection, Number of results, Domain restrictions, etc.[18] For a Basic and starter guide to Yahoo Search, they also provided a Search Basics tutorial.[19] In 2005, Yahoo began to provide links to previous versions of pages archived on the Wayback Machine.[20] In the first week of May 2008, Yahoo launched a new search mash up called Yahoo Glue, which is in beta testing.[21]
Selection-based search
On June 20, 2007, Yahoo introduced a selection-based search feature called Yahoo Shortcuts. When activated this selection-based search feature enabled users to invoke search using only their mouse and receive search suggestions in floating windows while remaining on Yahoo properties such as Yahoo Mail. This feature was only active on Yahoo web pages or pages within the Yahoo Publisher Network. Yahoo Shortcuts required the content-owner to modify the underlying HTML of his or her webpage to call out the specific keywords to be enhanced. The technology for context-aware selection-based search on Yahoo pages was first developed by Reiner Kraft.[22]
SearchScan
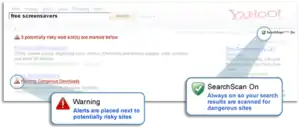
On May 11, 2008, Yahoo introduced SearchScan. If enabled this add-on/feature enhanced Yahoo Search by automatically alerting users of viruses, spyware and spam websites.[23]
Search verticals
Yahoo Search provided the ability to search across numerous vertical properties outside just the Web at large. These included Images, Videos, Local, Shopping, Yahoo! Answers, Audio, Directory, Jobs, News, Mobile, Travel and various other services as listed on their About Yahoo Search page.
See also
References
- Roger Chapman. "Top 40 Website Programming Languages". roadchap.com. Archived from the original on September 27, 2011. Retrieved September 6, 2011.
- "Ad Tech And Mobile In Focus In Microsoft And Yahoo's Renewed Search Deal". TechCrunch. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- EL. "Yahoo search". Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- "Microsoft and Yahoo seal web deal". BBC News. July 29, 2009. Retrieved November 10, 2012.
- "Search engine market share in the United States 2018 - Statistic". Statista.
- "Yahoo!, AOL, OneSearch results biased in favor of parent company Verizon Media's websites". Ctrl blog. March 6, 2020.
- Oppitz, Marcus; Tomsu, Peter (2017). Inventing the Cloud Century: How Cloudiness Keeps Changing Our Life, Economy and Technology. Springer. p. 238. ISBN 9783319611617.
- "Yahoo! Search". Yahoo!. November 28, 1996. Archived from the original on November 28, 1996. Retrieved September 5, 2019.
- "What is first mover?". SearchCIO. TechTarget. September 2005. Retrieved September 5, 2019.
- "Yahoo! Inc. - Company Timeline". Wayback Machine. July 13, 2008. Archived from the original on July 13, 2008. Retrieved July 19, 2016.CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- "Yahoo Opens Up Search Technology Infrastructure for Innovative, New Search Experiences, Providing Third Parties with Unprecedented Access, Re-Ranking and Presentation Control of Web Search Results". Yahoo. July 10, 2008. Archived from the original on December 20, 2010. Retrieved July 25, 2008.
- "Yahoo Partners With Yelp To Bring Local Data To Its Search Tools". TechCrunch. Retrieved February 21, 2017.
- "New Search Strategy for Firefox: Promoting Choice & Innovation". The Mozilla Blog.
- "Yahoo enters deal to display Google search results". The Verge. October 20, 2015. Retrieved October 21, 2015.
- "Microsoft loses exclusivity in shaken up Yahoo search deal". Ars Technica. April 16, 2015. Retrieved June 30, 2015.
- "Yahoo! Search Blog". Ysearchblog.com. Archived from the original on December 6, 2012. Retrieved November 10, 2012.
- "Yahoo international presence". World.yahoo.com. Retrieved November 10, 2012.
- "Yahoo Advanced Web Search".
- Search Basics tutorial Archived October 2, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- Yahoo Cache Now Offers Direct Links to Wayback Machine Archived May 1, 2011, at the Wayback Machine Search Engine Watch, September 18, 2005
- Hopkins, Mark (November 13, 2008). "Yahoo! Glue Launches in America". Mashable.com. Retrieved February 21, 2015.
- "Yahoo shortcuts".
- "Yahoo SearchScan information page". Tools.search.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on October 19, 2012. Retrieved November 10, 2012.