0s
The 0s cover the first nine years of the Anno Domini era, which began on January 1, 1 AD and ended on December 31, 9 AD. It is one of the two "0-to-9" decade-like timespans (along with 0s BC) that contain 9 years, and are not decades (10 years).
| Millennium: | 1st millennium |
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | |
| Years: | |
| Categories: |
|
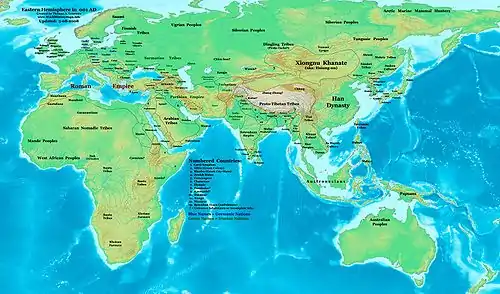
In Europe, the 0s saw the continuation of conflict between the Roman Empire and Germanic tribes in the Early Imperial campaigns in Germania. Tiberius, Ahenobarbus, Vinicius and Varus led Roman forces in multiple punitive campaigns, before sustaining a major defeat at the hands of Arminius in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. Concurrently, the Roman Empire fought the Bellum Batonianum against an alliance of native peoples of in two regions of Illyricum, Dalmatia and Pannonia, led by Bato the Daesitiate. In AD 8, the Breuci of the Sava valley surrendered, but it took a winter blockade and another season of fighting before the surrender in Dalmatia in AD 9. A conflict also took place in Korea, where Daeso, King of Dongbuyeo invaded Goguryeo with a 50,000-man army in 6 AD. He was forced to retreat when heavy snow began to fall, stopping the conflict until the next decade. In China, Wang Mang established the Xin dynasty.
Literary works from the 0s include works from the ancient Roman poet Ovid; the Ars Amatoria, an instructional elegy series in three books, Metamorphoses, a poem which chronicles the history of the world from its creation to the deification of Julius Caesar within a loose mythico-historical framework, and Ibis, a curse poem written during his years in exile across the Black Sea for an offense against Augustus. Nicolaus of Damascus wrote the 15-volume History of the World.
A census was concluded in China in 2 AD: final numbers showed a population of nearly 60 million (59,594,978 people in slightly more than 12 million households). The census is one of the most accurate surveys in Chinese history. Dionysius Exiguus assigned Jesus's birth date in 1 AD, in his anno Domini era according to at least one scholar. However, most scholars think Dionysius placed the birth of Jesus in the previous year, 1 BC. Furthermore, most modern scholars do not consider Dionysius' calculations authoritative, placing the event several years earlier (see Chronology of Jesus).
Events
== {{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<10|a}}}} == {{trim|{{transcluded section|{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}}} {{#section-h::{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}|Events}}}} == {{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<10|a}}}} == {{trim|{{transcluded section|{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}}} {{#section-h::{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}|Events}}}} == {{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<10|a}}}} == {{trim|{{transcluded section|{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}}} {{#section-h::{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}|Events}}}} == {{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<10|a}}}} == {{trim|{{transcluded section|{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}}} {{#section-h::{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}|Events}}}} == {{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<10|a}}}} == {{trim|{{transcluded section|{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}}} {{#section-h::{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}|Events}}}} == {{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<10|a}}}} == {{trim|{{transcluded section|{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}}} {{#section-h::{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}|Events}}}} == {{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<10|a}}}} == {{trim|{{transcluded section|{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}}} {{#section-h::{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}|Events}}}} == {{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<10|a}}}} == {{trim|{{transcluded section|{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}}} {{#section-h::{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}|Events}}}} == {{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<10|a}}}} == {{trim|{{transcluded section|{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}}} {{#section-h::{{dr|y|y|{{{year}}}0|{{{1}}}|n{{#ifexpr:{{{year}}}<100|a}}}}|Events}}}}
Significant people
- Erato, Artaxiad Dynasty Queen of Armenia, 8–5 BC, 2 BC – 2 AD, 6–11
- Ariobarzan of Atropatene, Client King of Armenia, r. 1 BC – 2 AD
- Artavazd V, Client King of Armenia, r. 2–11
- Tigranes V, Artaxiad Dynasty King of Armenia, r. 2–6
- Ping Di, Emperor of Han Dynasty China, r. 1 BC – 5 AD
- Ruzi Ying, Emperor of Han Dynasty China, r. 6–9
- Wang Mang, Usurper Emperor of the short-lived Xin Dynasty in China r. 9–23
- Antiochus III, King of Commagene, r. 12 BC – 17 AD
- Arminius, German war chief
- Arshak II, King of Caucasian Iberia, r. 20 BC-1 AD
- Pharasmanes I, King of Caucasian Iberia, r. 1-58
- Strato II and Strato III, co-kings of the Indo-Greek Kingdom, r. 25 BC – 10 AD
- Crimthann Nia Náir, Legendary High King of Ireland, r. 8 BC – AD 9
- Cairbre Cinnchait, Legendary High King of Ireland, r. 9–14
- Suinin, Legendary Emperor of Japan, r. 29 BC – 70 AD
- Natakamani, King of Kush, r. (1 BC – AD 20)
- Abgar V of Edessa, King of Osroene, 4 BC–AD 7, 13–50
- Ma'nu IV, King of Osroene, 7–13
- Phraates V, King of the Parthian Empire, r. 2 BC – 4 AD
- Musa of Parthia, mother and co-ruler with Phraates V, r. 2 BC – 4 AD
- Orodes III, King of the Parthian Empire, r. 4–6
- Vonones I, King of the Parthian Empire, r. 8–12
- Artabanus of Parthia, pretender to the Parthian throne and future King of Parthia
- Caesar Augustus, Roman Emperor (27 BC – AD 14)
- Gaius Caesar, Roman general
- Livy, Roman historian
- Ovid, Roman poet
- Quirinius, Roman nobleman and politician
- Hillel the Elder, Jewish scholar and Nasi of the Sanhedrin, in office c. 31 BC – 9 AD
- Shammai, Jewish scholar and Av Beit Din of the Sanhedrin, in office 20 BC – 20 AD
- Tiberius, Roman general, statesman, and future emperor
- Hyeokgeose, King of Silla, r. 57 BC – 4 AD
- Namhae, King of Silla, r. 4–24
== {{ucfirst:{{{1}}}}} == {{preprocess|{{((}}transcluding articles {{!}} {{#ifeq:{{{decade}}}|0|{{void|There is no AD year 0}}|{{Year article|{{{decade}}}0}}}} {{!}} {{for loop|{{!}}|call=Year article|pc1n=1|pc1v={{{decade}}}0|pv=2|1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9}} {{))}}}} {{#ifeq:{{{decade}}}|0|{{void|There is no AD year 0}}| {{Transclude {{{1}}}|{{{decade}}}0}} }} {{for loop| |call=Transclude {{{1}}}|{{{decade}}}1|{{{decade}}}2|{{{decade}}}3|{{{decade}}}4|{{{decade}}}5|{{{decade}}}6|{{{decade}}}7|{{{decade}}}8|{{{decade}}}9}} == {{ucfirst:{{{1}}}}} == {{preprocess|{{((}}transcluding articles {{!}} {{#ifeq:{{{decade}}}|0|{{void|There is no AD year 0}}|{{Year article|{{{decade}}}0}}}} {{!}} {{for loop|{{!}}|call=Year article|pc1n=1|pc1v={{{decade}}}0|pv=2|1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9}} {{))}}}} {{#ifeq:{{{decade}}}|0|{{void|There is no AD year 0}}| {{Transclude {{{1}}}|{{{decade}}}0}} }} {{for loop| |call=Transclude {{{1}}}|{{{decade}}}1|{{{decade}}}2|{{{decade}}}3|{{{decade}}}4|{{{decade}}}5|{{{decade}}}6|{{{decade}}}7|{{{decade}}}8|{{{decade}}}9}}
See also
References
Sources
- Declercq, Georges (2000). Anno Domini: The origins of the Christian Era. Turnhout, Belgium: Brepols. pp. 143–147. ISBN 978-2503510507.
- Declercq, Georges (2002). "Dionysius Exiguus and the introduction of the Christian Era". Sacris Erudiri. Brussels: Brepols. 41: 165–246. doi:10.1484/J.SE.2.300491. ISSN 0771-7776.
Annotated version of a portion of Anno Domini
- Dunn, James D. G. (2003). Jesus Remembered. Christianity in the Making. 1. Eerdmans Publishing. p. 324. ISBN 978-0802839312.
- Klingaman, William K. (1990). The First Century: Emperors, Gods and Everyman. Harper-Collins. ISBN 978-0785822561.
- Mommsen, Theodore (1996), A History of Rome Under the Emperors, UK: Routledge, ISBN 0-415-10113-1
- Sanders, Ed P. (1993). The Historical Figure of Jesus. Allen Lane Penguin Press. ISBN 978-0-14-192822-7.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 0s. |
