1951 Argentine general election
The Argentine general election of 1951, the first to have enfranchised women at the national level, was held on 11 November. Voters chose both the President of Argentina and their legislators and with a turnout of 88.0%, it produced the following results:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
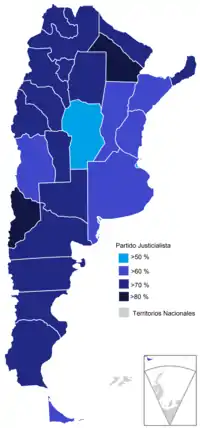 Most voted party by province. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
President
| Party/Electoral Alliance | Votes | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Peronist Party | 4,745,168 | 62.5% |
| Radical Civic Union | 2,415,750 | 31.8% |
| National Democratic Party | 174,399 | 2.3% |
| Communist Party | 71,318 | 0.9% |
| Socialist Party | 54,920 | 0.7% |
| Others | 22,404 | 0.3% |
| Positive votes | 7,483,959 | 98.6% |
| Blank and nullified votes | 109,989 | 1.4% |
| Total votes | 7,593,948 | 100.0% |
Note: The 1949 Constitution abolished the Electoral College.
Argentine Chamber of Deputies
| Party/Electoral Alliance | Seats | % of votes |
|---|---|---|
| Peronist Party | 135 | 63.5% |
| Radical Civic Union | 14 | 32.3% |
| Others and blanks | 4.2% | |
| Total | 149 | 100.0% |
Background
President Juan Perón (1895-1974) had become President for the first time in June 1946 (see 1946 Argentine general election). His popularity was riding high following five years of social reforms and a vigorous public works program, faced intensifying opposition during 1951. His decision to expropriate the conservative La Prensa (then the nation's second-most circulated daily), though lauded by the CGT labor union, damaged his standing elsewhere at home and his reputation in the World, as did the climate of political liberties: the opposition UCR's nominee, Congressman Ricardo Balbín, had spent much of the previous year as a political prisoner, to name one of many such examples. Economically, the year was an improvement over the 1949-50 recession and saw the completion of a number of landmark public works and the inaugural of Channel 13 (Public Television), the first regular broadcast station in Latin America; but growing inflation (50%, a record at the time) led to increasing strike activity.


The UCR and other parties in opposition, harassed and deprived of access to the media, boycotted a number of Congressional races and all Senate races, as well. The vice president, Hortensio Quijano, had requested leave from the campaign due to failing health and, on August 22, the CGT organized a rally on Buenos Aires' massive Ninth of July Avenue in support of the influential first lady Eva Perón as her husband's running mate, though unbeknownst to the crowd, the popular Evita was, like Quijano, dying, and thus refused the acclamation. Quijano reluctantly stayed on; but her stepping aside did not prevent a September 28 coup attempt against Perón on the part of ultraconservative elements in the Army. Ultimately, these ill-considered attacks, the Peróns' popularity and their control of much of the media combined to give the Peronist Party a landslide in this, the first Argentine national election in which the vote was extended to women.
Candidates
- Peronist Party: President Juan Perón of Buenos Aires Province
- Radical Civic Union: Congressman Ricardo Balbín of Buenos Aires Province
 Incumbent President Juan Perón
Incumbent President Juan Perón Balbín (left) and running mate Arturo Frondizi
Balbín (left) and running mate Arturo Frondizi
Governors
| Election of Provincial Governors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elected positions: 14 governors, 14 legislative bodies
Presidential appointment: 9 territorial governors, Mayor of the city of Buenos Aires | ||||
| Date | Province | Elected | Winner | Runner-up |
| 11 November | Buenos Aires | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Carlos Aloé (Partido Peronista) (62,99 %) |
Crisólogo Larralde (Unión Cívica Radical) (33,30 %) |
| Catamarca | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Armando Casas Nóblega (Partido Peronista) (76,66 %) |
Ramón Edgardo Acuña (Unión Cívica Radical) (21,58 %) | |
| Córdoba | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Raúl Lucini (Partido Peronista) (51,98 %) |
Arturo Umberto Illia (Unión Cívica Radical) (43,08 %) | |
| Corrientes | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Raúl Benito Castillo (Partido Peronista) (64,36 %) |
Héctor Lomónaco (Unión Cívica Radical) (26,70 %) | |
| Entre Ríos | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Felipe Texier (Partido Peronista) (63,07 %) |
Fermín J. Garay (Unión Cívica Radical) (32,68 %) | |
| Jujuy | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Jorge Villafañe (Partido Peronista) (79,29 %) |
Horacio Guzmán (Unión Cívica Radical) (15,01 %) | |
| La Rioja | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Juan Melis (Partido Peronista) (73,97 %) |
Herminio Torres Brizuela (Unión Cívica Radical) (26,03 %) | |
| Mendoza | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Carlos Horacio Evans (Partido Peronista) (66,89 %) |
Leopoldo Suárez (Unión Cívica Radical) (21,22 %) | |
| Salta | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Ricardo Joaquín Durand (Partido Peronista) (76,37 %) |
Ricardo E. Aráoz (Unión Cívica Radical) (23,34 %) | |
| San Juan | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Rinaldo Viviani (Partido Peronista) (78,67 %) |
Juan Pascual Pringles (Unión Cívica Radical) (16,57 %) | |
| San Luis | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Víctor Endeiza (Partido Peronista) (71,16 %) |
Julio Domeniconi (Unión Cívica Radical) (15,83 %) | |
| Santa Fe | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Luis Cárcamo (Partido Peronista) (64,92 %) |
Alfredo Julio Grassi (Unión Cívica Radical) (33,08 %) | |
| Santiago del Estero | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Francisco González (Partido Peronista) (78,72 %) |
Hugo Catella (Unión Cívica Radical) (14,06 %) | |
| Tucumán | Governor
Vice Governor Provincial legislatures |
Luis Cruz (Partido Peronista) (70,70 %) |
Celestino Gelsi (Unión Cívica Radical) (27,40 %) | |
Footnotes
- Nohlen, Dieter. Elections in the Americas. Oxford University Press, 2005.
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)