2011 Argentine general election
Argentina held national presidential and legislative elections on Sunday, 23 October 2011. Incumbent president Cristina Fernández de Kirchner of the Front for Victory won via landslide, with 54.11% of votes against Hermes Binner of Broad Progressive Front, she also secured a second term in office after the Front for Victory won just over half of the seats in the National Congress.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Presidential election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Registered | 28,916,183 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 79.39% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
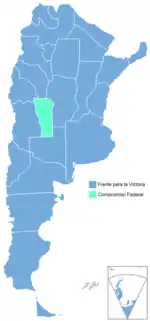 .svg.png.webp) Most voted party by province (left) and department (right). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legislative election | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
130 of 254 seats in the Chamber of Deputies 27 of 75 seats in the Senate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 79.39% (Deputies) 81.75% (Senate) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This lists parties that won seats. See the complete results below. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
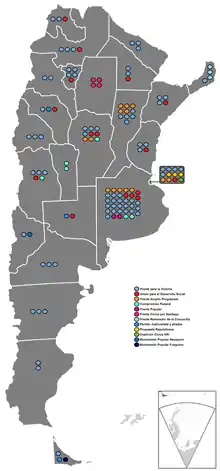 Chamber of Deputies results by province | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mercosur Parliamentarians were also popularly elected for the first time. Another novelty was the introduction of open, simultaneous and mandatory primaries. These took place 14 August 2011 to select the candidates of each political party or coalition.[1]
Presidential campaign

The nation's myriad parties forged seven coalitions, of which five became contenders for a possible runoff election:
- Front for Victory: the ruling party, led by President Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, and allies, including the New Encounter.[2] The FPV is mostly based on the center-left Justicialist Party (PJ) factions that support the current government.
- Federal Peronism, or Dissident Peronism: centrist or conservative PJ figures opposed to the government and allies, including the Republican Proposal. This coalition remained divided between Eduardo Duhalde's Popular Front and Alberto Rodríguez Saá's Federal Commitment both before and after the August primaries.
- Union for Social Development: the Radical Civic Union (UCR), led by Congressman Ricardo Alfonsín, and allies, which initially included Federal Peronist Francisco de Narváez.
- Broad Progressive Front: the Socialist Party, led by Governor Hermes Binner, and allies, including GEN and the New Party. Proyecto Sur had briefly joined this coalition.
- Civic Coalition: the party, led by Congresswoman Elisa Carrió, had been part of the Civic and Social Agreement, but separated from the latter in August 2010.[3]
Other coalitions of note include the Workers' Left Front, led by Jorge Altamira, and Proyecto Sur, led by Pino Solanas; the latter left the Socialist Party-led coalition and instead formed an alliance with the MST and the PSA.[4]
The Civic and Social Agreement was an alliance between the UCR and most of what became the Progressive Ample Front and the Civic Coalition, with other, minor allies. This coalition proved unwieldy as the 2011 campaign progressed, however, though various forms of it will be retained in certain provinces for strategic purposes.[5]
Front for Victory (incumbents)
The Front for Victory (FPV) candidate for the Justicialist Party primaries was current President Cristina Fernández de Kirchner. Her husband and predecessor, Néstor Kirchner, was considered a top candidate to succeed her until his death on 27 October 2010.[6]
She had suffered a significant decline in approval during the 2008 Argentine government conflict with the agricultural sector and the subsequent recession, and the ruling Front for Victory lost its absolute majority in both houses of Congress during the June 2009 mid-term elections.[7] The economy, and her approval ratings, recovered steadily during 2010,[8] however, and the 2011 electoral season began with Fernández de Kirchner's job approval at around 58 percent,[9] with polling indicating that she would likely be reelected in the first round.[10]
She avoided committing herself to running for a second term during the early months of 2011.[11] Two days before the 23 June deadline, however, she announced her decision to run for reelection.[12] She nominated the nation's Economy Minister, Amado Boudou, as her running mate on 25 June.[13] Their ticket won a landslide victory in the 14 August primaries, obtaining just over 50% and besting the runner-up (Alfonsín) by nearly 38%; they won in the City of Buenos Aires and in every province except San Luis (won by Rodríguez Saá).[14]
Support for Fernández de Kirchner was strongest among the poor (65.2%) and those aged 30 to 44 (54.6%). Her support was weakest among the upper middle class (43.5%), though she remained over 24% ahead of the runner-up (Binner) among those polled within that segment.[15]
Federal Peronists
The leaders of the center-right Federal Peronism were torn between running for primary elections within the PJ against the Front for Victory, or running instead in the general election through another political alliance. Former President Eduardo Duhalde was the first to informally start his pre-candidacy campaign, announcing hypothetical cabinet picks as early as December 2009.[16] The Governors of Chubut, Mario Das Neves, and of San Luis, Alberto Rodríguez Saá, as well as former Governor of Buenos Aires Province Felipe Solá, also stated their intention to run for president. Das Neves became the first Federal Peronist to drop out, while Solá boosted his own prospects by securing an alliance with the conservative Republican Proposal (PRO) on 16 May.[17] Duhalde narrowly defeated Rodríguez Saá in a Buenos Aires Federal Peronism primary held on 22 May, though both men remained front-runners for their party's nomination.[18] Ultimately, each ran on separate Federal Peronist tickets.
Duhalde formally announced his Popular Union candidacy on 9 June, nominating Das Neves as his running mate.[19] Rodríguez Saá, in turn, nominated former Santa Fe Governor José María Vernet as his running mate on his Federal Commitment ticket.[20] Solá, who struggled in the polls, withdrew on 11 June, encouraging local candidates in his fold to form alliances with Duhalde and the party's candidate for Buenos Aires Governor, Francisco de Narváez.[21] De Narváez later endorsed Rodríguez Saá.[22]
Support for Duhalde was strongest among the working class (14.2%) and weakest among young voters (3.9%).[15] Rodríguez Saá polled best among upper middle class voters (14%) and those age 30 to 44 (11.9%); worst among the poor.[15]
Radical Civic Union
The center-left Radical Civic Union had scheduled primaries for 28 April. Both Ricardo Alfonsín, son of the late former President Raúl Alfonsín, and current party leader Ernesto Sanz started pre-candidacy campaigns; Sanz, however, dropped out on 28 April. Vice President Julio Cobos, considered a likely UCR primary candidate, had stated his intention to run only in August, during the coalition primaries; he dropped out in April as well.[11]
The UCR and the Socialist Party (partners in the Civic and Social Agreement) parted ways in May 2011, with Alfonsín and Santa Fe Governor Hermes Binner running on separate slates for the primaries in August, and likely in the general election, as well.[5] Alfonsín secured an alliance with Federal Peronist candidate Francisco de Narváez in Buenos Aires Province,[23] De Narváez ran for governor with his senior partner's endorsement in return for his support for Alfonsín's presidential campaign.[23][24] Alfonsín nominated former Central Bank President Javier González Fraga, a non-partisan economist close to both the UCR and Federal Peronism, as his running-mate on 2 June.[5]
De Narváez withdrew his endorsement of Alfonsín in favor of Rodríguez Saá following the 14 August primaries,[22] though he continued his campaign for Governor of Buenos Aires with Alfonsín's endorsement.[25]
Alfonsín's support was strongest among those age 45 to 59 (14.6%), and weakest among young voters (5.3%).[15]
Socialists
Binner endorsed GEN leader Margarita Stolbizer for Governor of Buenos Aires following his break with Alfonsín,[24] and formally announced his Broad Progressive Front candidacy on 11 June; he nominated Córdoba Senator Norma Morandini as his running mate.[26] His alliance with Pino Solanas was dissolved the following week, however, and the Proyecto Sur leader instead joined a coalition of minor, left-wing parties.[4]
Binner, despite obtaining fourth place, fared better than expected by local analysts in the 14 August primary,[27] and became the runner-up in subsequent polls. His support was strongest among the middle (18.8%) and upper middle classes (18.9%), while weakest among the poor (6.5%); among the broad age groups, voters 30 to 44 were the most supportive (19.3%).[15]
Civic Coalition
The leader of the centrist Civic Coalition, Elisa Carrió, reversed her earlier intention to opt out of the 2011 race, and following the departure of her Civic Coalition from the Civic and Social Agreement formed in 2009 with the UCR, she announced her candidacy for president on 12 December 2010.[28] Carrió withdrew her presidential bid following a poor showing in the 14 August primaries, where she obtained 3%.[29]
Other candidates
Numerous other candidates, or potential candidates, dropped out in May 2011, notably Buenos Aires Mayor Mauricio Macri, who instead sought a second term as mayor, and left-wing film maker Fernando Solanas (who ran unsuccessfully for the same post).[30] Solanas nominated Congresswoman Alcira Argumedo as Proyecto Sur's candidate for president on 22 June.[31] The 14 August primary effectively ended Argumedo's campaign, as well as those of Neighbors' Action Movement (MAV) candidate Sergio Pastore, and People's Countryside Party (PCP) candidate José Bonacci; neither had reached the requisite 1.5% threshold needed to advance to the general election.[32]
The candidate for the Workers' Left Front (FIT), Jorge Altamira, fared unexpectedly well and advanced to the general election.[33] Altamira polled best among the poor (7.9%) and among the upper middle class (5.4%).[15]
Results
Primary elections
Open primary elections for the Presidency were held nationwide on 14 August.
With this system, all parties run primary elections in a same general elections. All parties must take part in it, both the parties with internal factions and parties with a single candidate list. Citizens may vote for any candidate of any party, but may only cast a single vote. The most voted candidate of parties gaining 1.5% or higher of the valid votes will be allowed to run in the main elections.
| Presidential candidate |
Vice Presidential candidate |
Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cristina Fernández de Kirchner | Amado Boudou | Front for Victory (FPV) | 10,762,217 | 47.98 | |
| Ricardo Alfonsín | Javier González Fraga | Union for Social Development (UDESO) | 2,614,211 | 11.65 | |
| Eduardo Duhalde | Mario Das Neves | Popular Front (FP) | 2,595,996 | 11.57 | |
| Hermes Binner | Norma Morandini | Broad Progressive Front (FAP) | 2,180,110 | 9.72 | |
| Alberto Rodríguez Saá | José María Vernet | Federal Commitment (CF) | 1,749,971 | 7.80 | |
| Elisa Carrió | Adrián Pérez | Civic Coalition ARI (CC ARI) | 689,033 | 3.07 | |
| Jorge Altamira | Christian Castillo | Left and Worker's Front (FIT) | 527,237 | 2.35 | |
| Alcira Argumedo | Jorge Cardelli | Project South | 190,094 | 0.85 | |
| Sergio Pastore | Gilda Rodríguez | Neighborhood Action Movement | 65,031 | 0.29 | |
| José Bonacci | José Villena | People's Countryside Party | 48,774 | 0.22 | |
| Blank votes | 1,007,753 | 4.49 | |||
| Total | 22,430,427 | 100 | |||
| Valid votes | 22,430,427 | 98.79 | |||
| Invalid votes | 274,951 | 1.21 | |||
| Total votes | 22,705,378 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 28,861,216 | 78.67 | |||
| Source:[34] | |||||
President

The president and vice-president were chosen directly in a two-round system election. Candidates who obtained less than 1.5% during the preliminary round on 14 August were excluded from the general election on 23 October.[32]
Early results on election night awarded incumbent president Cristina Fernández de Kirchner of the Front for Victory (FPV) a second, four-year term. Winning in the City of Buenos Aires and every province except San Luis (won by Federal Commitment candidate Alberto Rodríguez Saá),[35] she became the first candidate to obtain an absolute majority of the popular vote (54%) since Raúl Alfonsín in 1983, and upon completion of ballot processing, the margin of victory (37.1%) exceeded Juan Perón's record 36% margin obtained in 1973.[36] Fernández de Kirchner became the first woman re-elected as head of state in Latin American history.[37]
| Presidential candidate |
Vice Presidential candidate |
Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cristina Fernández de Kirchner | Amado Boudou | Front for Victory (FPV) | 11,865,055 | 54.11 | |
| Hermes Binner | Norma Morandini | Broad Progressive Front (FAP) | 3,684,970 | 16.81 | |
| Ricardo Alfonsín | Javier González Fraga | Union for Social Development (UDESO) | 2,443,016 | 11.14 | |
| Alberto Rodríguez Saá | José María Vernet | Federal Commitment (CF) | 1,745,354 | 7.96 | |
| Eduardo Duhalde | Mario Das Neves | Popular Front (FP) | 1,285,830 | 5.86 | |
| Jorge Altamira | Christian Castillo | Left and Worker's Front (FIT) | 503,372 | 2.30 | |
| Elisa Carrió | Adrián Pérez | Civic Coalition ARI (CC ARI) | 399,685 | 1.82 | |
| Total | 21,927,282 | 100 | |||
| Positive votes | 21,927,282 | 95.52 | |||
| Blank votes | 803,362 | 3.50 | |||
| Invalid votes | 225,741 | 0.98 | |||
| Total votes | 22,956,385 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 28,916,183 | 79.39 | |||
| Sources:[38][39] | |||||
Chamber of Deputies
All 23 provinces and the city of Buenos Aires held elections to renew half of the Chamber of Deputies (lower house). Each province and the autonomous city elects a number of at-large representatives on a party list system roughly proportional to their population, and no province is allotted fewer than five Deputies. The system used to know how many deputies per party in each district is D'Hondt method.
Early projections suggested that President Cristina Kirchner's FpV would increase their representation in the Lower House from 87 seats (out of 257),[40] to around 116; the presence of an estimated ten allies would put them three votes shy of an absolute majority.[41]
| Party | Votes | % | Seats won | Total seats | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Front for Victory (FPV) | 10,757,804 | 52.22 | 85 | 129 | |
| Union for Social Development (UDESO) | 2,790,964 | 13.55 | 16 | 44 | |
| Broad Progressive Front (FAP) | 2,780,984 | 13.50 | 14 | 20 | |
| Federal Commitment (CF) | 1,278,617 | 6.21 | 6 | 35[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Popular Front (FP) | 1,123,269 | 5.45 | 2 | ||
| Rioja Popular Front | 42,736 | 0.21 | 1 | ||
| Civic Coalition ARI (CC ARI) | 617,747 | 3.00 | 1 | 8 | |
| Left and Worker's Front (FIT) | 590,114 | 2.86 | — | — | |
| Republican Proposal (PRO) | 427,429 | 2.07 | 3 | 12 | |
| Neuquén People's Movement (MPN) | 88,197 | 0.43 | 1 | 3 | |
| Project South | 47,886 | 0.23 | — | 4 | |
| Jujuy First Front | 25,025 | 0.12 | — | — | |
| Fueguian People's Movement (MOPOF) | 13,788 | 0.07 | 1 | 1 | |
| Citizen Dignity | 7,491 | 0.04 | — | — | |
| Patagonian Social Party | 4,712 | 0.02 | — | — | |
| Popular Party of Tierra del Fuego | 1,363 | 0.01 | — | — | |
| City in Action Party | 947 | 0.00 | — | — | |
| Fuegian Federal Party | Did not run | — | 1 | ||
| Total | 20,599,073 | 100 | 130 | 257 | |
| Positive votes | 20,599,073 | 89.74 | |||
| Blank votes | 2,138,970 | 9.32 | |||
| Invalid votes | 217,232 | 0.95 | |||
| Total votes | 22,955,275 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 28,916,230 | 79.39 | |||
| Sources:[42][39] | |||||
Senate
Eight districts (Buenos Aires Province, Formosa, Jujuy, La Rioja, Misiones, San Juan, San Luis and Santa Cruz) also elected three National Senators each (two for the most voted party or coalition, one for the second most voted party or coalition), to renew a third of the upper house.[43]
The opposition fared better in the Senate, which remained nearly unchanged; the upper house would continue divided between the FpV with a majority of 40 seats (out of 72), and the UCR (around 16) and others with the remainder.[40][41] The departure of Vice President Julio Cobos of the UCR (distanced politically from the President since 2008) deprived the opposition of a tie-breaking vote in the Senate.[41]
| Party | Votes | % | Seats won | Total seats | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Front for Victory (FPV) | 5,739,247 | 57.28 | 15 | 40 | |
| Union for Social Development (UDESO) | 1,198,259 | 11.96 | 3 | 16 | |
| Broad Progressive Front (FAP) | 1,133,486 | 11.31 | 1 | 4 | |
| Federal Commitment (CF) | 692,421 | 6.91 | 3 | 7[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Popular Front (FP) | 658,416 | 6.57 | — | ||
| Rioja Popular Front | 56,409 | 0.56 | 2 | ||
| Left and Worker's Front (FIT) | 288,515 | 2.88 | — | — | |
| Civic Coalition ARI (CC ARI) | 196,033 | 1.96 | — | 4 | |
| Jujuy First Front | 24,127 | 0.24 | — | — | |
| Republican Proposal (PRO) | 11,527 | 0.12 | — | — | |
| Renewal Crusade | 10,873 | 0.11 | — | — | |
| Citizen Dignity | 7,450 | 0.07 | — | — | |
| Project South | 2,151 | 0.02 | — | — | |
| Neuquén People's Movement (MPN) | Did not run | — | 1 | ||
| Total | 10,018,914 | 100 | 27 | 72 | |
| Positive votes | 10,018,914 | 90.24 | |||
| Blank votes | 1,013,390 | 9.13 | |||
| Invalid votes | 70,403 | 0.63 | |||
| Total votes | 11,102,707 | 100 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 13,581,951 | 81.75 | |||
| Sources:[44][39] | |||||
Provincial
All but two of the 23 provinces will also elect governors and provincial legislative officials on staggered dates through the year, and nine of them will hold elections on the same day as the General Elections.[45] There will be also simultaneous local elections, whereby a number of Municipalities elect municipal legislative officials (concejales), and in some cases also a mayor (or equivalent).[46]
Some of the most high-profile gubernatorial races include that of Governor of Buenos Aires Province (the nation's largest), where Governor Daniel Scioli of the FpV defeated Federal Peronist Deputy Francisco de Narváez,[47] and in Santa Fe Province, where the incumbent Socialist Governor, Hermes Binner, would run for president.[48] Socialist nominee Antonio Bonfatti was elected to succeed him.[49] The Mayor of Buenos Aires, Mauricio Macri faced Senator Daniel Filmus of the FpV and film-maker Fernando Solanas of Proyecto Sur.[30] He was overwhelmingly re-elected in a runoff vote held on 31 July.[50]
Results throughout the year and in the general election handed candidates for the FpV or its allies the governor's house in every province except San Luis (won by Federal Commitment) and Santa Fe (won by the Socialist Party).[47]
Opinion polls
Numerous consulting firms conducted polling throughout the campaign, whereby respondents chose from a number of declared or potential first-round candidates.
| Pollster | Date published | Alfonsín | Binner | Carrió | Duhalde | Fernández de Kirchner | Macri | Rodríguez Saá | Others | DK/NR | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibarómetro | 12 January | 12.1 | – | – | 10.4 | 40.0 | 8.7 | – | 4.2 | – | |
| Opinión Autenticada | 9 March | 11.6 | – | 3.9 | 7.2 | 30.5 | 12.6 | 3.1 | 19.4 | 11.7 | |
| Aresco | 7 April | 9.6 | – | 6.6 | 14.2 | 49.9 | 12.7 | – | 6.9 | – | |
| Equis | 28 April | 6.1 | – | 2.4 | 5.3 | 44.0 | 11.1 | – | 14.4 | 16.9 | |
| Aresco | 16 May | 10.8 | – | 7.2 | 15.3 | 45.1 | * | – | – | – | |
| Ibarómetro | 16 May | 12.0 | – | – | – | 44.6 | 9.9* | 9.0 | – | – | |
| OPSM | 16 May | 18.4 | – | 5.1 | 11.1 | 41.7 | * | 7.3 | – | – | |
| Ricardo Rouvier | 16 May | 22.3 | – | 4.8 | 6.6 | 49.8 | * | 6.0 | – | – | |
| Isonomía | 25 May | 12.6 | 5.6 | 8.0 | 10.1 | 41.2 | * | 5.4 | 9.3 | – | |
| OPSM | 7 June | 14.6 | 13.4 | 4.8 | 9.7 | 40.8 | * | 8.2 | – | 10.5 | |
| CEOP | 12 June | 12.8 | 4.3 | 5.9 | 7.5 | 48.2 | * | 5.5 | 4.5 | 8.4 | |
| Management & Fit | 12 June | 15.3 | 5.1 | 4.0 | 5.8 | 33.4 | * | 7.0 | 1.1 | 23.5 | |
| Nueva Comunicación | 14 June | 16.7 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 12.3 | 34.3 | * | 8.0 | 3.7 | 9.3 | |
| Aresco | 20 June | 14.0 | 7.5 | 6.9 | 16.3 | 40.5 | * | 5.1 | 9.7 | – | |
| Aresco | 28 July | 15.3 | 6.9 | 8.2 | 21.1 | 36.1 | * | 3.6 | 8.8 | – | |
| Graciela Römer & Asoc. | 1 August | 15.9 | 6.3 | 5.5 | 9.9 | 40.4 | * | 4.1 | 1.0 | 16.9 | |
| Opinión Autenticada | 1 August | 19.7 | 5.2 | 4.0 | 13.1 | 38.1 | * | 6.1 | 1.1 | 12.0 | |
| Equis | 28 August | 8.2 | 13.4 | 1.4* | 7.6 | 52.1 | * | 9.9 | 4.8 | 2.6 | |
| Nueva Comunicación | 12 September | 7.6 | 15.8 | 1.5* | 9.1 | 51.7 | * | 8.8 | 1.7 | 3.8 | |
| OPSM | 2 October | 9.8 | 13.9 | 3.5* | 5.7 | 45.7 | * | 8.5 | 2.5 | 10.4 | |
| Analogías | 3 October | 9.0 | 13.2 | 1.1* | 6.8 | 52.9 | * | 5.2 | -- | 12.0 | |
| Equis | 7 October | 7.8 | 14.8 | 1.4* | 6.5 | 52.6 | * | 10.6 | 1.1 | 4.8 | |
| Giacobbe & Asoc. | 21 October | 9.1 | 16.6 | * | 7.9 | 53.1 | * | 10.2 | 3.1 | -- |
* Withdrew
Favourability
A poll conducted by Mora y Araujo for Ipsos on 28 September revealed favourability and unfavourability ratings for six of the seven candidates appearing on the general election ballot.[15]
| Candidate | Favorable | Unfavorable | Neither/NR | Net Approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ricardo Alfonsín | 29% | 61% | 10% | −32% |
| Hermes Binner | 39% | 32% | 29% | 7% |
| Elisa Carrió | 15% | 74% | 11% | −59% |
| Eduardo Duhalde | 21% | 74% | 5% | −53% |
| Cristina Fernández de Kirchner | 65% | 33% | 2% | 32% |
| Alberto Rodríguez Saá | 40% | 46% | 14% | −6% |
Notes
- Total seats for Federal Peronism.
References
- (in Spanish) Ley de Democratización de la Representación Política, la Transparencia y la Equidad Electoral
- "Sabbatella y el FPV tendrán una misma lista de diputados en la Provincia". M24 Digital. Archived from the original on 18 June 2011.
- "Con más críticas, Carrió se aleja del Acuerdo Cívico". La Nación.
- "Movimiento Proyecto Sur se fraccionó entre Binner y Pino Solanas". M24 Digital. Archived from the original on 11 July 2011.
- "Alfonsín picks economist Javier González Fraga as running mate". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Argentine ex-leader Kirchner dies". Al Jazeera News.
- "Argentine head set for poll blow". BBC News. 29 June 2009.
- "Poliarquía: Cristina comenzó a bajar en las encuestas". Urgente24. Archived from the original on 5 May 2011. Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- "La imagen positiva de Fernández sube a niveles de comienzos de su Gobierno". Agencia EFE.
- "Cristina, en todas las encuestas, gana cómoda en primera vuelta". Diagonales. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- "Will she, won't she?". The Economist. 26 May 2011.
- "CFK announces she will be seeking reelection". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Cristina eligió a Boudou como su compañero de fórmula". Clarín.
- "Fernández wins Argentina primary, looks poised for re-election". CNN. Archived from the original on 16 September 2011. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- "Cómo será el voto a la oposición". La Nación.
- "Eduardo Duhalde anunció a su posible Gabinete". TN Noticias.
- "El PRO iría con Solá de candidato". La Razón. Archived from the original on 29 August 2012. Retrieved 30 May 2011.
- "Duhalde beats Rodríguez Saá in dissident PJ primaries by narrow margin". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Eduardo Duhalde officially launches presidential campaign". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Vernet confirms he will be Rodríguez Saá's running mate". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Felipe Solá descartó pelear por la Casa Rosada". La Nación.
- "Rodríguez Saá y De Narváez, juntos y de campaña". El Argentino. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- "de Narváez sería el gobernador de Alfonsín". El Reacado.
- "Frente progresista ya ensaya fórmula Binner-Stolbizer". Ámbito Financiero.
- "Optimismo de UDESO de cara a las elecciones de octubre". La Voz.
- "Binner officializes presidential candidacy, Morandini running mate". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Sondeos pronostican amplio triunfo de Cristina Fernández". Milenio.
- "Se lanzó la candidatura de Carrió-Pérez". Coalición Cívica. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011.
- "'After 18 years, I no longer have power,' Carrió says". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Pino Solanas said that in a Filmus-Macri ballotage "we probably would leave freedom of conscience" to the voters". M24 Digital. Archived from the original on 4 April 2012.
- "Proyecto Sur breaks off with Progressive Front". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Argumedo, Pastore and Bonacci become the first casualties in the presidential race". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Altamira: 'We've reached our aim', dedicates it to Mariano Ferreyra". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Recorriendo las Elecciones de 1983 a 2013 - Presidenciales PASO". Dirección Nacional Electoral.
- "Elecciones Nacionales: Presidente". Dirección Nacional Electioral. Archived from the original on 6 September 2012.
- "Historia Electoral Argentina" (PDF). Ministerio del Interior.
- "Argentine president wins landslide re-election". NBC News.
- "Recorriendo las Elecciones de 1983 a 2013 - Presidenciales". Dirección Nacional Electoral.
- "Resultados Nacionales 2011 Total País" (PDF). Ministry of the Interior. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 January 2012.
- "Cómo están las cámaras antes de las elecciones". Clarín.
- "Congreso: final para el Grupo A y la presidencia opositora en el Senado". Tiempo Argentino. Archived from the original on 26 October 2011.
- "Recorriendo las Elecciones de 1983 a 2013 - Diputados Nacionales". Dirección Nacional Electoral.
- "Elecciones en Argentina 2011: Cargos a renovar". Atlas Electoral de Andy Tow. Archived from the original on 29 August 2012. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- "Recorriendo las Elecciones de 1983 a 2013 - Senadores Nacionales". Dirección Nacional Electoral.
- "¿Qué se vota?". Clarín.
- (in Spanish) Decreto 17.262/59
- "El kirchnerismo se impuso en todas las gobernaciones menos en San Luis". Clarín.
- "El Partido Socialista impulsará a "Binner Presidente"". Agencia Fe. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011.
- "Bonfatti: the people of Santa Fe casted a punishing vote". Buenos Aires Herald.
- "Macri re-elected BA Mayor after defeating Filmus by 28.5 points". Buenos Aires Herald.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 2011 Argentine general election. |
- (in Spanish) Dirección Nacional Electoral – Elecciones Nacionales 2011 – Ministry of Interior of Argentina.
- Andy Tow's Argentina Electoral Atlas (in Spanish)





