Ahtna language
Ahtna or Ahtena (/ˈɑːtnə/, from 'At Na' "Copper River")[5] is the Na-Dené language of the Ahtna ethnic group of the Copper River area of Alaska. The language is also known as Copper River or Mednovskiy.
| Ahtna | |
|---|---|
| Koht’aene Kenaege', Atnakenaege’ | |
| Native to | United States |
| Region | Alaska (Copper River region) |
| Ethnicity | 500 Ahtna (1995)[1] |
Native speakers | 45 (2015 census)[1] 30 (2011)[2] |
| Latin (Ahtna alphabet) | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | aht |
| Glottolog | ahte1237 Ahtena |
| ELP | Ahtna[4] |
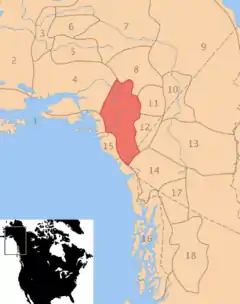 Pre-contact distribution of Ahtna | |
| Coordinates: 62°10′N 143°49′W | |
The Ahtna language consists of four different dialects: Upper, Central, Lower, and Western. Three of the four are still spoken today. Ahtna is closely related to Dena'ina.
The similar name "Atnah" occurs in the journals of Simon Fraser and other early European diarists in what is now British Columbia as a reference to the Tsilhqot'in people, another Northern Athapaskan group.
Classification
Eyak-Athabaskan, Athabaskan, Northern Athabaskan.[6]
History
Ahtna is one of the eleven Athabaskan languages native to Alaska. The Ahtna language comes from the proto-Athabaskan language possibly evolving 5,000 to 10,000 years ago when humans migrated from Eurasia to The New World over the Bering Sea floor (Beringia) when it was dried up and exposed creating a natural land bridge. Many indigenous Native American languages are to have derived from this proto-Athabaskan language, Navajo is one language derived from this early language and consequently Ahtna and Navajo have many similarities. The Ahtna Language has changed very much and very often, it is still changing today. Within the past century more than one hundred words have made their way into the Ahtna vocabulary mostly due to Euro-American influences. Contact with Russians influenced the Ahtna language with many Russian loanwords being introduced. With contact from English speakers, especially recently, English words have also been introduced. Some words are also borrowed from the Alaskan Tlingit and Alutiiq native people.[5]
Geographic distribution
The Ahtna region consists of the Copper River Basin and the Wrangell Mountains. The Ahtna Region is bordered by the Nutzotin river in the Northeast and the Alaska Range in the North. The Talkeetna Mountains are to the Chugach Mountains are to the South.[7] The Upper Ahtna live on the upper portion of the Copper River, The Middle or Central Ahtna live slightly down river from there, The Lower Ahtna live near the mouth of the Copper River, which opens into the Gulf of Alaska, and the Western Ahtna live to the West of the River.
The Ahtna people live on and near traditional villages. There are eight villages within the Ahtna Region: Cantwell, Chistochina, Chitina, Copper Center, Gakona, Gulkana, Mentasta and Tazlina' They are all recognized federally.[8]
Use and revitalization efforts
There are 30 elderly speakers out of a population of 500, and the language is facing extinction.
The subsistence and fishing-rights activist Katie John (1915–2013) of Mentasta helped develop an Ahtna alphabet in the 1970s[9] and recorded a pronunciation guide of the Mentasta Dialect.[10] [11]
In 2012 a facing-bilingual collection of poetry in Ahtna and English, The Indian Prophet, was published by poet John Smelcer.
In a revitalization program, the Ya Ne Dah Ah School in Sutton, Alaska teaches the Ahtna language as a part of its curriculum.[12][13]
As of 2010, a digital archiving project of Ahtna was underway.[14]
Dialects and bands
There are four main dialect divisions and eight bands (tribal unions):[15]
- Lower Ahtna (own name Atnahwt'aene)
- Chitina/Taral Band
- Tonsina/Klutina Band
- Central Ahtna or Middle Ahtna (own name Dan'ehwt'aene)
- Gulkona/Gakona Band
- Western Ahtna (own name Tsaay Hwt'aene)
- Tyone/Mendeltna Band
- Cantwell/Denali Band
- Upper Ahtna (own name Tatl'ahwt'aene)
Vocabulary comparison
The comparison of some animal names in the three Athabaskan languages:[17]
| Ahtna | Tanacross | Lower Tanana | meaning |
| udzih | wudzih | bedzeyh | caribou |
| ggax | gah | gwx | rabbit |
| tsa' | tsá' | tso' | beaver |
| dzen | dzenh | dzenh | muskrat |
| niduuyi | niidûuy | niduuy | lynx |
| debae | demee | deba | Dall sheep |
| sos | shos | sresr | bear |
| dliigi | dlêg | dlega | squirrel |
| łuk'ae | łuk'a | łuk'a | salmon |
Phonology
Athabaskan languages are primarily prefixing. Many prefixes are presented together. There is limited suffixation and often one word has as much meaning as an English language sentence. Verbs are very complex therefore creating many different meanings or analysis of verbs. Some verbs include syntactic principles in addition to and/or replacement of morphological principles when constructing a word.[18]
Consonants
This consonant chart is in Kari's practical orthography and phonology and is taken from the Ahtna Athabaskan Dictionary.[19]
| Labial | Alveolar | Lateral | Alveo- palatal |
Front Velar |
Back Velar |
Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stops | Plain | b [p] | d [t] | dl [tɬ] | dz [ts] | g [k] | gg [q] | ' [ʔ] |
| Aspirated | p [pʰ] | t [tʰ] | tl [tɬʰ] | ts [tsʰ] | c [kʰ] | k [qʰ] | ||
| Ejective | t' [tʼ] | tl' [tɬʼ] | ts' [tsʼ] | c' [kʼ] | k' [qʼ] | |||
| Fricatives | Voiced | v [v] | l [l] | z [z] | y [ɣ] | gh [ʁ] | ||
| Voiceless | hw [hʷ] | ł [ɬ] | s [s] | yh [x] | x [χ] | h [h] | ||
| Nasals | m [m] | n [n] | ng [ŋ] |
Vowels
This vowel chart is in Kari's practical orthography and phonology and is taken from the Ahtna Athabaskan Dictionary.[20]
| Long | Short | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Front | Back | Front | Back | |
| High | ii [iː] | uu [uː] | i [ɪ] | u [ʊ] |
| Mid | oo [oː] | e [ɛ] | o [ɔ] | |
| Low | ae [æ] | aa [ɑː] | a [ɐ] | |
Because of the different Ahtna dialects, people may say the same words differently.
Grammar
Possession is indicated by prefixes. s- 'my', u- or yu'- 'his/her', ne- 'our'; as in snaan 'my mother', unaan (or yu'naan) 'his/her mother', nenaan 'our mother'.[5]
Verb Themes
Verbs are primarily prefixing. There are often six or more prefixes before the stem and then one or more suffixes. (1a) displays a surface form in Ahtna spelling while (1b) is the verb theme. Three prefixes are present that have to be listed with the stem to make up the form. Anything adjacent in a verb theme can be separated by morphemes in the forms surface.[18] Verb themes display what elements should be listed in a dictionary for a speaker to be able to reconstruct the verb. '#' displays an important word-internal boundary known as a disjunct boundary. '+' indicates a morpheme boundary.[18]
(1) a. Tadeldlo'
'Water is gurgling.' (Surface form)
b. ta # d+ l+ dlok'
into water # qualifier+ classifier+ 'laugh
(Lexical listing: verb theme)
In the Ahtna language the verb typically goes after the noun.
Noun Modification
Modifiers usually go after the noun it is modifying in the Ahtna Language. Smelcer (1998) provides this example in his Ahtna Language Dictionary: "as in the word for Raven (the deity, trickster figure), which in Ahtna is called Saghani Ggaay (literally "Little Raven"). Saghani is a noun for the word for the species of raven (Corax corax), while ggaay means "little or small." Thus, the syntax is actually expressed as "Raven little." Consider other words such as nen ten, the word for permafrost (literally "frozen ground"). The word nen means "land or ground"; the modifier ten means "frozen." Thus, the syntax is "Land frozen." Other examples include the word for Denali/Mount McKinley, which is Dghelaay Ce'e (literally "Big Mountain"). The word dghelaay means "mountain," while ce'e means "big, biggest, or large." Thus, the syntax is "Mountain Biggest." Another example using ce'e is the place name for Lake Susitna, which is Ben Ce'e (literally "Big Lake"). In this case, the noun ben is a general term meaning "lake" modified by the word for "big or large."[5]
References
- Ahtna at Ethnologue (21st ed., 2018)
- Directional Reference, Discourse, and Landscape in Ahtna. Berez, Andrea L. (2011) "There are about thirty first-language speakers still alive today (all 60+ years of age)"
- https://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2014/04/21/305688602/alaska-oks-bill-making-native-languages-official
- Endangered Languages Project data for Ahtna.
- Smelcer, John (1998). Ahtna Noun Dictionary and Pronunciation Guide 2nd Edition. United States of America: The Ahtna Heritage Foundation. ISBN 0-9656310-2-8.
- "Athena".
- "Ahtna Land and Resource Department | Ahtna". ahtna-inc.com. Retrieved 2016-05-01.
- "Ahtna Villages | Ahtna". ahtna-inc.com. Retrieved 2016-05-01.
- "Fishing Rights, Language and Culture Advocate, Katie John, Walks On". Indian Country Today Media Network. 2013-06-03. Retrieved 2013-07-07.
- "Ahtna Language, Mentasta Dialect, Recorded by Katie John". Yukon Native Language Centre. 2008. Archived from the original on 2017-05-20. Retrieved 2013-07-07.
- Mary Beth Smetzer, "Katie John, advocate for indigenous Rights, Dies", Fairbanks News-Miner, May 31, 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2014.
- "Case Studies, The Harvard Project on American Indian Economic Development". Archived from the original on 2012-06-24. Retrieved 2012-09-09.
- "Ahtna Athabascan Language Rejuvenation and Curriculum Program". Chickaloon Village Traditional Council. Archived from the original on 2013-05-30. Retrieved 2013-07-07.
- "Digital Archive Project". Ahtna Heritage Foundation Cultural Center Projects. Archived from the original on 2011-03-24. Retrieved 2013-07-07.
- "Native American Tribal Arts & Architecture, SUBARCTIC ARTS". Archived from the original on 2012-09-29. Retrieved 2011-03-18.
- Ahtna language, Chistochina Dialect Archived 2012-11-11 at the Wayback Machine
- "Ahtna Noun Dictionary" by John E. Smelcer (2009)
- Tuttle, Siri G. (2008). "Phonetics and Word Definition in Ahtna". Linguistics. doi:10.1515/LING.2008.015.
- Kari, James (1990). Ahtna Ahtabaskan Dictionary. Fairbanks: Alaska Native Language Center. p. 12. ISBN 1-55500-033-9.
- Kari, James (1990). Ahtna Athabaskan Dictionary. Fairbanks: Alaska Native Language Center. p. 12. ISBN 1-55500-033-9.