Athabaskan languages
Athabaskan (also spelled Athabascan, Athapaskan or Athapascan, and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific Coast and Southern (or Apachean). Kari and Potter 2010:10 place the total territory of the 53 Athabaskan languages at 4,022,000 square kilometres (1,553,000 sq mi).
| Athabaskan | |
|---|---|
| Dene | |
| Geographic distribution | Western North America |
| Linguistic classification | Dené-Yeniseian?
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Athabaskan |
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | ath |
| Glottolog | atha1247 |
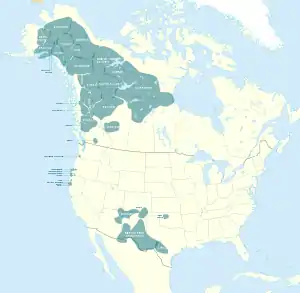 Geographic distribution of the Athabaskan languages | |
Chipewyan is spoken over the largest area of any North American native language, while Navajo is spoken by the largest number of people of any native language north of Mexico.
Name
The word Athabaskan is an anglicized version of a Cree language name for Lake Athabasca (Cree: Āðapāskāw "[where] there are reeds one after another") in Canada. Cree is one of the Algonquian languages and therefore not itself an Athabaskan language.[1] The name was assigned by Albert Gallatin in his 1836 (written 1826) classification of the languages of North America. He acknowledged that it was his choice to use this name for the language family and associated peoples, writing:
I have designated them by the arbitrary denomination of Athabascas, which derived from the original name of the lake.
— Albert Gallatin, 1836:116–7
The four spellings—"Athabaskan", "Athabascan", "Athapaskan", and "Athapascan"—are in approximately equal use. Particular communities may prefer one spelling over another (Krauss 1987). For example, the Tanana Chiefs Conference and Alaska Native Language Center prefer the spelling "Athabascan".[2] Ethnologue uses "Athapaskan" in naming the language family and individual languages.[3]
Although the term Athabaskan is prevalent in linguistics and anthropology, there is an increasing trend among scholars to use the terms Dené and Dené languages, which is how many of their native speakers identify it. They are applying these terms to the entire language family. For example, following a motion by attendees in 2012, the annual Athabaskan Languages Conference changed its name to the Dené Languages Conference.[4]
Languages
Linguists conventionally divide the Athabaskan family into three groups, based on geographic distribution:
- Northern Athabaskan languages
- Pacific Coast Athabaskan languages
- Southern Athabaskan languages or "Apachean"
The 32 Northern Athabaskan languages are spoken throughout the interior of Alaska and the interior of northwestern Canada in the Yukon and Northwest Territories, as well as in the provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba. Five Athabaskan languages are official languages in the Northwest Territories, including Chipewyan (Dënesųłıné), Dogrib or Tłı̨chǫ Yatıì, Gwich'in (Kutchin, Loucheux), and the Northern and Southern variants of Slavey.
The seven or more Pacific Coast Athabaskan languages are spoken in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. These include Applegate, Galice, several Rogue River area languages, Upper Coquille, Tolowa, and Upper Umpqua in Oregon; Eel River, Hupa, Mattole–Bear River, and Tolowa in northern California; and possibly Kwalhioqua-Clatskanie in Washington.
The seven Southern Athabaskan languages are isolated by considerable distance from both the Pacific Coast languages and the Northern languages. Reflecting an ancient migration of peoples, they are spoken by Native Americans in the American Southwest and the northwestern part of Mexico. This group comprises the six Southern Athabaskan languages and Navajo.
The following list gives the Athabaskan languages organized by their geographic location in various North American states and provinces (including some languages that are now extinct). Speakers of several languages, such as Navajo and Gwich'in, span the boundaries between different states and provinces. These languages are repeated by location in this list. For alternative names for the languages, see the classifications given later in this article.
- Alaska: Ahtna, Deg Hit'an, Dena'ina/Tanaina, Gwich'in/Kutchin, Hän, Holikachuk, Koyukon, Lower Tanana, Middle Tanana, Tanacross, Upper Tanana, Upper Kuskokwim
- Yukon Territory: Gwich'in/Kutchin, Hän, Kaska, Mountain, Tagish, Northern Tutchone, Southern Tutchone, Upper Tanana
- Northwest Territories: Bearlake, Dëne Sųłiné/Chipewyan, Gwich'in, Hare, Mountain, Slavey, Tłįchǫ Yatiì/Dogrib
- Nunavut: Dëne Sųłiné
- British Columbia: Babine–Witsuwit'en, Bearlake, Beaver, Chilcotin, Dakelh/Carrier, Hare, Kaska, Mountain, Nicola Athapaskan, Sekani/Tsek'ene, Slavey, Tagish, Tahltan, Tsetsaut
- Alberta: Beaver, Dëne Sųłiné, Slavey, Tsuut'ina/Sarcee
- Saskatchewan: Dëne Sųłiné
- Washington: Kwalhioqua-Clatskanai (Willapa, Suwal)
- Oregon: Applegate, Clatskanie, Galice, Rogue River (Chasta Costa, Euchre Creek, Tututni, Upper Coquille), Tolowa, Upper Umpqua
- Northern California: Eel River, Hupa, Mattole–Bear River, Tolowa
- Utah: Navajo
- Colorado: Jicarilla, Navajo
- Arizona: Chiricahua, Navajo, Western Apache
- New Mexico: Chiricahua, Mescalero, Jicarilla, Lipan, Navajo
- Texas: Mescalero, Lipan
- Oklahoma: Chiricahua, Plains Apache
- Northwestern Mexico: Chiricahua
Alaskan Athabaskan languages
| Language | Population | Speakers | Percent Speakers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahtna | 500 | 80 | 16.0% |
| Dena'ina | 1,400 | 980 | 70.0%[5] |
| Deg Xinag | 275 | 40 | 14.6% |
| Eyak | 50 | 0 | 0.0% |
| Gwich'in | 1,100 | 300 | 27.3% |
| Hän | 50 | 12 | 24.0% |
| Holikachuk | 200 | 12 | 6.0% |
| Koyukon | 2,300 | 300 | 13.0% |
| Tanana | 380 | 30 | 7.9% |
| Tanacross | 220 | 65 | 29.6% |
| Upper Kuskokwim | 160 | 40 | 25.0% |
| Upper Tanana | x | x | x |
| Source: Information in this table was retrieved from the Alaska Native Language Center.[6] | |||
External classification
Eyak and Athabaskan together form a genealogical linguistic grouping called Athabaskan–Eyak (AE) – well demonstrated through consistent sound correspondences, extensive shared vocabulary, and cross-linguistically unique homologies in both verb and noun morphology.
Tlingit is distantly related to the Athabaskan–Eyak group to form the Na-Dene family, also known as Athabaskan–Eyak–Tlingit (AET). With Jeff Leer's 2010 advances, the reconstructions of Na-Dene (or Athabascan–Eyak–Tlingit) consonants, this latter grouping is considered by Alaskan linguists to be a well-demonstrated family. Because both Tlingit and Eyak are fairly remote from the Athabaskan languages in terms of their sound systems, comparison is usually done between them and the reconstructed Proto-Athabaskan language. This resembles both Tlingit and Eyak much more than most of the daughter languages in the Athabaskan family.
Although Ethnologue still gives the Athabaskan family as a relative of Haida in their definition of the Na-Dene family, linguists who work actively on Athabaskan languages discount this position. The Alaska Native Language Center, for example, takes the position that recent improved data on Haida have served to conclusively disprove the Haida-inclusion hypothesis. Haida has been determined to be unrelated to Athabaskan languages.
A symposium in Alaska in February 2008 included papers on the Yeniseian and Na-Dené families. Edward Vajda of Western Washington University summarized ten years of research, based on verbal morphology and reconstructions of the proto-languages, indicating that these languages might be related.[7]
Internal classification
The internal structure of the Athabaskan language family is complex, and its exact shape is still a hotly debated issue among experts. The conventional three-way split into Northern, Pacific Coast, and Southern is essentially based on geography and the physical distribution of Athabaskan peoples rather than sound linguistic comparisons. Despite this inadequacy, current comparative Athabaskan literature demonstrates that most Athabaskanists still use the three-way geographic grouping rather than any of the proposed linguistic groupings given below, because none of them has been widely accepted. This situation will presumably change as both documentation and analysis of the languages improves.
Overview
Besides the traditional geographic grouping described previously, there are a few comparatively based subgroupings of the Athabaskan languages. Below the two most current viewpoints are presented.
The following is an outline of the classification according to Keren Rice, based on those published in Goddard (1996) and Mithun (1999). It represents what is generously called the "Rice–Goddard–Mithun" classification (Tuttle & Hargus 2004:73), although it is almost entirely due to Keren Rice.
- Southern Alaska (Dena'ina, Ahtna)
- Central Alaska–Yukon (Deg Hit'an, Holikachuk/Kolchan, Koyukon, Upper Kuskokwim, Lower Tanana, Tanacross, Upper Tanana, N. Tutchone, S. Tutchone, Gwich'in, Hän)
- Northwestern Canada (Tagish, Tahltan, Kaska, Sekani, Dunneza/Beaver, Slavey, Mountain, Bearlake, Hare, Tłįchǫ Yat'iì/Dogrib, Dëne Sųłiné/Chipewyan)
- Tsetsaut
- Central British Columbia (Babine–Witsuwit'en, Dakelh/Carrier, Chilcotin, Nicola?)
- Tsuut'ina/Sarsi
- Kwalhioqua–Clatskanai
- Pacific Coast Athabaskan (Upper Umpqua, Tututni, Galice–Applegate, Tolowa, Hupa, Mattole, Eel River, Kato)
- Apachean (Navajo, White Mountain Apache, Tonto Apache, San Carlos Apache, Mescalero–Chiricahua, Jicarilla, Lipan, Plains)
Branches 1–7 are the Northern Athabaskan (areal) grouping. Kwalhioqua–Clatskanai (#7) was normally placed inside the Pacific Coast grouping, but a recent consideration by Krauss (2005) does not find it very similar to these languages.
A different classification by Jeff Leer is the following, usually called the "Leer classification" (Tuttle & Hargus 2004:72–74):
- Alaskan (Ahtna, Dena'ina, Deg Hit'an, Koyukon, Holikachuk/Kolchan, Lower Tanana, Tanacross, Upper Tanana, Gwich'in, Hän)
- Yukon (Tsetsaut, N. Tutchone, S. Tutchone, Tagish, Tahltan, Kaska, Sekani, Dunneza/Beaver)
- British Columbia (Babine–Witsuwit'en, Dakelh/Carrier, Chilcotin)
- Eastern (Dëne Sųłiné/Chipewyan, Slavey, Mountain, Bearlake, Hare, Tłįchǫ Yat'iì/Dogrib)
- Southerly Outlying (Tsuut'ina/Sarsi, Apachean, Pacific Coast Athabaskan, Kwalhioqua–Tlatskanai)
Neither subgrouping has found any significant support among other Athabaskanists. Details of the Athabaskan family tree should be regarded as tentative. As Tuttle and Hargus put it, "we do not consider the points of difference between the two models ... to be decisively settled and in fact expect them to be debated for some time to come." (Tuttle & Hargus 2004:74)
The Northern group is particularly problematic in its internal organization. Due to the failure of the usual criteria of shared innovation and systematic phonetic correspondences to provide well-defined subgroupings, the Athabaskan family – especially the Northern group – has been called a "cohesive complex" by Michael Krauss (1973, 1982). Therefore, the Stammbaumtheorie or family tree model of genetic classification may be inappropriate. The languages of the Southern branch are much more homogeneous and are the only clearly genealogical subgrouping.
Debate continues as to whether the Pacific Coast languages form a valid genealogical grouping, or whether this group may instead have internal branches that are tied to different subgroups in Northern Athabaskan. The position of Kwalhioqua–Clatskanai is also debated, since it may fall in either the Pacific Coast group – if that exists – or into the Northern group. The records of Nicola are so poor – Krauss describes them as "too few and too wretched" (Krauss 2005) – that it is difficult to make any reliable conclusions about it. Nicola may be intermediate between Kwalhioqua–Tlatskanai and Chilcotin.
Similarly to Nicola, there is very limited documentation on Tsetsaut. Consequently, it is difficult to place it in the family with much certainty. Athabaskanists have concluded that it is a Northern Athabaskan language consistent with its geographical occurrence, and that it might have some relation to its distant neighbor Tahltan. Tsetsaut, however, shares its primary hydronymic suffix ("river, stream") with Sekani, Beaver, and Tsuut'ina – PA *-ɢah – rather than with that of Tahltan, Tagish, Kaska, and North and South Tutchone – PA *-tuʼ (Kari 1996; Kari, Fall, & Pete 2003:39). The ambiguity surrounding Tsetsaut is why it is placed in its own subgroup in the Rice–Goddard–Mithun classification.
For detailed lists including languages, dialects, and subdialects, see the respective articles on the three major groups: Northern Athabaskan, Pacific Coast Athabaskan, Southern Athabaskan. For the remainder of this article, the conventional three-way geographic grouping will be followed except as noted.
Northern Athabaskan
The Northern Athabaskan languages are the largest group in the Athabaskan family, although this group varies internally about as much as do languages in the entire family. The urheimat of the Athabaskan family is most likely in the Tanana Valley of east-central Alaska. There are many homologies between Proto-Athabaskan vocabulary and patterns reflected in archaeological sites such as Upward Sun, Swan Point and Broken Mammoth (Kari 2010). The Northern Athabaskan group also contains the most linguistically conservative languages, particularly Koyukon, Ahtna, Dena'ina, and Dakelh/Carrier (Leer 2008).
- Southern Alaskan subgroup
- Central Alaska–Yukon subgroup
- 3. Deg Xinag (also known as Deg Hitʼan, Ingalik (deprecated))
- 4. Holikachuk (also known as Innoko)
- 5. Koyukon (also known as Denaakkʼe, Tenʼa)
- 6. Upper Kuskokwim (also known as Kolchan)
- 7. Lower Tanana and Middle Tanana (also known as Tanana)
- 8. Tanacross
- 9. Upper Tanana
- 10. Southern Tutchone
- 11. Northern Tutchone
- 12. Gwich'in (also known as Kutchin, Loucheux, Tukudh)
- 13. Hän (also known as Han)
- Northwestern Canada subgroup
- A. Tahltan–Tagish–Kaska (also known as "Cordilleran")
- 17. Sekani (also known as Tsekʼehne)
- 18. Dane-zaa (also known as Beaver)
- B. Slave–Hare
- 19. Slavey (also known as Southern Slavey)
- 20. Mountain (Northern Slavey)
- 21. Bearlake (Northern Slavey)
- 22. Hare (Northern Slavey)
- 23. Dogrib (also known as Tłįchǫ Yatiì)
- 24. Dene Suline (also known as Chipewyan, Dëne Sųłiné, Dene Soun'liné)
Very little is known about Tsetsaut, and for this reason it is routinely placed in its own tentative subgroup.
- Tsetsaut subgroup
- 25. Tsetsaut (also known as Tsʼetsʼaut, Wetalh)
- Central British Columbia subgroup (also known as "British Columbian" in contrast with "Cordilleran" = Tahltan–Tagish–Kaska)
- 26. Babine–Witsuwit'en (also known as Northern Carrier, Bulkley Valley/Lakes District)
- 27. Dakelh (also known as Carrier)
- 28. Chilcotin (also known as Tsilhqot'in)
The Nicola language is so poorly attested that it is impossible to determine its position within the family. It has been proposed by some to be an isolated branch of Chilcotin.
- 29. Nicola (also known as Stuwix, Similkameen)
- Sarsi subgroup
- 30. Tsuut'ina (also known as Sarcee, Sarsi, Tsuu T'ina)
The Kwalhioqua–Clatskanie language is debatably part of the Pacific Coast subgroup, but has marginally more in common with the Northern Athabaskan languages than it does with the Pacific Coast languages (Leer 2005). It thus forms a notional sort of bridge between the Northern Athabaskan languages and the Pacific Coast languages, along with Nicola (Krauss 1979/2004).
- Kwalhioqua–Clatskanie subgroup (also called Lower Columbia Athapaskan)
- 31. Kwalhioqua–Clatskanie (also known as Kwalhioqua–Tlatskanie or Kwalhioqua-Tlatskanai)
Pacific Coast Athabaskan
- California Athabaskan subgroup
- 32. Hupa (also known as Hupa-Chilula, Chilula, Whilkut)
- 33. Mattole–Bear River
- 34. Eel River (also known as Wailaki, Lassik, Nongatl, Sinkyone)
- 35. Kato (also known as Cahto)
- Oregon Athabaskan subgroup
- 36. Upper Umpqua (also known as Etnemitane)
- 37a. Lower Rogue River and Upper Coquille (also known as Tututni, Chasta Costa, Euchre Creek and Coquille)
- 37b. Upper Rogue River (also known as Galice/Taltushtuntede, Applegate/Dakubetede)
- 38. Tolowa (also known as Smith River, Chetco, Siletz Dee-ni)
Southern Athabaskan (Apachean)
- Plains Apache subgroup
- 39. Plains Apache (also known as Kiowa-Apache)
- Western Apachean subgroup
- A. Chiricahua–Mescalero
- 40. Chiricahua
- 41. Mescalero
- 42. Navajo (also known as Navaho)
- 43. Western Apache (also known as Coyotero Apache)
- Eastern Apachean subgroup
Sicoli & Holton (2014)
Using computational phylogenetic methods, Sicoli & Holton (2014)[8] proposed the following classification for the Athabaskan languages based exclusively on typological (non-lexical) data. However, this phylogenetic study was criticized as methodologically flawed by Yanovich (2020), since it did not employ sufficient input data to generate a robust tree that does not depend on the initial choice of the "tree prior", i.e. the model for the tree generation.[9]
- (Yeniseian)
- (Tlingit-Eyak)
- South Pacific Coast Athabaskan (California)
- (unnamed clade)
- Tsetsaut
- Upper Kuskokwim
- Ahtna
- Dena'ina
- West Alaska (Koyukon)
- North Pacific Coast (Oregon)
- Alaska-Canada-2
- Plains-Apachean
- Alaska-Canada-1
- Tanana
- Northwestern Canada
- Hän
- South Slavey, Kaska
- Dene, Northern Tutchone, Southern Tutchone
Proto-Athabaskan
Proto-Athabaskan is the reconstructed ancestor of the Athabaskan languages.
See also
- Broken Slavey, a trade language based on Slavey, French, and Cree.
- Dené–Yeniseian languages
- Loucheux Pidgin, another trade language based on at least Dëne Sųłiné (Chipewyan) and Gwich'in (Loucheux).
References
- Bright, William (2004). Native American Place Names of the United States. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, pg. 52
- Alaska Native Language Center: "The Name Athabascan" Archived June 25, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- Ethnologue: Language Family Trees – Athapaskan
- "Dené (Athabaskan) Languages Conference". Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- Dena'ina#Language
- Alaska Native Language Center (ANLC). University of Alaska Fairbanks.
- Kari, James M.; Potter, Ben Austin (2011). The Dene-Yeniseian Connection: Anthropological Papers of the University of Alaska. Alaska Native Language Center. ISBN 978-1-55500-112-4.
- Sicoli, Mark A.; Holton, Gary (2014). "Linguistic Phylogenies Support Back-Migration from Beringia to Asia". PLOS ONE. 9 (3): e91722. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...991722S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0091722. PMC 3951421. PMID 24621925.
- Yanovich, Igor (2020). "Phylogenetic linguistic evidence and the Dene-Yeniseian homeland". Diachronica. 37 (3): 410–446. doi:10.1075/dia.17038.yan.
Bibliography
- Boas, Franz. 1917. Grammatical notes on the language of the Tlingit Indians. (University Museum Anthropological Publications 8.1). Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania.
- California Indian Library Collections Project. California Athapaskan Bibliography
- Campbell, Lyle. 1997. American Indian languages: The historical linguistics of Native America. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-509427-1.
- Cook, Eung-Do. 1981. Athabaskan linguistics: Proto-Athapaskan phonology. Annual Review of Anthropology 10. 253–273.
- Cook, Eung-Do. 1992. Athabaskan languages. In William Bright (ed.), International encyclopedia of linguistics, 122–128. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-505196-3.
- Cook, Eung-Do & Keren Rice. 1989. Introduction. In Eung-Do Cook & Keren Rice (eds.), Athapaskan linguistics: Current perspectives on a language family, 1–61. (Trends in Linguistics, State-of-the-art Reports 15). Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 0-89925-282-6.
- Golla, Victor. 2011. California Indian Ianguages. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Hoijer, Harry. 1938. The southern Athapaskan languages. American Anthropologist 40(1). 75–87.
- Hoijer, Harry. 1956. The Chronology of the Athapaskan languages. International Journal of American Linguistics 22(4). 219–232.
- Hoijer, Harry. 1963. The Athapaskan languages. In Harry Hoijer (ed.), Studies in the Athapaskan languages, 1–29. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Hoijer, Harry (ed.). 1963. Studies in the Athapaskan languages. (University of California publications in linguistics 29). Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Hoijer, Harry. 1971. The position of the Apachean languages in the Athpaskan stock. In Keith H. Basso & M. E. Opler (eds.), Apachean culture history and ethnology, 3–6. (Anthropological papers of the University of Arizona 21). Tucson: University of Arizona Press.
- Hymes, Dell H. 1957. A note on Athapaskan glottochronology. International Journal of American Linguistics 23(4). 291–297.
- Kari, James. 1989. Affix positions and zones in the Athapaskan verb complex: Ahtna and Navajo. International Journal of American Linguistics 55(4). 424–454.
- Kari, James. 1996. A Preliminary View of Hydronymic Districts in Northern Athabaskan Prehistory. Names 44:253-271.
- Kari, James. 2010. The concept of geolinguistic conservatism in Na-Dene prehistory . In The Dene–Yeniseian Connection. (Anthropological Papers of the University of Alaska). Vol. 5, new series. pp. 194–222.
- Kari, James, James A. Fall, & Shem Pete. 2003. Shem Pete's Alaska: The territory of the Upper Cook Inlet Denaʼina. Fairbanks, AK: University of Alaska Press. ISBN 1-889963-56-9 (cloth); ISBN 1-889963-57-7 (pbk.).
- Kari, James and Ben A. Potter. (2010). The Dene–Yeniseian Connection, ed. by J. Kari and B. Potter, 1–24. (Anthropological Papers of the University of Alaska), new series, vol. 5. Fairbanks: University of Alaska Fairbanks, Department of Anthropology.
- Kari, James and Ben A. Potter. (2010). The Dene-Yeniseian Connection: Bridging Asian and North America. In The Dene–Yeniseian Connection, ed. by J. Kari and B. Potter, 1–24. (Anthropological Papers of the University of Alaska), new series, vol. 5. Fairbanks: University of Alaska Fairbanks, Department of Anthropology, pp. 1–24.
- Kibrik, Andrej A. 1993. "Transitivity increase in Athabaskan languages". In Bernard Comrie & Maria Polinsky (eds.), Causatives and Transitivity, 47–68. (Studies in Language Comparison Series 23.) Philadelphia: John Benjamins. ISBN 978-1-55619-375-0 (hbk).
- Kibrik, Andrej A. 1996. "Transitivity decrease in Navajo and Athabaskan: Actor-affecting propositional derivations". In Eloise Jelinek, Sally Midgette, Keren Rice, & Leslie Saxon (eds.) Athabaskan language studies: Essays in honor of Robert W. Young, 259–304. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico. ISBN 0-8263-1705-7 (cloth).
- Kibrik, Andrej A. 2001. "A typologically oriented portrait of the Athabaskan language family". Presented at ALT-IV, Santa Barbara, CA.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1964. "The proto-Athapaskan–Eyak and the problem of Na-Dene, I: The phonology". International Journal of American Linguistics 30(2). 118–131.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1965. "The proto-Athapaskan–Eyak and the problem of Na-Dene, II: The morphology". International Journal of American Linguistics 31(1). 18–28.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1968. "Noun-classification systems in the Athapaskan, Eyak, Tlingit and Haida verbs". International Journal of American Linguistics 34(3). 194–203.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1969. On the classification in the Athapascan, Eyak, and the Tlingit verb. Baltimore: Waverly Press, Indiana University.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1973. Na-Dene. In Thomas A. Sebeok (ed.), Linguistics in North America, 903–978. (Current trends in linguistics 1.) The Hague: Mouton. (Reprinted as Krauss 1976.)
- Krauss, Michael E. 1976a." Na-Dene". In Thomas A. Sebeok (ed.), Native languages of the Americas, 283–358. New York: Plenum. Reprint of Krauss 1973.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1976b. Proto-Athabaskan–Eyak fricatives and the first person singular. Unpublished manuscript.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1979. "Na-Dene and Eskimo". In Lyle Campbell & Marianne Mithun (eds.), The languages of native America: Historical and comparative assessment. Austin: University of Texas Press.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1979. Athabaskan tone. Unpublished manuscript. Published with revisions as Krauss 2005.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1981. On the history and use of comparative Athapaskan linguistics. Unpublished manuscript.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1986. "Edward Sapir and Athabaskan linguistics". In W. Cowan, M. Foster, & K. Koerner (eds.), New perspectives in language, culture, and personality, 147–190. Amsterdam: Benjamins.
- Krauss, Michael E. 1987. The name Athabaskan. In Peter L. Corey (ed.), Faces, Voices & Dreams: A celebration of the centennial of the Sheldon Jackson Museum, Sitka, Alaska, 1888–1988, 105–08. Sitka, AK: Division of Alaska State Museums and the Friends of the Alaska State Museum. PDF version available from the Alaska Native Language Center.
- Krauss, Michael E. 2005. Athabaskan tone. In Sharon Hargus & Keren Rice (eds.), Athabaskan Prosody, 51–136. Amsterdam: John Benjamins. Revision of unpublished manuscript dated 1979.
- Krauss, Michael E. & Victor Golla. 1981. Northern Athapaskan languages. In J. Helm (ed.), Subarctic, 67–85. (Handbook of North American Indians 6). Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution.
- Krauss, Michael E. & Jeff Leer. 1981. Athabaskan, Eyak, and Tlingit sonorants. (Alaska Native Language Center research papers 5). Fairbanks, AK: University of Alaska, Alaska Native Language Center.
- Leer, Jeff. 1979. Proto-Athabaskan verb stem variation I: Phonology. (Alaska Native Language Center research papers 1). Fairbanks, AK: Alaska Native Language Center.
- Leer, Jeff. 1982. Navajo and comparative Athabaskan stem list. Unpublished manuscript. ANLA CA965L1982
- Leer, Jeff. 1990. Tlingit: A portmanteau language family? In Philip Baldi (ed.), Linguistic change and reconstruction methodology, 73–98. (Trends in Linguistics: Studies and monographs 45). Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-011908-4.
- Leer, Jeff. 2005. How stress shapes the stem-suffix complex in Athabaskan. In Sharon Hargus & Keren Rice (eds.), Athabaskan Prosody, 278–318. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
- Leer, Jeff. 2008. Recent advances in AET comparison. ANLA CA965L2008b
- Leer, Jeff. 2010. The Palatal Series in Athabascan-Eyak-Tlingit, with an Overview of the Basic Sound Correspondences. In The Dene–Yeniseian Connection, ed. by J. Kari and B. Potter, p. 168-193. Anthropological Papers of the University of Alaska, new series, vol. 5. Fairbanks: University of Alaska Fairbanks, Department of Anthropology.
- Mithun, Marianne. 1999. The languages of Native North America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-23228-7 (hbk); ISBN 0-521-29875-X (pbk).
- Naish, Constance & Gillian Story. 1973. Tlingit verb dictionary. Fairbanks, AK: Alaska Native Language Center. ISBN 0-933769-25-3.
- Rice, Keren. 1997. "A reexamination of Proto-Athabaskan y". Anthropological Linguistics 39(3). 423–426.
- Rice, Keren. 2000. Morpheme order and semantic scope: Word formation in the Athapaskan verb. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-58354-1 (hbk); ISBN 978-0-521-02450-1 (pbk).
- Sapir, Edward. 1915. The Na-Dene languages, a preliminary report. American Anthropologist 17(3). 534–558.
- Sapir, Edward. 1916. Time perspective in aboriginal American culture: A study in method. (Anthropology series 13; Memoirs of the Canadian Geological Survey 90). Ottawa: Government Printing Bureau.
- Sapir, Edward. 1931. "The concept of phonetic law as tested in primitive languages by Leonard Bloomfield". In S. A. Rice (ed.), Methods in social science: A case book, 297–306. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Sapir, Edward. 1936. Linguistic evidence suggestive of the northern origin of the Navaho. American Anthropologist 38(2). 224–235.
- Sapir, Edward, & Victor Golla. 2001. "Hupa Texts, with Notes and Lexicon". In Victor Golla & Sean O'Neill (eds.), Collected Works of Edward Sapir, vol. 14, Northwest California Linguistics, 19–1011. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
- Saville-Troike, Muriel. 1985. On variable data and phonetic law: A case from Sapir's Athabaskan correspondences. International Journal of American Linguistics 51(4). 572–574.
- Sturtevant, William C. (ed.). 1978–present. Handbook of North American Indians, vols. 1–20. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution. Vols. 1–3, 16, 18–20 not yet published.
- Vajda, Edward. 2010. "A Siberian Link with Na-Dene Languages". In The Dene–Yeniseian Connection, ed. by J. Kari and B. Potter, 33–99. Anthropological Papers of the University of Alaska, new series, vol. 5. Fairbanks: University of Alaska Fairbanks, Department of Anthropology.
- Vajda, Edward J. (2011). Oxford Bibliographies Online: "Dene-Yeniseian".
Further reading
- Thompson, Chad (1984). "Athabaskan Languages and the Schools: A Handbook for Teachers". Juneau: Alaska Native Language Center. Retrieved 2 July 2020.
- Leer, Jeff. 1992. Na-La-Dene cognate sets. Item CA965L1992b. Ms. (March 17, 1992), Alaska Native Language Archive.
- Leer, Jeff. 1996. Comparative Athabaskan Lexicon. Item CA965L1996. Ms., Alaska Native Language Archive.
- Leer, Jeff. 2008. Recent advances in AET comparison. Paper prepared for the Dene-Yeniseian Symposium. Fairbanks, Feb. 26, 2008. Item CA965L2008b. Ms., Alaska Native Language Archive.
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Athapascan. |
- Pan-Dene Comparative Lexicon (PanDeneComPlex; formerly the Pan-Athapaskan Comparative Lexicon)
- Alaska Native Language Center
- Comparative Athabaskan Lexicon (University of Alaska Fairbanks)
- Athabaskan Satellites & ASL Ion-Morphs
- Yukon Native Language Center
- Athapascan Bibliography
- Don Macnaughtan. "Oregon Athapaskan Languages: Bibliography of the Athapaskan Languages of Oregon". Retrieved 2018-05-30.
- California Athapascan
- ATHAPBASCKAN-L mailing list for Athabaskan linguistics