Arado Ar 79
The Arado Ar 79 was a German aircraft of the 1930s, designed as an aerobatic two-seat trainer and touring aircraft.[1]
| Ar 79 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Aerobatic trainer |
| Manufacturer | Arado |
| First flight | 20 April 1938 |
| Introduction | 1938 |
| Produced | 72 |
The Ar 79 was a monoplane with retractable, tailwheel undercarriage. The wings were constructed of fabric over plywood, the forward fuselage was of fabric over steel tube, and the rear fuselage was a monocoque structure.[1]
Operational history
The Ar 79 set a number of speed records in 1938:[1]
- On 15 July the solo 1,000 km (621.4 mi) at 229.04 km/h (142.32 mph),[1]
- On 29 July the 2,000 km (1,242.8 mi) at 227.029 km/h (141.069 mph).[1]
- From 29 to 31 December, a modified Ar 79, with a jettisonable 106 L (28 US gal) fuel tank and extra 520 L (140 US gal) tank behind the cabin, completed a non-stop 6,303 km (3,917 mi) flight from Benghazi, Libya to Gaya, India, at an average speed of 160 km/h (100 mph).[1]
Specifications
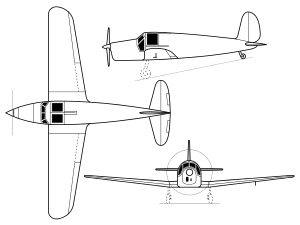
Data from Aircraft of the Third Reich,[2] Flugzeug-Typenbuch. Handbuch der deutschen Luftfahrt 1944[3]
General characteristics
- Crew: two
- Length: 7.6 m (24 ft 11 in)
- Wingspan: 10 m (32 ft 10 in)
- Height: 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in)
- Wing area: 14 m2 (150 sq ft)
- Aspect ratio: 7.14
- Empty weight: 460 kg (1,014 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 760 kg (1,676 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 120 l (32 US gal; 26 imp gal) fuel + 4 l (1.1 US gal; 0.88 imp gal) oil
- Powerplant: 1 × Hirth HM 504A-2 inverted 4-cyl. air-cooled in-line piston engine 105 PS (104 hp; 77 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed pitch propeller, 2 m (6 ft 7 in) diameter
Performance
- Maximum speed: 230 km/h (140 mph, 120 kn) at sea level
- Cruise speed: 205 km/h (127 mph, 111 kn) 75 PS (74 hp; 55 kW) at sea level
- Range: 1,025 km (637 mi, 553 nmi)
- Endurance: 5 hours 18 minutes
- Service ceiling: 5,300 m (17,400 ft) solo
- 4,500 m (14,764 ft) dual
- g limits: +10.8 (ultimate)
- Rate of climb: 4 m/s (790 ft/min)
- Time to altitude:
- 1,000 m (3,281 ft) in 3 minutes 48 seconds
- 2,000 m (6,562 ft) in 8 minutes 24 seconds
- Wing loading: 57 kg/m2 (12 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.1314 PS/kg (0.0588 hp/lb; 0.0966 kW/kg)
- Fuel consumption: 11 l/km (4.7 US gal/mi; 3.9 imp gal/mi)
- Oil consumption: 0.15 l/km (0.064 US gal/mi; 0.053 imp gal/mi)
- Take-off run: 180 m (591 ft)
Notes
- Donald, p. 60.
- Green, William (2010). Aircraft of the Third Reich. 1 (1st ed.). London: Aerospace Publishing Limited. pp. 36–37. ISBN 978 1 900732 06 2.
- Schneider, Helmut (1944). Flugzeug-Typenbuch. Handbuch der deutschen Luftfahrt- und Zubehör-Industrie (in German) (Sonderausg ed.). Leipzig: Herm. Beyer Verlag. pp. 22–23. ISBN 381120484X.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
