Arkansas-class ironclad
The Arkansas-class ironclads were a class of two casemate ironclads ordered by the Confederate States Navy in 1861 to operate in the Western and Trans-Mississippi theaters of the American Civil War.[1]
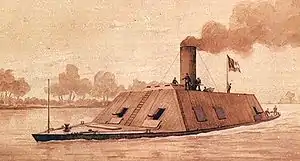 The C. S. S. Arkansas by R. G. Skerrett | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Arkansas-class ironclad |
| Builders: | John T. Shirley, Memphis, Tennessee |
| Operators: |
|
| Built: | 1861–1862 |
| In service: | 1862 |
| Planned: | 2 |
| Completed: | 1 |
| Lost: | 2 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Casemate ironclad |
| Length: | 165 ft (50 m) |
| Beam: | 35 ft (11 m) |
| Draft: | 11 ft 6 in (3.51 m) |
| Installed power: | 2 propellers |
| Propulsion: | 2 Steam engines |
| Speed: | 7 knots (13 km/h; 8.1 mph) |
| Complement: | 200 officers and enlisted men |
| Armament: | Designed for 6–8 guns |
Ships
| Ship name | Builder[1] | Laid down[1] | Launched[1] | Commissioned[1] | Fate[1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSS Arkansas | John T. Shirley, Memphis, Tennessee | October 1861 | 22 April 1862 | 26 May 1862 | Destroyed to prevent capture, 6 August 1862 |
| CSS Tennessee | N/A | Burned to prevent capture, 5 June 1862 | |||
Notes
- This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships.
References
- Silverstone, Paul H. (2006). Civil War Navies 1855–1883. The U.S. Navy Warship Series. New York: Routledge. pp. 150–51. ISBN 0-415-97870-X.
Further reading
- Bisbee, Saxon T. (2018). Engines of Rebellion: Confederate Ironclads and Steam Engineering in the American Civil War. Tuscaloosa, Alabama: University of Alabama Press. ISBN 978-0-81731-986-1.
- Still, William N., Jr. (1985). Iron Afloat: The Story of the Confederate Armorclads (Reprint of the 1971 ed.). Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press. ISBN 0-87249-454-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.