Awara, Fukui
Awara (あわら市, Awara-shi) is a city located in Fukui Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 May 2018, the city had an estimated population of 28,405 in 10,140 households and the population density of 240 persons per km².[1] The total area of the city was 116.98 square kilometres (45.17 sq mi). It is one of the few Hiragana cities in Japan. Awara is a city famous for its onsen resorts and natural hotwater springs.
Awara
あわら市 | |
|---|---|
 Awara City Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
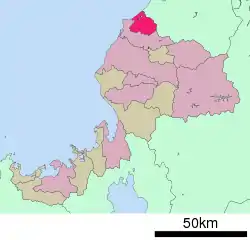 Location of Awara in Fukui Prefecture | |
 Awara | |
| Coordinates: 36°12′40.7″N 136°13′44.3″E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Chūbu (Hokuriku) |
| Prefecture | Fukui |
| Area | |
| • Total | 116.98 km2 (45.17 sq mi) |
| Population (May 2018) | |
| • Total | 28,405 |
| • Density | 240/km2 (630/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| City symbols | |
| -Tree | Prunus mume |
| -Flower | Iris |
| -Bird | Egret |
| Phone number | 0776-73-1221 |
| Address | 2-1-1, Ichihime, Awara-shi, Fukui-ken 919-0692 |
| Website | www |
Geography
Awara is located in far northern Fukui Prefecture, bordered by Ishikawa Prefecture to the north and the Sea of Japan to the northeast, The city of Sakai surrounds the city to the east, south and west.
Neighbouring municipalities
- Fukui Prefecture
- Ishikawa Prefecture
Climate
Awara has a Humid climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by warm, wet summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Awara is 14.2 °C. The average annual rainfall is 2481 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 26.8 °C, and lowest in January, at around 2.8 °C.[2]
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[3] the population of Awara has remained steady over the past 40 years.
| Census Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1970 | 29,436 |
| 1980 | 30,975 |
| 1990 | 31,743 |
| 2000 | 32,178 |
| 2010 | 29,989 |
History
Awara is part of ancient Echizen Province. During the Edo period, the area was divided between the holdings of Fukui Domain, Maruoka Domain and Nishio Domain. Following the Meiji restoration, it was organised into part of Sakai District in Fukui Prefecture. Awara Onsen was developed from June 1884. With the establishment of the modern municipalities system on April 1, 1889, the town of Kanazu and villages of Awara, Ii, Tsuboe, Hosorogi, Yoshizaki, Kitagata and Honjō were established. Awara was raised to town status in February 1935. The villages of Ii, Tsuboe, Hosoroe, and Yoshizaki merged into Kanazu in October 1954, and Kitagata and Honsho were merged into Awara in March 1955. Most of Awara Onsen burned down in a fire in April 1956. Awara and Kanazu merged to form the city of Awara on March 1, 2004.
Government
Awara has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 18 members.
Economy
The economy of Awara is mixed, with agriculture and the tourism industry centered on Awara Onsen playing prominent roles. Hitachi Zosen Fukui Corporation, a hydraulic press manufacturer, is headquartered in Awara.
Education
Awara has seven public elementary schools and two middle schools operated by the city government, and one public high school operated by the Fukui Prefectural Board of Education.
High school
- Kanazu High School (金津高校)
Junior high schools
- Awara Junior High School (芦原中学校)
- Kanazu Junior High School (金津中学校)
Elementary schools
- Awara Elementary School (芦原小学校)
- Kitagata Elementary School 北潟小学校)
- Kanazu Elementary School (金津小学校)
- Hosorogi Elementary School (細呂木小学校)
- Kanazu Higashi Elementary School (金津東小学校)
- Ii Elementary School (伊井小学校)
- Honjo Elementary School (本荘小学校)
Transportation
Railway
Local attractions
References
- "Official website of Awara City" (in Japanese). Japan: Awara City. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- Awara climate data
- Awara population statistics
External links
 Media related to Awara, Fukui at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Awara, Fukui at Wikimedia Commons- Awara City official website (in Japanese)