Aztec religion
The Aztec religion originated from the indigenous Aztecs of central Mexico. Like other Mesoamerican religions, it also has practices such as human sacrifice in connection with many religious festivals[1] which are in the Aztec calendar. This polytheistic religion has many gods and goddesses; the Aztecs would often incorporate deities that were borrowed from other geographic regions and peoples into their own religious practices.
The cosmology of Aztec religion divides the world into thirteen heavens and nine earthly layers or netherworlds. The first heaven overlaps with the first terrestrial layer, so that heaven and the terrestrial layers meet at the surface of the Earth. Each level is associated with a specific set of deities and astronomical objects. The most important celestial entities in Aztec religion are the Sun, the Moon, and the planet Venus (both as "morning star" and "evening star"). The Aztecs were popularly referred to as "people of the sun".
Many leading deities of the Aztecs are worshiped in the contemporary or present-day world. These deities are known by names such as Tlaloc, Quetzalcoatl and Tezcatlipoca, who are venerated by different names in multiple cultures and have been throughout the history of Mesoamerica. For the Aztecs, deities of particular importance are the rain god Tlaloc; Huitzilopochtli, patron of the Mexica tribe; Quetzalcoatl, the feathered serpent and god of wind and learning; and Tezcatlipoca, the shrewd, elusive god of destiny and fortune. Tezcatlipoca was also connected to war and sorcery. Tlaloc and Huitzilopochtli were worshipped in shrines at the top of the largest pyramid (Templo Mayor) in the Aztec capital Tenochtitlan. A third monument in the plaza in front of Templo Mayor was devoted to the wind god, Ehecatl, who was an aspect or form of Quetzalcoatl.[2]
Teotl
The concept of teotl is central to the Aztecs. The term is often translated as "god", but it may have held more abstract aspects of divinity or supernatural energy, akin to the Polynesian concept of Mana.[3]
The nature of teotl is a key element in the understanding of the fall of the Aztec empire. It seems that the Aztec ruler at that time, Moctezuma II and the Aztecs, in general, referred to Cortés and the conquistadors as "teotl". It has been widely believed that this means that they believed them to be gods, but a better understanding of teotl might suggest that they were merely seen as "mysterious" or "inexplicable".[4]
Pantheon
The Aztecs would often adopt gods from different cultures and allow them to be worshiped as part of their pantheon. For example, the fertility god, Xipe Totec, was originally a god of the Yopi (the Nahuatl name of the Tlapanec people), but became an integrated part of the Aztec belief system. Further, sometimes foreign gods would be identified with an already existing god. Other deities, such as Tezcatlipoca and Quetzalcoatl, had roots in earlier civilizations of Mesoamerica, and were worshiped by many cultures under different names.
The many gods of the Aztecs can be grouped into complexes related to different themes. Some were associated with aspects of nature, such as Tlaloc and Quetzalcoatl, and other gods were associated with specific trades. Reflecting the complexity of ritual in Aztec society, there were deities related to pulque, a sacred alcoholic beverage, but also deities of drunkenness, excess, fun, and games. Many gods had multiple aspects with different names, where each name highlighted a specific function or trait of the god. Occasionally, two distinct gods were conflated into one, and quite often, deities transformed into one another within a single story. Aztec images sometimes combined attributes of several divinities.
Aztec scholar H. B. Nicholson (1971) classed the gods into three groups according to their conceptual meaning in general Mesoamerican religion. The first group he called the "celestial creativity—divine paternalism group". The second: the Earth-mother gods, the pulque gods, and Xipe Totec. The third group, the War-Sacrifice-Sanguinary Nourishment group, contained such gods as Ometochtli, Huitzilopochtli, Mictlantecuhtli and Mixcoatl. A more specific classification based upon the functional attributes of the deities is as follows:
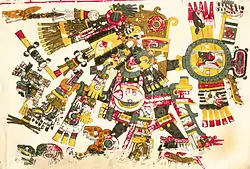
Cultural Gods
- Tezcatlipoca: meaning "smoking mirror", a Pan-Mesoamerican shaman god, omnipotent universal power
- Quetzalcoatl: meaning "feathered serpent", a Pan-Mesoamerican god of life, the wind and the morning star
- Tlaloc: a Pan-Mesoamerican god of rainstorm, water, and thunder (or any storm)
- Mixcoatl: meaning "cloud serpent", the tribal god of many of the Nahua people such as the Tlaxcalteca, god of war, sacrifice and hunting
- Huitzilopochtli: meaning "left-handed hummingbird", the patron god of the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, the sun
Nature gods
- Metztli: the moon
- Tlaltecuhtli: meaning "earth lord", goddess of the Earth
- Chalchiuhtlicue: meaning "jade her skirt", goddess of springs
- Centzon Huitznahua: meaning "the 400 southerners", gods of the stars
- Ehecatl: the wind, often conflated with Quetzalcoatl and called "Quetzalcoatl-Ehecatl"
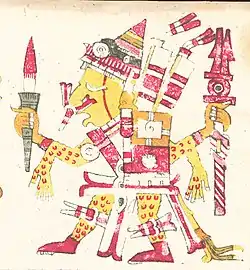
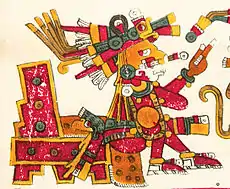

Gods of creation
- Ōmeteōtl/Tōnacātēcuhtli: creator gods
- Huehuetéotl/Xiuhtecuhtli: meaning "old god" and "turquoise lord", god of origin, time, fire and old age
- Coatlicue/Toci/Teteoinnan/Tonantzin: progenitor goddesses
Gods of pulque and excess
- Tlazolteotl: goddess of filth, guilt, and of cleansing
- Tepoztecatl: god of pulque worshipped at Tepoztlan
- Xochiquetzal: goddess of pleasure, indulgence, and sex
- Mayahuel: goddess of pulque and maguey
- The Ahuiateteo:
- Macuiltochtli
- Macuilxochitl
- Macuil Cuetzpalin
- Macuilcozcacuauhtli
- Macuil Malinalli
- Centzon Totochtin: meaning "the 400 rabbits", god of intoxication
- Ometochtli: meaning "two rabbit", leader of the Centzon Totochtin, god of fertility and intoxication
Gods of maize and fertility
- Xipe Totec: meaning "our flayed lord", fertility god associated with spring, patron god of goldsmiths
- Centeotl: god of maize
- Xilonen/Chicomecoatl: goddess of tender maize
- Xochipilli: meaning "flower prince", god of happiness, flowers, pleasure, and fertility
Gods of death and the underworld
- Mictlantecuhtli: lord of the underworld
- Mictlancihuatl: queen of the underworld
- Xolotl: meaning "the animal", lord of the evening star
Trade gods
- Yacatecuhtli: meaning "nose lord", god of merchants
- Patecatl: god of doctors and medicine
Religion and society
Religion was part of all levels of Aztec society. On the state level, religion was controlled by the Tlatoani and the high priests governing the main temples in the ceremonial precinct of the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan. This level involved the large monthly festivals and a number of specific rituals centered around the ruler dynasty and attempted to stabilize both the political and cosmic systems. These rituals were the ones that involved a sacrifice of humans. One of these rituals was the feast of Huey Tozoztli, when the ruler himself ascended Mount Tlaloc and engaged in autosacrifice in order to petition the rains. Throughout society, each level had their own rituals and deities and played their part in the larger rituals of the community. For example, the class of Pochteca merchants were involved in the feast Tlaxochimaco, where the merchant deity would be celebrated and slaves bought on specific slave markets by long-distance traders would be sacrificed. On the feast of Ochpaniztli all commoners participated in sweeping the streets. Afterwards, they also undertook ritual bathing. The most spectacular ritual was the New Fire ceremony which took place every 52 years and involved every citizen of the Aztec realm. During this, commoners would destroy house utensils, quench all fires, and receive new fire from the bonfire on top of Mt. Huixachtlan, lit on the chest of a sacrificed person by the high priests.
Priests and temples
In the Nahuatl language, the word for priest was tlamacazqui meaning "giver of things"—the main responsibility of the priesthood was to make sure that the gods were given their due in the form of offerings, ceremonies, and sacrifices.
The Tlatoani of Tenochtitlan was the head of the cult of Huitzilopochtli and of the state religion of the Aztec empire. He had special priestly duties in different rituals on the state level.
However, the Aztec religious organization was not entirely under his authority. Bernardino de Sahagún and Duran describe the pairs of high priests (quetzalcoatlus) who were in charge of the major pilgrimage centres (Cholula and Tenochtitlan) as enjoying immense respect from all levels of Aztec society—akin to archbishops—and a level of authority that partly transcended national boundaries. Under these religious heads were many tiers of priests, priestesses, novices, nuns, and monks (some part-time) who ran the cults of the various gods and goddesses. Sahagún reports that the priests had very strict training, and had to live very austere and ethical lives involving prolonged vigils, fasts, and penances. For instance, they often had to bleed themselves and undertake prescribed self-mortifications in the buildup to sacrificial rites.
Additionally, Sahagún refers to classes of religious specialists not affiliated with the established priesthood. This included wandering curers, black magicians, and other occultists (of which the Aztecs identified many types, most of which they feared) and hermits. Finally, the military orders, professions (e.g. traders (pochteca)) and wards (calpulli) each operated their own lodge dedicated to their specific god. The heads of these lodges, although not full-time religious specialists, had some ritual and moral duties. Duran also describes lodge members as having the responsibility of raising sufficient goods to host the festivals of their specific patron deity. This included annually obtaining and training a suitable slave or captive to represent and die as the image of their deity in that festival.
Aztec temples were basically offering mounds: solid pyramidal structures crammed with special soils, sacrifices, treasures and other offerings. Buildings around the base of the pyramid, and sometimes a small chamber under the pyramid, stored ritual items and provided lodgings and staging for priests, dancers, and temple orchestras. The pyramids were buried under a new surface every several years (especially every 52 years—the Aztec century). Thus the pyramid-temples of important deities constantly grew in size.
In front of every major temple lay a large plaza. This sometimes held important ritual platforms such as the "eagle stone" where some victims were slain. Plazas were where the bulk of worshippers gathered to watch rites and dances performed, to join in the songs and sacrifices (the audience often bled themselves during the rites), and to partake in any festival foods. Nobility sat on tiered seating under awnings around the plaza periphery, and some conducted part of the ceremonies on the temple.
Continual rebuilding enabled Tlatoani and other dignitaries to celebrate their achievements by dedicating new sculptures, monuments, and other renovations to the temples. For festivals, temple steps and tiers were also festooned with flowers, banners and other decorations. Each pyramid had a flat top to accommodate dancers and priests performing rites. Close to the temple steps there was usually a sacrificial slab and braziers.
The temple house (calli) itself was relatively small, although the more important ones had high and ornately carved internal ceilings. To maintain the sanctity of the gods, these temple houses were kept fairly dark and mysterious—a characteristic that was further enhanced by having their interiors swirling with smoke from copal (meaning incense) and the burning of offerings. Cortes and Diaz describe these sanctuaries as containing sacred images and relics of the gods, often bejeweled but shrouded under ritual clothes and other veils and hidden behind curtains hung with feathers and bells. Flowers and offerings (including a great amount of blood) generally covered much of the floors and walls near these images. Each image stood on a pedestal and occupied its own sanctuary. Larger temples also featured subsidiary chambers accommodating lesser deities.
In the ceremonial center of Tenochtitlan, the most important temple was the Great Temple which was a double pyramid with two temples on top. One was dedicated to Huitzilopochtli; this temple was called Coatepec (meaning "snake mountain"), and the other temple was dedicated to Tlaloc. Below the Tlatoani were the high priests of these two temples. Both high priests were called by the title Quetzalcoatl—the high priest of Huitzilopochtli was Quetzalcoatl Totec Tlamacazqui and the high priest of Tlaloc was Quetzalcoatl Tlaloc Tlamacazqui.[5] Other important temples were located in the four divisions of the town. One example was the temple called Yopico in Moyotlan which was dedicated to Xipe Totec. Furthermore, all the calpullis had special temples dedicated to the patron gods of the calpulli.[6] Priests were educated at the Calmecac if they were from noble families and in the Telpochcalli if they were commoners.
Cosmology and ritual
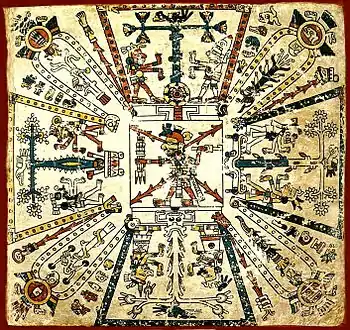
The Aztec world consisted of three main parts: the earth world on which humans lived (including Tamoanchan, the mythical origin of human beings), an underworld which belonged to the dead (called Mictlan, "place of death"), and the upper plane in the sky. The earth and the underworld were both open for humans to enter, whereas the upper plane in the sky was impenetrable to humans. Existence was envisioned as straddling the two worlds in a cycle of birth, life, death and rebirth. Thus as the sun was believed to dwell in the underworld at night to rise reborn in the morning and maize kernels were interred to later sprout anew, the human and divine existence was also envisioned as being cyclical. The upper and nether worlds were both thought to be layered. Mictlan had nine layers which were inhabited by different deities and mythical beings. The sky had thirteen layers, the highest of which was called Omeyocan ("place of duality") and served as the residence of the progenitor dual god Ometeotl. The lowest layer of the sky was a verdant spring-like place with abundant water called Tlalocan ("the place of Tlaloc").
After death, the soul of the Aztec went to one of three places: the sun, Mictlan, or Tlalocan. Souls of fallen warriors and women that died in childbirth would transform into hummingbirds that followed the sun on its journey through the sky. Souls of people who died from less glorious causes would go to Mictlan. Those who drowned would go to Tlalocan.[7]
In Aztec cosmology, as in Mesoamerica in general, geographical features such as caves and mountains held symbolic value as places of crossing between the upper and nether worlds. The cardinal directions were symbolically connected to the religious layout of the world as well; each direction was associated with specific colors and gods.
To the Aztecs, death was instrumental in the perpetuation of creation, and gods and humans alike had the responsibility of sacrificing themselves in order to allow life to continue. This worldview is best described in the myth of the five suns recorded in the Codex Chimalpopoca, which recounts how Quetzalcoatl stole the bones of the previous generation in the underworld and how later the gods created four successive worlds or "suns" for their subjects to live in, all of which were destroyed. Then, by an act of self-sacrifice, one of the gods, Nanahuatzin ("the pimpled one"), caused a fifth and final sun to rise where the first humans, made out of maize dough, could live thanks to his sacrifice. Humans were responsible for the sun's continued revival. Blood sacrifice in various forms were conducted. Both humans and animals were sacrificed, depending on the god to be placated and the ceremony being conducted, and priests of some gods were sometimes required to provide their own blood through self-mutilation.
Sacrificial rituals among the Aztecs, and in Mesoamerica in general, must be seen in the context of religious cosmology: sacrifice and death was necessary for the continued existence of the world. Likewise, each part of life had one or more deities associated with it and these had to be paid their dues in order to achieve success. Gods were paid with sacrificial offerings of food, flowers, effigies, and quail. But the larger the effort required of the god, the greater the sacrifice had to be. Blood fed the gods and kept the sun from falling. For some of the most important rites, a priest would offer his own blood by cutting his ears, arms, tongue, thighs, chest, genitals, or offer a human life or a god's life. The people who were sacrificed came from many segments of society and might have been a war captive, slave, or a member of Aztec society; the sacrifice might also have been man or woman, adult or child, or noble or commoner.
Deity impersonation
An important aspect of Aztec ritual was the impersonation of deities. Priests or otherwise specially elected individuals would be dressed up to achieve the likeness of a specific deity. A person with the honourable charge of impersonating a god was called ixiptla tli and was venerated as an actual physical manifestation of the god until the inevitable end when the god's likeness had to be killed as the ultimate sacrifice under great circumstance and festivities.
Reenactment of myth
As with the impersonation of gods, Aztec ritual was often a reenactment of a mythical event which at once served to remind the Aztecs of their religion, but it also served to perpetuate the world by repeating the important events of the creation.
Calendar
The Aztec religious year was connected mostly to the natural 365-day calendar, the xiuhpohualli ("yearcount"), which followed the agricultural year. Each of the 18 twenty-day months of the religious year had its particular religious festival—most of which were connected to agricultural themes. The greatest festival was the xiuhmolpilli, or New Fire ceremony, held every 52 years when the ritual and agricultural calendars coincided and a new cycle started. In the table below, the veintena festivals are shown, the deities with which they were associated and the kinds of rituals involved. The descriptions of the rites are based on the descriptions given in Sahagún's Primeros Memoriales, the Florentine Codex, and of Diego Durán's Of the Gods and Rites—all of which provide detailed accounts of the rituals written in Nahuatl soon after the conquest.
| Festival | Period[8] | Principal deity | Theme | Rituals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlcahualo also called "Xilomanaliztli", "Spreading of corn" |
14 February–5 March | The Tlalocs | Fertility, sowing | Cuahuitl Ehua: a ceremonial raising of a tree, the sacrifice of children to Tlaloc |
| Tlacaxipehualiztli "Flaying of men" |
6 March–25 March | Xipe Totec | Spring, sprouting, fertility | Sacrifice and Flaying of Captives, mock battles, gladiatorial sacrifice, priests wear victims skin for 20 days, military ceremonies |
| Tozoztontli "Little vigil" |
26 March–14 April | Tlaltecuhtli (as well as the Tlalocs and Xipe Totec) |
Planting, sowing | Bloodletting, burial of the skins of the flayed captives, offering of flowers and roasted snakes to the earth. |
| Huey Tozoztli "Great vigil" |
15 April–4 May | Cinteotl (as well as the Tlalocs and Chicomecoatl) | Maize, seed, sowing | Feasts to Tlaloc and the maize gods, blessing of seed corn, sacrifice of children at Mt. Tlaloc. |
| Toxcatl "Drought" |
5 May–22 May | Tezcatlipoca and Huitzilopochtli | Renewal | Feasting, dancing, the sacrifice of small birds, the sacrifice of Tezcatlipoca |
| Etzalcualiztli "Eating of fresh maize" |
23 May–13 June | Tlaloc, Chalchiuhtlicue, Quetzalcoatl | Young crops, end of dry season | Sacrifice of Tlaloc, new mats made |
| Tecuilhuitontli "Small festival of lords" |
14 June–3 July | Xochipilli | Feasts to goddesses of grain, sacrifice of Huixtocihuatl | |
| Huey Tecuilhuitl "Great festival of lords" |
4 July–23 July | Xilonen, maize gods | The Lords, tender maize | Feast of Xilonen, the sacrifice of Cihuacoatl and Xilonen, lords feed the commoners, dancing |
| Tlaxochimaco "Giving of flowers" (also called Miccailhuitontli—"Small feast of the dead") |
24 July–12 August | Huitzilopochtli | Flowers, trade | A small feast for the dead, feast of the merchants, the making of the Xocotl pole |
| Xocotl Huetzi "Fruits fall" (also called Huey Miccailhuitontli—"Great feast of the dead") |
13 August–1 September | Huehueteotl, Xiuhtecuhtli | Fruits, harvest | The feasts of the Xocotl pole, bloodletting |
| Ochpaniztli "Sweeping" |
2 September–21 September | Tlazolteotl, Toci, Teteo Innan, Coatlicue, Cinteotl | Harvest, cleansing | Ritual sweeping, ritual bathing, the sacrifice of Teteo Innan |
| Teteo Eco "The gods arrive" |
22 September–11 October | All deities | Arrival of the gods | Bloodletting, the feast of Huitzilopochtli, the dance of the old men |
| Tepeilhuitl "Mountain feast" |
12 October–31 October | Xochiquetzal, The Tlalocs, Trade Gods | Mountains | Mountain feasts, sacrifice of Xochiquetzal, feasts of the gods of different trades |
| Quecholli "Roseate Spoonbill" |
1 November–20 November | Mixcoatl | Hunting | Ritual hunts, the sacrifice of slaves and captives, weapon making, armories replenished |
| Panquetzaliztli "Raising of banners" |
21 November – 10 December | Huitzilopochtli | Tribal festival of the Aztecs, birth of Huitzilopochtli | Raising of banners, Great Huitzilopochtli Festival, sacrifices of slaves and captives, ritual battles, drinking of pulque, bloodletting |
| Atemoztli "Descent of water" |
11 December–30 December | The Tlalocs | Rain | Waterfeasts, the sacrifice of Tlaloc effigies made from maize dough |
| Tititl "Stretching" |
31 December–19 January | Ilamatecuhtli (Cihuacoatl) | Old age | Feasts to old people, the dance of the Cihuateteo, fertility rituals, merchants sacrifice slaves |
| Izcalli "Rebirth" |
20 January–8 February | Tlaloc, Xiuhtecuhtli | Fertility, water, sowing | Eating of Amaranth Tamales, feast for Xiuhtecuhtli every four years |
| Nemontemi | 9 February–13 February | Tzitzimime demons | Five unlucky days at the end of the year, abstinence, no business |
Mythology
The main deity in the Mexica religion was the sun god and war god, Huitzilopochtli. He directed the Mexicas to found a city on the site where they would see an eagle, devouring an animal (not all chronicles agree on what the eagle was devouring, one says it was a precious bird, and though Father Duran says it was a snake, this is not mentioned in any pre-Hispanic source), while perching on a fruit bearing nopal cactus. According to legend, Huitzilopochtli had to kill his nephew, Cópil, and throw his heart on the lake. But, since Cópil was his relative, Huitzilopochtli decided to honor him, and caused a cactus to grow over Cópil's heart which became a sacred place.
Legend has it that this is the site on which the Mexicas built their capital city of Tenochtitlan. Tenochtitlan was built on an island in the middle of Lake Texcoco, where modern-day Mexico City is located. This legendary vision is pictured on the Coat of Arms of Mexico.
According to their own history, when the Mexicas arrived in the Anahuac Valley around Lake Texcoco, they were considered by the other groups as the least civilized of all. The Mexicas decided to learn, and they took all they could from other peoples, especially from the ancient Toltec (whom they seem to have partially confused with the more ancient civilization of Teotihuacan). To the Mexicas, the Toltecs were the originators of all culture; toltecayotl was a synonym for culture. Mexica legends identify the Toltecs and the cult of Quetzalcoatl with the mythical city of Tollan, which they also identified with the more ancient Teotihuacan.
In the process, they adopted most of the Toltec/Nahua pantheon, but they also made significant changes in their religion. As the Mexica rose in power, they adopted the Nahua gods at equal status to their own. For instance, Tlaloc was the rain god of all the Nahuatl-speaking peoples. They put their local god Huitzilopochtli at the same level as the ancient Nahua god, and also replaced the Nahua Sun god with their own. Thus, Tlaloc/Huitzilopochtli represents the duality of water and fire, as evidenced by the twin pyramids uncovered near the Zocalo in Mexico City in the late 1970s, and it reminds us of the warrior ideals of the Aztec: the Aztec glyph of war is burning water.
Human sacrifice
.jpg.webp)
Human sacrifice was practiced on a grand scale throughout the Aztec empire, although the exact figures were unknown. At Tenochtitlán, the principal Aztec city, "between 10,000 and 80,400 people" were sacrificed over the course of four days for the dedication of the Great Pyramid in 1487, according to Ross Hassig .[9] Excavations of the offerings in the main temple has provided some insight in the process, but the dozens of remains excavated are far short of the thousands of sacrifices recorded by eyewitnesses and other historical accounts. For millennia, the practice of human sacrifice was widespread in Mesoamerican and South American cultures. It was a theme in the Olmec religion, which thrived between 1200 BCE and 400 BCE and among the Maya. Human sacrifice was a very complex ritual. Every sacrifice had to be meticulously planned from the type of victim to the specific ceremony needed for the god. The sacrificial victims were usually warriors but sometimes slaves, depending upon the god and needed ritual. The higher the rank of the warrior the better he is looked at as a sacrifice. The victim(s) would then take on the persona of the god he was to be sacrificed for. The victim(s) would be housed, fed, and dressed accordingly. This process could last up to a year. When the sacrificial day arrived, the victim(s) would participate in the specific ceremonies of the god. These ceremonies were used to exhaust the victim so that he would not struggle during the ceremony. Then five priests, known as the Tlenamacac, performed the sacrifice usually at the top of a pyramid. The victim would be laid upon the table, held down and subsequently have his heart cut out.[7]
See also
Notes
- "Ancient aztec festivals, celebrations and holidays". "Mexican Routes [mexicanroutes.com]".
- "Study the... WIND GOD". Mexicolore.
- Taube and Miller 1999, pp 89. For a lengthy treatment of the subject, see Hvidtfeldt, 1958
- Restall 2001 pp 11.6–118
- Townsend, 1992, p. 192
- Van Zantwijk 1985
- Tuerenhout, D. V. (2005). The Aztecs: New Perspectives
- According to Townsend (1992)
- Hassig (2003). "El sacrificio y las guerras floridas". Arqueología Mexicana. XI: 47.
References
- Hvidtfeldt, Arild (1958). Teotl and Ixiptlatli: some central conceptions in ancient Mexican religion: with a general introduction on cult and myth. Copenhagen: Munksgaard.
- Miller, Mary; Karl Taube (1993). The Gods and Symbols of Ancient Mexico and the Maya. London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 0-500-05068-6.
- Nicholson, H.B. (1971). "Religion in Pre-Hispanic Central Mexico". In G. Ekholm; I. Bernal (eds.). Handbook of Middle American Indians, Volume 10. Austin: University of Texas Press. pp. 395–446. ISBN 0-292-77593-8.
- Townsend, Richard F. (2000). The Aztecs (revised ed.). New York: Thames and Hudson.
- van Zantwijk, Rudolph (1985). The Aztec Arrangement: The Social History of Pre-Spanish Mexico. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press.
- van Tuerenhout, Dirk (2005). The Aztecs: New Perspectives. Santa Barbara, Calif.: ABC-Clio. ISBN 1-57607-924-4.
- Burland, C. A. (1985). The Aztecs: gods and fate in ancient Mexico. London: Orbis.
- Brundage, Burr Cartwright (c. 1979). The Fifth Sun: Aztec gods, Aztec world. Austin: University of Texas Press.
- Markman, Roberta H (c. 1992). The Flayed God: the mesoamerican mythological tradition: sacred texts and images from pre-Columbian Mexico and Central America. Harper San Francisco.
- Carrasco, David (1998). Daily Life of the Aztecs: People of the Sun and Earth. Greenwood Press, Connecticut.
- Smith, Michael E. (2003). the Aztecs 2nd Ed. Blackwell Publishing, UK.
- Aguilar- Moreno, Manuel (2006). Handbook to Life in the Aztec World. Facts On File, California State University University, Los Angeles.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aztec religion. |
- Aztecs at Mexicolore: constantly updated educational site specifically on the Aztecs, for serious students of all ages

