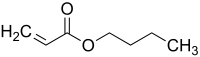
Butyl acrylate
Butyl acrylate is an organic compound with the formula C4H9O2CCH=CH2. A colorless liquid, it is the butyl ester of acrylic acid. It is used commercially on a large scale as a precursor to polybutylacrylate, which is used in paints, sealants, coatings, adhesives, fuel, textiles, plastics, and caulk.[4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Butyl prop-2-enoate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.983 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2348 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 128.171 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Strong, fruity[1] |
| Density | 0.89 g/mL (20°C)[1] |
| Melting point | −64 °C; −83 °F; 209 K [1] |
| Boiling point | 145 °C; 293 °F; 418 K [1] |
| 0.1% (20°C)[1] | |
| Solubility | ethanol, ethyl ether, acetone, carbon tetrachloride (slight) |
| Vapor pressure | 4 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H226, H315, H317, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P272, P280, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P370+378, P403+233, P403+235 | |
| Flash point | 39 °C; 103 °F; 313 K [1] |
| 267 °C (513 °F; 540 K)[2] | |
| Explosive limits | 1.5% - 9.9%[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
1800 mg/kg (dermal, rabbit)[3] |
LC50 (median concentration) |
1000 ppm (4 hr)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 10 ppm (55 mg/m3)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Production and properties
Butyl acrylate can be produced by the acid-catalyzed esterification acrylic acid with butanol. Since it polymerizes easily, commercial preparations may contain a polymerization inhibitor such as hydroquinone, phenothiazine, or hydroquinone ethyl ether.[2][4]
Safety
Butyl acrylate is of low acute toxicity with an LD50 (rat) of 3730 mg/kg.
In rodent models, butyl acrylate is metabolized by carboxylesterase or reactions with glutathione; this detoxification produces acrylic acid, butanol, and mercapturic acid waste, which is excreted.[5][6][7]
References
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0075". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- "Butyl Acrylate". International Chemical Safety Cards. NIOSH. July 1, 2014.
- "N-Butyl Acrylate". OSHA/NIOSH. September 28, 2011.
- Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Takahisa; Shimizu, Noboru; Prescher, Günter; Schwind, Helmut; Weiberg, Otto; Marten, Klaus; Greim, Helmut; Shaffer (2020). "Acrylic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. pp. 1–21. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_161.pub4.
- "Screening Information Data Set for n-Butyl acrylate, CAS #141-32-2". Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. October 2002. Archived from the original on 2015-11-07.
- Zondlo Fiume M (2002). "Final report on the safety assessment of Acrylates Copolymer and 33 related cosmetic ingredients". Int. J. Toxicol. 21 Suppl 3: 1–50. doi:10.1080/10915810290169800. PMID 12537929.
- "Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans". Geneva: World Health Organization: IARC. 1999.
