Chloramine-T
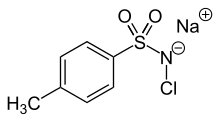
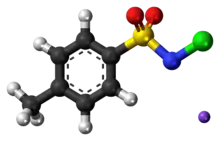
Chloramine-T is the organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2NClNa. Both the anhydrous salt and its trihydrate are known. Both are white powders. Chloramine-T is used as a reagent in organic synthesis.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-Chloro 4-methylbenzenesulfonamide, sodium salt | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.414 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H7ClNO2S·Na C7H7ClNO2S·Na·(3H2O) (hydrate) | |
| Molar mass | 227.64 g/mol 281.69 g/mol (trihydrate) |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Density | 1.4 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | Releases chlorine at 130 °C (266 °F; 403 K) Solid melts at 167–169 °C |
| >100 mg/mL (hydrate)[1] | |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AX04 (WHO) QP53AB04 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Corrosive |
| GHS pictograms | 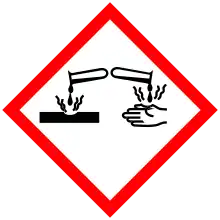   |
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H314, H334 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P280, P285, P301+312, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P304+341, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P330, P342+311, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Reactions
Chloramine-T contains active (electrophilic) chlorine. Its reactivity is similar to that of sodium hypochlorite. Aqueous solutions of chloramine-T are slightly basic (pH typically 8.5). The pKa of the closely related N-chlorophenylsulfonamide C6H5SO2NCl(H) is 9.5.[2]
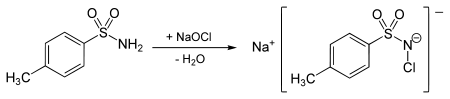
It is prepared by oxidation of toluenesulfonamide with sodium hypochlorite, with the latter being produced in situ from sodium hydroxide and chlorine (Cl2):[2]
Uses
Reagent in amidohydroxylation
The Sharpless oxyamination converts an alkene to a vicinal amino alcohol. A common source of the amido component of this reaction is chloramine-T.[3] Vicinal amino-alcohols are important products in organic synthesis and recurring pharmacophores in drug discovery.

Oxidant
Chloramine-T is a strong oxidant. It oxidizes hydrogen sulfide to sulfur and mustard gas to yield a harmless crystalline sulfimide.[4]
It converts iodide to iodine monochloride (ICl). ICl rapidly undergoes electrophilic substitution predominantly with activated aromatic rings, such as those of the amino acid tyrosine. Thus, chloramine-T is used to incorporate iodine into peptides and proteins. Chloramine-T together with iodogen or lactoperoxidase is commonly used for labeling peptides and proteins with radioiodine isotopes.[5]
Certifications
- EN 1276 Bactericidal
- EN 13713 Bactericidal
- EN 14675 Virucidal
- EN 14476 Virucidal Norovirus
- EN 1650 Fungicidal
- EN 13704 Sporicidal Clostridium difficile
References
- "Chloramine-T hydrate". Sigma-Aldrich.
- Campbell, Malcolm M.; Johnson, Graham. (1978). "Chloramine T and Related N-halogeno-N-metallo reagents". Chemical Reviews. 78: 65–79. doi:10.1021/cr60311a005.
- Bodkin, J. A.; McLeod, M. D. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1, 2002, 2733–2746. (doi:10.1039/b111276g)
- Ura, Yasukazu; Sakata, Gozyo (2007). "Chloroamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a06_553.
- F.Rösch. Radiochemistry and Radiopharmaceutical Chemistry in Life Sciences. Volume 4. Dordrecht/Boston/London: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
External links
- M. Shetty, T. B. Gowda (2004). "A Study of Substituent Effect on the Oxidative Strengths of N-Chloroarenesulphonamides: Kinetics of Oxidation of Leucine and Isoleucine in Aqueous Acid Medium". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung. 59: 63–72. doi:10.1515/znb-2004-0110. S2CID 46154131.</ref>
- Chemicalland21.com: Chloramine T (Tosylchloramide sodium)
- InChem.org: Chloramine T
- "Disifin USA". Archived from the original on 2009-12-25. Retrieved 2010-02-09.