Ciénaga, Magdalena
Ciénaga (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈsjenaɣa]) is a municipality and a town in the Magdalena Department, Colombia, the second largest population center in this department, after the city of Santa Marta. It is situated at 11° 00' North, 74° 15' West, between the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta, the Caribbean Sea and the Ciénaga Grande de Santa Marta marsh in northern Colombia. The town is situated in the northern part of Magdalena, 35 km from Santa Marta. According to estimations, in 2019, there were 105,510 inhabitants.[1] The mean annual temperature is 34 °C.
Ciénaga | |
|---|---|
municipality | |
 Central Park in the town of Ciénaga | |
.svg.png.webp) Flag  Seal | |
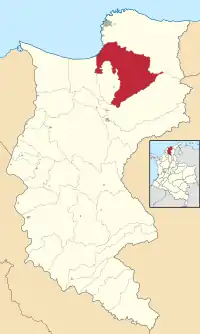 Location of the municipality and town of Cienaga in the Department of Magdalena | |
 Ciénaga Location of the municipality and town of Cienaga in the Department of Magdalena | |
| Coordinates: 11°00′25″N 74°15′00″W | |
| Country | Colombia |
| Region | Caribbean |
| Department | Magdalena |
| Foundation | 1521 |
| Incorporated | 1817 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Tete Luis Samper |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,812 km2 (700 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 10 m (30 ft) |
| Population (2019[1]) | |
| • Total | 105,510 |
| • Density | 58/km2 (150/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Cienaguero,-a |
| Time zone | UTC-5 |
| Area code(s) | 57 + 3 |
| Website | Official website (in Spanish) |
History
Prior to the arrival of the Spanish colonizers the area was vastly populated by Chimila indigenous people and a village known as Pongueyca. The foundation of Ciénaga has always been a matter of dispute due to many different historical theories and the lack of documented sources. It is believed to be founded first in what is now a small village known as Pueblo Viejo and the site of a former Chimila tribe. In 1529 monk Fray Tomás Ortiz established a parish that would later burn in a fire. It was then refounded as a city by Fernando de Mier y Guerra under the name of Villa de San Juan Bautista de la Ciénaga but also was known with the names of San Juan del Córdoba, Aldea Grande, Córdoba, Pueblo de la Ciénaga and simply Ciénaga.
During the war of independence from Spain, Ciénaga became a battle ground on November 10, 1820, between loyalists and independentists of what became known as the Battle of Ciénaga.
On December 6, 1928, the Banana massacre (in Spanish, matanza de las bananeras) occurred in this town. It was a massacre of workers for the United Fruit Company; an unknown number of workers died after the government decided to send the military forces to end a month-long strike organized by the workers' union in order to demand better working conditions. 100 - 2,000 people were massacred in the strike.
Culture
Ciénaga has been the place of birth and home to numerous notable people, including native Thousand Days' War hero, musician and farmer Colonel Clemente Escalona, father and teacher of vallenato composer Rafael Escalona. Guillermo Buitrago, who died very young - 29 years old - became a very important figure of the 20th century's folklore in Colombia. The city pays annual homage to him in the Guillermo de Jesús Buitrago Guitar Festival. It was also the birthplace of Andrés Paz Barrosthe, cumbia cienaguera founder and musical composer. Ciénaga celebrates every year on January 20 the Fiesta del Caimán (Feast of the Caiman) honoring a local legend known as La Historia de Tomasita.
The impact of the banana industry on Ciénaga and the surrounding region is depicted in several stories by Gabriel García Márquez in 100 Years of Solitude and The Leaf Storm.[2]
Important to note this town was also the principal port of Colombia during the late 19th century and was where the largest immigrant groups entered Colombia, mainly from Lebanon and Europe.
Gallery
See also
References
External links
- (in Spanish) Ciénaga official website





