Cinelerra
Cinelerra is a video editing and composition program (an NLE, Non-Linear Editor) designed for the Linux operating system. It is free software distributed under the open source GNU General Public License. In addition to editing, it supports advanced composition operations such as keying and mattes, including a title generator, many effects to edit video and audio, keyframe automation, and many other professional functions depending on the variant. It processes audio in 64 floating-point form. Video is processed in RGBA or YUVA color spaces, in 16-bit integer or floating-point form. It is resolution and image refresh rate independent, which means it can support video of any speed and size; this applies to the HV variant, the GG variant can support up to 8K video. The GG variant can also create DVDs and Blu-rays.
History
In 1996 Adam Williams of Heroine Virtual, lead developer of Cinelerra, released a Unix audio editor called Broadcast 1.0 which could handle 2G audio files. In 1997 Broadcast 2.0 was released, still audio only but unlimited tracks. 1999 saw Broadcast2000, which included video. Because of UI limitations Williams rewrote significant parts and released that as Cinelerra on August 12, 2002, while Broadcast2000 was withdrawn by Heroine Virtual in September 2001.[1] [2] Cinelerra became the first 64-bit media production application when it was rewritten to work with the AMD Opteron processor in June 2003 and was presented at SIGGRAPH 2004 in San Diego. Since then, many versions have been released. The original version is still being produced by Adam Williams. There have been several spin-offs made by the open source community, Cinelerra-GG and Cinelerra-CVE (a fork of Cinelerra-CV) are presently under active development. For a complete overview of versions, see the Variants section below. Even though the different variants look the same, there are considerable functional differences between them.
An overview of the different variants that released more than one version:
| Cinelerra variant | Last release date and version | First release date and version | Platforms (ready-to-run program) | New releases | Supported languages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GG Infinity | 2020-10-31, 2020-10 | 2016-03-31, 5.1 | 9 Linux, FreeBSD | Monthly | DE, EN, FR, RU, ES |
| HV | 2019-10-11, 7.2 | 2002-08-12, 1.0.0 | Ubuntu | Yearly | DE, ES, EU, FR, IT, NB, PT_BR, SL |
| CV | 2015-08-13, 2.3 | 2003-04-29, 1.1.5 | [In repos of Linux distros] | Frozen | DE, ES, EU, FR, IT, NB, PT_BR, RU, SL |
Interface
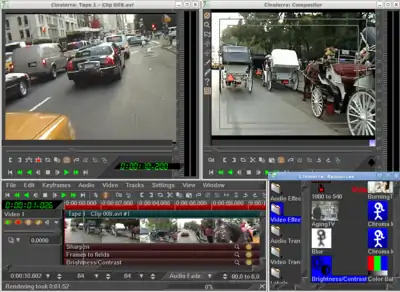
Cinelerra's interface is similar to that of other Non-linear editing systems, such as Adobe Premiere Pro, Final Cut Pro, and Avid Media Composer. However, because it includes a compositing engine, it may also be likened to compositing software such as Adobe After Effects, Smoke on Linux or Shake. The user is by default presented with four windows (clockwise from lower left in picture at top right):
- The timeline, which gives the user a time-based view of all video and audio tracks in the project, as well as keyframe data for e.g. camera movement, effects, or opacity;
- the viewer, which gives the user a method of "scrubbing" (manually moving the playhead forwards or backwards to locate a specific cue or word) through footage;
- the compositor, which presents the user with a view of the final project as it would look when rendered. The compositor is interactive in that it allows the user to adjust the positions of video objects; it also updates in response to user input.
- the resource window, which presents the user with a view of all audio and video resources in the project, as well as available audio and video effects and transitions; and
Cinelerra uses its own widget toolkit Guicast (the Cinelerra GUI library), not conforming to the human interface guidelines of major Linux desktops such as GNOME and KDE. This has the advantage that it looks and works the same no matter which distribution or desktop is used, and removes being dependent on a changing version of the desktop (for instance GNOME 2 / GNOME 3].
Usage and awards
Cinelerra has gained ground among some Linux enthusiasts looking for a native video editing system. Professional use was mostly promoted by Linux Media Arts, which sold an integrated hardware and software package for video production that includes Cinelerra. However, the company does not seem to be active in the Cinelerra field anymore.
At the National Association of Broadcasters' 2004 Electronic Media Show, Cinelerra received Bob Turner's "Making the Cut" award, given to "the best and most exciting post-production products seen at the convention".[3]
In December 2018 Libre Graphics World included Cinelerra in its comparison of the sustainability of video editors for Linux. [4]
Cinelerra.org
The cinelerra.org website was originally registered by a member of Cinelerra-CV Community Richard Baverstock on Jan 10 2004.[5] Around January 2014 the Cinelerra-CV Community overlooked the renewal of cinelerra.org. The domain was then taken over by a different project managed by Michael Collins, one of the founders of Cinelerra. The project was following commercial interests, aiming at offering professional support to its users. It was organized to merge all existing Cinelerra projects while also providing additional fixes and enhancements. Since early 2015, Cinelerra.org has an open Git repository on Google Code for analysis and for input;[6] however, that platform is read-only since 2015-08-24. At the present time, this repo does not contain source code. The project released a studio centric version 5.0 of Cinelerra. The goal of Cinelerra.org was to develop a more professional value to the product as of 2016. In January 2016, the main developer of the project William Morrow working behind cinelerra.org ("Good Guy") left cinelerra.org, continuing to work on Cinelerra 5.0, then on Cinelerra-GG 5.1 with help from the Cinelerra-CV Community.
At the present time, Cinelerra.org supports Cinelerra-HV work. Its website links in the download section to both the HV and GG versions.
Variants
Cinelerra-HV
 | |
| Original author(s) | Adam Williams |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Heroine Virtual |
| Initial release | August 12, 2002 |
| Stable release | 7.2
/ November 10, 2019 |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Linux |
| Type | Video editing software |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | heroinewarrior |
Heroine Virtual (HV), the producer of the original Cinelerra, generates a new release of Cinelerra annually, available as source code and a binary for Ubuntu. Although it is open source, the source is only made available as complete download for each release. Intermediate access to source files is not possible. HV has used SourceForge since the beginning (first source 2001-09-09), but does not react to bugs, patches and feature requests on that platform. Any bugs and usability issues found and resolved by the community that are submitted to Heroine Virtual often result in no immediate response, and it is not until a new release that there is any indication that Heroine Virtual has incorporated these changes.
To distinguish between the different variants of the software, the releases made by Heroine Virtual are also called Cinelerra-HV.[7]
A notable feature is that the HV version supports unlimited video sizes, so can be used for very large astronomical images.
Cinelerra-CV / Cinelerra-CVE
 | |
| Developer(s) | Cinelerra-CV Community |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 2.3
/ August 13, 2015 |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Linux |
| Type | Video editing software |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | cinelerra-cv |
Because of both the latency in development and the distribution-specific nature of the original Cinelerra from HeroineVirtual, a group of software developers created their own version of Cinelerra referred to as Cinelerra-CV (where CV stands for community version).
Cinelerra-CV allows the community to contribute to an open repository where changes to the code are accessible to everyone. Mailing lists and an IRC channel exist where more experienced users and developers can provide support to less experienced users, and developers can hold technical discussions. Cinelerra-CV is also packaged for a wider range of distributions. It also has a different compilation system: system libraries are used extensively, and the autoconf/automake tools are used to configure the compilation system.
Although Cinelerra-CV may technically be called a fork, the relationship between Heroine Virtual and Cinelerra-CV is rather friendly. Heroine Virtual at times contributes to discussions on the mailing lists, and incorporates many of the changes made in the repository. Heroine Virtual posted the following message on their website describing the relationship:
What you'll find here is the heroinewarrior version of Cinelerra. This is the version that supports what we need to do at Heroine Virtual Ltd. and is the same tree that was started in 1997. As time passes and new students come and go from the GNU/Linux scene, new forks of Cinelerra emerge that are more suited to the community but not what Heroine Virtual Ltd. needs. Today you'll probably find the cinelerra-cv.org fork more useful. They allow certain parts of our fork into their fork while contributing anything they want while we allow certain parts of their fork into our fork while contributing anything we want".[8]
Up until Cinelerra 2.1 the versioning of Cinelerra-CV followed that of Heroine Virtual. After Heroine Virtual released a new version, Cinelerra-CV merged relevant code from the new HV variant and into their variant. CV was appended to the end of the version number to indicate the community version. (For example, after the 2.1 merger the CV version was labeled 2.1CV.) Starting with release 2.2, Cinelerra-CV uses its own versioning scheme, but still merges code from Cinelerra-HV.[9] Following the 26th June 2019, the official web pages were taken offline and the URL redirects to the website for Cinelerra-GG.
The new official site of Cinelerra-CV was published on July 1 2020.[10] The source code of Cinelerra-CV is available from the new official repo on GitHub . The new official Cinelerra-CV Mailing List is available here. The Cinelerra-CV Mailing list from 2001 is archived. The complete collection of old (previous) Cinelerra-CV Mailing List archives is referenced/linked from this page of the new official Cinelerra-CV site.
Cinelerra-CVE is a Cinelerra-CV fork created for experimenting with Cinelerra's code. The fork was created by the main Cinelerra-CV developer (2012-2018) Einar Rünkaru in June 2008 and published in the middle of March 2010.[11]
The main difference between Cinelerra-CVE and (Cinelerra-HV, Cinelerra-CV, Cinelerra-GG) is attemtpt to use (in Cinelerra-CVE) seconds as timebase instead of framerate and samplerate. An implementation of PTS based timing enables to edit media with variable framerate and get rid of assumption that audio and video start simultaneously... Big plan is to get Cinelerra-CVE to the level where a user can mix (in Cinelerra) media from different origins, with different frame rates, resolutions, sample rates, color spaces and get the result he/she needs. If the result is not satisfying, the user will have the tools to tweak the project until the result is perfect..[12]
The repository of Cinelerra-CVE is available on GitHub and shows frequent updates. To know more about Cinelerra-CVE, visit this page on the new official Cinelerra-CV site.
Lumiera
In the beginning of April 2008, the Cinelerra community announced a complete rewrite of the current community version, named as Lumiera. It was born as a rewrite of the Cinelerra codebase called Cinelerra3 but soon was separated into an independent project with its own name. There is no usable application as of March 2019. The project remains in a pre-alpha status of development with a yearly development news update Lumiera news. It has build instructions,[13] and there is a binary Debian/Ubuntu build of the development preview available.[14]
Lumiera's native interface is written in GTK+, although other interfaces will be possible.
Cinelerra-GG Infinity
| Developer(s) | Cinelerra-GG community |
|---|---|
| Initial release | March 31, 2016 |
| Stable release | 2020-10
/ October 31, 2020 |
| Written in | C++ |
| Operating system | Linux, FreeBSD |
| Type | Video editing software |
| License | GNU General Public License, external plug-ins may differ |
| Website | cinelerra-gg |
Cinelerra-GG, a separate branch of Cinelerra, originated from Cinelerra-HV. It was first developed within Cinelerra.org (Cinelerra 4.6-mod, Cinelerra 5.0), then within the site of Cinelerra-cv.org (Cinelerra 5.0, Cinelerra 5.1, Cinelerra GG 5.1), and since December 2018 with its own website cinelerra-gg.org as Cinelerra-GG Infinity.
An important issue is that Cinelerra-GG reduces reliance on system libraries by including them where practical, like ffmpeg and OpenEXR. This makes it more predictable on different platforms, and also allows it to pick up new versions before the platform does.
Cinelerra-GG is determined to get as close as possible to what can be expected from professional level video editing software (NLE) for the Linux platform.
Its software features include support for recent versions of ffmpeg, extensive color correction tools, Ultra HD up to 8K, more than 400 video- and audio effects, two interfaces for audio plug-ins (LADSPA, and LV2 such as Calf Studio Gear), multiple denoisers and motion stabilizers, multi-camera editing, proxies, smart folders media filtering, 10-bit color space, advanced trim, live preview of resources, shared tracks, group edits, horizontal and/or vertical timeline split, rendering pre-configuration options, and the ability to save workspace layouts. It supports over 400 video/picture formats for decoding, and over 140 for encoding, including Apple ProRes, AV1, and WEBP. It has a ¨Sketcher" plug-in for free-hand drawing, supports creating HD Blu-ray, and DVDs, and some OpenCV plugins like FindObj. It allows nested clips, and clip sharing between projects ("file-by-reference").
Its hardware support is for jog-wheels ShuttlePRO V.2 and ShuttleXpress from Contour Design, multiple monitors, HiDPI, and hardware-supported decoding/encoding via VAAPI/VDPAU/CUDA.
Like the other Cinelerra variants (except Lumiera) Cinelerra-GG uses its own GUI. It has eleven GUI themes to cater to user preferences.
The GG variant is under active development, with a stable release at the end of every month. It is supplied as a multi user program pre-packaged for eight different Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Debian, Arch, OpenSuse, Slackware, Fedora, Centos, Mint), and FreeBSD. When the applicable repository is added to a distribution's update manager, the monthly updates will appear automatically. In addition, there are single-user builds for the eight Linux distributions plus Gentoo, as tar files. All builds are available in 64-bit, for Debian 9, Slackware and Ubuntu 14 there are also 32-bit single user builds. The source code is available as (manual) monthly download or from the git. As a proof-of-concept, since the 2020-01 release there is a Windows version with limited functionality; for details see the manual's chapter 1.
In addition to the GG variant's monthly releases, it is also available in two Linux variants dedicated to multimedia : AVLinux and Bodhi Linux Media.
Cinelerra-GG communicates with it users and developers through three platforms: its forum (user oriented), a bug tracker (feature requests, bugs, roadmap), and a mailing list (developers discussions). Each monthly release has a significant number of changes resulting from discussions and exchanges of information on these platforms.
Cinelerra-GG has an extensive, actively maintained manual, which is also accessible from within the Cinelerra-GG program. The manual is helpful for both beginners (e.g. Quickstart section) and professionals. There is also a YouTube channel with tutorials.
The differences between the GG and other Cinelerra variants can be found in .
History of Cinelerra versions
Events from the original creator Heroine Virtual have been indicated with HV, those of the "community version" with CV, and those of the GG Infinity variant with GG.
| Variant | Version | Release date | Changes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000-06-15 | Founding of the Cinelerra project. After numerous discussions between Adam Williams and Michael Collins about the direction of Non-Linear Editing on Linux, Williams presented the name and concept of Cinelerra to business partner Michael Collins in Sunnyvale, California. | ||
| HV | Beta 1 | 2002-06-10 | HV's SourceForge backup files show frequent activity up since 2001-09-09 straight up to release 1.1.0 . |
| HV | Beta 2 | 2002-07-12 | |
| HV | 1.0.0 | 2002-08-12 | Initial release. |
| HV | 110802 | 2002-11-08 | This release still identified itself as version 1.1.0, but had considerable changes compared to the 2002-08-12 release, for instance LADSPA support and titler changes. Because there are 3 separate blocks of comment in the change log since the 2002-08-12 release, this is more like a version 1.1.3 . |
| HV | 1.1.5 | 2003-02-11 | From the change log in the source[15] (selection):
|
| CV | 1.1.5 | 2003-04-29 | HV code "forked" into a community CVS version. |
| HV | 1.1.6 | 2003-05-12 | From the change log in the source[15] (selection):
|
| HV | 1.1.7 | 2003-08-11 | From the change log in the source[15] (selection):
|
| CV | 1.1.7 | 2003-10-05 | Merge with community CVS version. |
| HV | 1.1.8 | 2003-11-11 | From the change log in the source[15] (selection):
|
| HV | 1.1.9 | 2004-02-11 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:
|
| CV | 1.1.9 | 2004-02-17 | Merge with community CVS version. |
| HV | 1.2.0 | 2004-05-11 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:
|
| HV | 1.2.1 | 2004-08-12 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:
|
| CV | 1.2.1 | 2004-08-16 | Merged with community CVS version. Special enhancements were added to this version E.g. H264 Kod. Cineon used at NAB under Fedora 1,2 and BSD 5, this could handle 4k film 4096x4096 if graphics card permits. Fast frame rate in excess of 210 frames per second at 720x480 29.97, while bringing in live HD video in the timeline from a video camera. video4linux driver Zoran chip. |
| HV | 1.2.2 | 2005-01-10 | From the change log in the source[15] (selection):
|
| CV | 1.2.2 | 2005-01-18 | Merged with community CVS version. |
| CV | 2.0 | 2005-09-29 | Merge with community SVN version. |
| HV | 2.0 | 2005-10-04 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:
|
| HV | 2.1 | 2006-07-02 | From the change log in the source[15] (selection):
|
| CV | 2.1 | 2006-09-07 | Merge with community SVN version. (The first use of git and a multi-person merge) |
| HV | 4.0 | 2008-08-11 | Since all versions 2.0 onward 10bit (useful for prof. Cinepaint) and 16bit RGB(A),YUV(A) have been removed and replaced with RGB YUV Float instead. |
| HV | 4.1 | 2009-09-25 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| HV | 4.2 | 2010-10-17 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| CV | 2.1.5 | 2010-11-21 | From the Cinelerra-CV website's NEWS section:[9]
|
| HV | 4.3 | 2011-08-06 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| CV | 2.2 | 2011-11-13 | From the Cinelerra-CV website's NEWS section:[9]
|
| HV | 4.4 | 2012-09-07 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| HV | 4.5 | 2013-10-25 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| HV | 4.6 | 2014-09-10 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| org | 5.0 | 2015-07-04 | Cinelerra.org releases a studio centric version of Cinelerra titled 5.0. Cinelerra is now fully integrated with FFMPEG and supports numerous 4K and 2K uncompressed cinema standards from such camera manufacturers as AJA, Blackmagic Design, and Red. |
| CV | 2.3 | 2015-08-13 | From the Cinelerra-CV website's NEWS section:[17]
|
| HV | 4.6.1 | 2015-11-09 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| 5.1 (GG) | 5.1 | 2016-03-31 | The first of monthly releases of a branch separate from the HV, CV and .org versions, first under the name Cinelerra 5.1, but from September 2018 as Cinelerra-GG Infinity. |
| HV | 6.0 | 2016-11-17 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| HV | 7.0 | 2017-10-13 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| GG | 2018-09 | 2018-09-30 | First of monthly releases of the Cinelerra-GG Infinity version, this is a rolling release. See the release notes[18] which cover monthly releases since mid-2016, initially not under the GG name but as version 5.1 . |
| HV | 7.1 | 2019-01-23 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| GG | 2019-01 | 2019-01-31 | The 5th monthly release of Cinelerra-GG Infinity adds support for jog-wheels ShuttlePRO V.2 and ShuttleXpress from Contour Design. |
| GG | 2019-04 | 2019-04-30 | The 8th monthly release of Cinelerra-GG Infinity allows GPU-accelerated decoding for some video formats. |
| GG | 2019-05 | 2019-05-31 | The 9th monthly release of Cinelerra-GG Infinity adds GPU-accelerated encoding for some video formats. |
| GG | 2019-07 | 2019-07-31 | The 11th monthly release of Cinelerra-GG Infinity has significant improvements in masking. |
| HV | 7.2 | 2019-10-11 | From the Heroine Virtual website's NEWS section:[16]
|
| GG | 2019-10 | 2019-10-31 | The 14th monthly release of Cinelerra-GG Infinity adds scaling for HiDPI monitors, and speeds up AV1 decoding. |
| GG | 2020-01 | 2020-01-31 | The 17th monthly release of Cinelerra-GG Infinity adds OpenSuse Tumbleweed as supported platform, and Gentoo as single user platform. In addition, a limited Windows version is available. |
| GG | 2020-07 | 2020-07-31 | The 23rd monthly release of Cinelerra-GG Infinity adds aligning video using timecodes, two more subtitle formats, and auto-rotate for videos with rotation metadata set. |
References
- Broadcast 2000 Removed From Public Access, Slashdot, 2011-09-10
- History of Cinelerra in cinelerra.090901.tar.bz2 doc/manual.pdf
- "The Making The Cut Awards", eNews, Primedia Business, archived from the original on 2012-07-22.
- Prokoudine, Alexandre. "The quest for sustainable free/libre non-linear video editors". Libre Graphics World. Retrieved 2019-09-02.
- "About cinelerra.org". Cinelerra-CV Community. Retrieved 2020-07-10.
- Cinelerra.org git
- About Cinelerra.
- "Cinelerra-CV fork". Heroine Virtual. Retrieved 2019-01-30.
- "Cinelerra-CV news archive". Cinelerra-CV community. Retrieved 2020-07-03.
- "Cinelerra-CV news". Cinelerra-CV community. Retrieved 2020-07-03.
- "About Cinelerra-CVE". Cinelerra-CV community. Retrieved 2020-07-10.
- "Cinelerra-CVE: differences". Cinelerra CV Community. Retrieved 2020-07-10.
- Build and install Lumiera.
- Lumiera Debian Depot.
- Cinelerra-HV releases 2002-2008 on sourceforge.net.
- "Cinelerra-HV news". Heroine Virtual. Retrieved 2019-01-30.
- "Cinelerra-CV news". Cinelerra-CV community. Retrieved 2020-07-01.
- Smith, Phyllis. "Cinelerra-GG release notes" (PDF).
Further reading
- Kline, Dave (2005-07-15). "Cinelerra: Rough and ready video editor". Linux.com. SourceForge, Inc. Archived from the original on 2009-05-05. Retrieved 2012-10-05.
- Reuben (2006-08-05). "MainActor vs Cinelerra — Simple Editing, Part 2". Flavor8.com. Archived from the original on 2012-10-12. Retrieved 2012-10-05.
- Traniello, Raffaella (2012-08-21). "Cinelerra for Grandma". g-raffa.eu. Retrieved 2012-10-05.
- It's FOSS Team (2019-01-16). "9 best free video editing software for Linux (2019)". It's FOSS. Retrieved 2019-01-17.
- Collins, Michael (2014-05-22). "The beginnings of Cinelerra". Cinelerra.org. Retrieved 2019-01-20.
- Todorov, Marin (2019-03-06). "8 Best free video editing softwares I discovered for linux". TecMint.com. Retrieved 2019-03-06.
External links
- Differences between Cinelerra versions
- Cinelerra.org website managed by Michael Collins
- Cinelerra-HV website
- Cinelerra-HV source (2019) and bug tracker
- Cinelerra-HV manual "Secrets of Cinelerra" (2009)
- Cinelerra-CV website
- Cinelerra-CV source
- Cinelerra-CV manual
- Cinelerra-CV mailing list
- Cinelerra-GG website
- Cinelerra-GG source (2019)
- Cinelerra-GG manual (2020)
